- Description of the insect and its life cycle Varroa mite - description of females and males
- Life cycle of an insect
- Pericin for varroa mites
- Drone brood cutting
- Pine flour
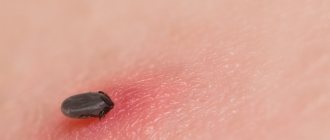
The varroa mite is a small insect, no more than 2 mm in size, that is the causative agent of a serious disease in bee colonies and a carrier of various infections. Previously, because of this pest, beekeepers had to burn apiaries, but in recent decades, effective means of combating it have appeared. Let's look at how the parasite develops and how to counteract it.
Description of the insect and its life cycle
The varroa mite is an ectoparasite that lives on bees. The insect has a flat body with legs covered with hair and 4 pairs of legs, thanks to which it moves and clings to the bee.
Varroa mite - description of females and males
Females are colored dark brown, their size is 2 mm. The mouthparts are hidden under the body and have a piercing-sucking appearance. The females use it to pierce the bee’s shell and feed on its blood.
Female varroa mites have the following morphological structure:
- they have a movable peritremal tube, thanks to which breathing is regulated in different living conditions;
- the specific shape of the body allows it to be firmly held on the bee’s body;
- with small teeth on the chelicerae, the females are firmly kept from falling out of the bee's wound;
- the springy cover prevents the females from sticking to the sticky substance.
Male varroa mites are smaller and have a round body shape. Their bodies are painted in white and gray tones with an inconspicuous yellow tint. The oral apparatus of males is designed to pump semen during fertilization of females. The ends of their legs are crowned with suction cups.
Life cycle of an insect
The entire life cycle of these arachnid representatives consists of the following stages:
- The females move from the bee to the honeycomb and climb into the cell with the bee larva until it is sealed. 3 days after the cell is sealed, the female begins laying eggs. Usually there are 5 eggs in a clutch, half a millimeter long.
- The eggs hatch into larvae, which soon turn into nymphs. Nymphs are equipped with 4 pairs of legs. The nymphs molt and enter the next stage, the deutonymph. They feed on the hemolymph of bees.
- Males, staying in cells, fertilize young females, then their mission is considered completed, and they die of hunger. In this regard, only females parasitize bees.
- Young bees, having completed their development, are selected from the cells. At the same time, the cells are left by mites. They climb onto bees or drones, where they remain until the next oviposition.
Important! During the season, a female varroa is capable of laying eggs 3-4 times.
The entire life cycle, which starts from the moment the egg is laid and ends with the appearance of an adult (imago), lasts from 8 to 11 days for females, and 9 days for males. In summer, the life expectancy of females is no more than 120 days, and in winter – almost 150 days.
In winter, there is no bee brood, so mites do not reproduce, and every tenth of them dies. However, with the onset of spring, their number begins to increase sharply and can increase 20 times.
At +24 degrees, female varroa can live without food for almost a week. When the temperature drops, the varroa mite stops breathing and hides in the cells of the honeycomb. It becomes difficult to destroy it.
Typically, 4-5 parasites are attached to a worker bee, 8 female mites are parasitizing on drones, and up to 20 can be counted on bee and drone pupae.
Attention! If you do not fight the varroa mite, this parasite will completely destroy the bee colony in 3-4 years. Weak families suffer the most from it.
Description
This type of mite parasitizes bees, which causes great inconvenience and danger, since there is a possibility of infection with dangerous diseases. Their body is oval in shape, they have 4 pairs of legs, which are covered with small hairs. They adhere very well to any surface.
Females and males have several differences. The female has a brown body; they can be seen quite well on the insect, since their size reaches 1.6-2 mm. The proboscis, with which the female punctures and feeds, is hidden under the body. They feed on the blood of not only adults, but also attack pupae and larvae.
Regarding their differences, it should be noted that females can regulate and control their breathing, thanks to the peritremal tube, which has a movable part. Also different is the rather specific shape of the body, but it allows it to hold onto its victim perfectly. In addition, the cover of their body has a springy structure, which prevents them from sticking to surfaces in the bee house.
Regarding males, they differ significantly from females. Their body size is much smaller, the color is light gray, and may have a yellow tint. The paws have suction cups, thanks to which they stick well to any surface. The pharynx is poorly developed and has practically no muscles. But the proboscis in this case is intended only for fertilization of females. In the photo you can see what a tick looks like.
How does infection occur?
Infection of bees with the varroa mite leads to a severe invasive disease of bees, their pupae and larvae, called varroatosis. This disease is a real scourge of the beekeeping industry and causes enormous damage to it.
In summer, the spread of mites from infected bees to healthy ones occurs in the following way:
- wandering bees;
- thieving bees;
- when removing apiaries;
- during swarming of bees;
- when purchasing bees and queens;
- when introducing infected brood into families;
- when infected bees come into contact with healthy ones, during pollination of flowers;
- due to improper storage of drone brood.
Varroa can spread at a speed of 10 km per quarter, and this depends on the presence of apiaries in the vicinity. It has been noted that in regions with a hot climate, varroatosis spreads faster.
Important! We should not forget that bees suffer from not only varroa because of mites. These insects carry dangerous infections of paratyphoid, nosematosis and American foulbrood. In this case, the death of bees accelerates and becomes widespread.
Symptoms and signs
The main symptom of a swarm being infected by the varroa mite is the appearance near the hive of insects with deformed or missing wings (less often legs). The development of the disease can be suspected based on the following signs:
- insects become lethargic;
- adult bees fly much less;
- the amount of honey produced decreases;
- Fewer and fewer young insects appear.
When examining larvae and adults, you can notice small brown plaques on their bodies, that is, the ticks themselves.
Symptoms of infection
After a bee colony is infected with varroa, the disease occurs without visible signs for the first 2 years. In the third year, the number of mites increases sharply and they infect a third of the bees in the hive.
Affected bees and drones have characteristic deficiencies:
- they have no or incompletely developed wings and legs;
- the bees' body is deformed;
- the brood is variegated;
- by autumn the number of bees sharply decreases;
- During the wintering process, bees do not behave calmly;
- the bottom of the hive is covered with dead bees, on which parasites are visible;
- heavily infected colonies may leave the hive after migrating.
Signs of infection
The big difficulty is that the disease is almost impossible to detect for 2 years. Since the infection develops during this period, it does not manifest itself in any way. Next, the mite population increases significantly, which leads to the defeat of 30% of the bee colony. At this stage of development of the infection, clear signs of infection can be seen, since drones and bees have a deformed body, legs and wings are not fully developed, or even absent. In addition, the brood will have an uncharacteristic variegated color.
Infestation increases significantly in October and November, and bee losses increase rapidly. In autumn, bees are very exhausted and weakened; already at this stage, colonies can die. The wintering of infected individuals is very turbulent; they can jump out and make a lot of noise. A large number of dead bees appear at the bottom of the hives, which are parasitized by mites.
With significant infestation, mass death of families can begin as early as the first half of winter. A very common situation is when, after the main honey collection period, bee families simply leave their hives.
Application of purchased acaricides
When using chemicals against ticks, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
Their use is strictly prohibited on the eve of honey collection or during the process. Neglecting this rule can result in dangerous toxins in the honey.
It is necessary to use only those drugs that are approved for treatments against varroa mites. Formic acid may only be used in the form of Illert tiles. Before using a chemical, you must carefully read the instructions.
The honeycombs that are in the hive at the time of processing cannot be used later, like honeycombs. They definitely need to be melted.
In the process of pumping out honey, you need to use a sieve to separate wax particles from the honey. The wax may contain pesticide residues.
Chemical-based products are used against ticks that kill them or severely damage them. Drugs can be fed to bees and affect the parasite through the blood.
In addition, they can evaporate in the hive and infect the pest through the respiratory system. Also, some drugs act through the contact of bees with them through the strips along which they move.
The following drugs are currently used:
Pericin for varroa mites
This chemical acts on the parasite through the bee's blood. It kills ticks that are on it. It is used in winter, when there is no brood. Usually 2 treatments are planned at intervals of a week, at temperatures close to zero.
A colony in a two-hull hive uses 30 ml of emulsion. Treatment is carried out with a spray bottle or syringe.
Apitol
This water-soluble drug easily penetrates honey, which requires careful use. The product powder should be dissolved in water and applied by spraying.
Formic acid on Illert tiles
The method is based on the evaporation of the product from the surface of the tile. Vapors of the drug penetrate into the hive with the air and affect mites through the respiratory system. Apply the chemical in the evening, with the taphole open, at a temperature of 12 to 20 degrees Celsius.
Such treatments can be planned 4 per season, with intervals between them of 15 days. For a single-hull hive, 1 tile is enough.
Cecafix against varroa mite
This drug is in many ways similar to pericin, but it is better tolerated by bees.
Bayvarol
The product is sold in the form of special strips, which should be hung along the inner perimeter of the hive. The product gets on the bees when they come into contact with the strips.
Possible methods of control
To get rid of parasites and save bee colonies, you need to apply a number of measures and fight comprehensively. It will be necessary to apply organizational, beekeeping and veterinary measures that are carried out comprehensively and annually. Mandatory measures include special conditions of housing, breeding and feeding; treatment is an integral part of the fight.
An important step is to reduce the parasite population; this must be done after the last honey pumping has been carried out. This will allow the bees to survive the winter. Although the infection cannot be completely eliminated, it can be reduced to a minimum. The next stage of processing must be carried out in winter, when the brood hatching is completed. Next, we will consider the most popular and effective methods of control.
Chemicals
A fairly popular and effective method, but it has many features.
When using such products, you must follow a number of recommendations:
- This method must not be used during the honey collection period, as well as before it begins. This is due to honey collection, which may begin earlier than the planned period, and spring processing will lead to chemicals getting into the honey.
- Only a number of chemicals that are approved for use are allowed to be used. This rule is mandatory, its implementation is monitored by quality control bodies, and non-compliance is punishable. All beekeeping products undergo diagnostics, during which the presence/absence of chemicals is determined.
- It is imperative that before using any product, you must study the instructions for use and strictly adhere to its implementation.
- When pumping out, you should use gauze or a sieve to separate the wax particles. This will eliminate the possibility of drugs getting into the honey.
The mechanism of action of such drugs is as follows. The active substances in the composition can have a detrimental effect on varroa mites. The effect on ticks can be through toxic fumes or through contact with drugs.
Herbal syrup
A fairly effective remedy that is used in the fight against ticks, and also serves as an excellent preventive method.
To prepare this product, you will need a decoction of herbs and syrup. To prepare the decoction you need to take 2 tbsp. mint and St. John's wort, as well as 1 tbsp. calendula, pour into a saucepan and pour boiling water over it. There is no need to cook it right away; you will need to let it sit for 15 minutes, and then boil for another 15 minutes. Separately prepare very concentrated sugar syrup, then mix with the broth 1:1. It is used as a top dressing for three weeks.
Capsicum
If you want to use this method, you should note that the processing should not be carried out during the period when honey is being pumped out, since it may affect the taste. But at this time it can be added to the syrup, which is used for feeding. True, some individuals may refuse such a specific delicacy.
And so, both fresh and dry products are suitable for cooking. The fresh product must be crushed with a knife, and the dry product must be prepared into a powder. Next, add water to the pepper and boil for 10 minutes. The broth should be infused for 24 hours, after which it is filtered; for this it is necessary to use several layers of gauze. Bees are sprayed 1 to 3 times a week.
Oxalic acid
A fairly effective method, but when using it, certain conditions must be met, otherwise it will be less effective. The use of oxalic acid or the manufactured drug Rosinka is allowed.
There are 2 application options:
- First you need to bring the water to a boil, and then cool it to a temperature of 30°. Next, oxalic acid is added to the water in the form of a 2% solution. When processing, it is necessary that the air temperature is not lower than 15°. This method is used 4 times in 1 season. Sprayed onto frames and streets.
- The second option involves using the evaporation method. It should be applied during the period when the parasites are still in brood, namely in early spring, but the air temperature should be more than 10°. The following proportions should be adhered to: 2 g of acid is used for 12 frames, a smoke gun or smoker is used.
Pine flour
The undoubted advantage of this method is safety for bees, and also does not have any effect on the quality of honey. Pine flour must be poured into gauze or a chintz bag. Gently try to ensure that all individuals of the bee colony are treated. Thanks to the use of pine flour, you can get rid of parasites in 1 day. It is also an ideal preventive method.
Pericin
This drug has the following mechanism of action. The active substances of the product penetrate into the blood of bees; when the parasite attacks it, it becomes saturated with blood, which contains toxic components. Treatment is carried out only in winter, when there is no brood. Use at an air temperature of 0 °C, 2 times with a break of 7 days.
Regarding the consumption of the drug, as the instructions say, a single dose is 50 ml, but practice shows that this amount is too much. Treatment is carried out with a dosage kit, but if it is not available, it can easily be replaced with a regular disposable syringe and without wasting money.
Apitol
You must work with this product very carefully and follow the recommendations. You should be aware that the substance dissolves very easily in water and can easily get into honey. It is prohibited to use the substance for feeding. It is available in powder form, from which you must prepare an aqueous solution according to the instructions. It is recommended for use only in cases where ticks have developed immunity to other active substances.
Bipin
The advantage is the effectiveness of a powerful active substance with complete safety for insects. In this case, the action is carried out thanks to the amitraz component. It is produced in the form of a concentrated emulsion from which an aqueous solution is prepared. The treatment is carried out using a syringe, the solution is applied between the frames. After a week, the procedure is repeated.
Formic acid
When using this method, Illert tiles are used, which act due to toxic fumes. The air temperature should be between 12-20°, the procedure is carried out with the tray open, in the evening. During the honey harvest period, use is prohibited.
Smoke
This is perhaps the most common method, used by both experienced beekeepers and beginners. Does not require special training, is safe and easy to use. To do this, the hive is cleaned and fumigated, then a canvas is placed, which is moistened with propolis in a smoke cannon and the procedure is carried out. For example, oak bark is very effective in summer and autumn.
Biotechnical
In this case, the technique involves changing the course of events, which relates to the biology of parasite development. Namely, the drone brood, where the clutches of parasite eggs are located, is removed. A honeycomb trap is also used and the queen is transplanted into an empty comb. You can also use heat treatment, in this case it is carried out by exposure to temperature, namely temperature, which is detrimental to the tick, but safe for insects.
Biotechnical measures against varroa mite
The essence of this negative impact on ticks lies in human intervention in the course of their biological development. The list of such events includes:
Drone brood cutting
Female mites often lay eggs in honeycomb cells containing drone brood. If you cut it out and then destroy it, you can reduce the number of parasites. This work should be planned for the junction of March and April.
Destruction of a honeycomb trap with a queen locked in it
According to this method, the queen is placed 3 times in turn for 10 days on an empty honeycomb in a frame. The queen begins to worm and soon does not remain outside the cage with the open brood queen.
Female mites crawl onto the open brood of honeycomb traps to reproduce. All that remains is to freeze it in order to destroy the individual.
Heat treatment
The trap honeycombs or all the honeycombs with brood are heated to a temperature level at which the mites die, but the bees still survive. This method is considered quite effective, but very labor-intensive.
Important! In practice, it has been found that the greatest effect in the fight against varroa mites can be achieved by combining chemicals with a biotechnical method.
How to recognize the disease?
Diagnosis of varroatosis should be given special attention. In the early stages, measures to combat bee varroa will be more effective and will help avoid the loss of entire colonies.
Tick infestation is an insidious disease that may not manifest itself until a “critical mass” has accumulated. The first signs may be the appearance of small bees and drones. If the family does not leave the hive for a long time and does not show activity or it is significantly reduced, this is also a symptom of damage. At later stages of tick infection, visible signs appear:
- Defects in the development of bees and drones - lack of legs and wings, shortened life expectancy, weakened individuals that become unable to perform their work in the hive.
- The appearance of variegated brood, the death of larvae and adult bees, from which able-bodied insects clear their home, throwing out the corpses of the dead.
- Change in the appearance of the brood - larvae infected with varrotosis become yellow, as if covered with mold. It looks like a foulbrood attack. Drones that emerge from the brood and are unsuitable for reproduction are expelled from the hive.
- The most advanced stage is considered to be when the bee colony begins to fuss and behave extremely irritably. As a result, they begin to form a club later, which is also characterized by low density, which affects the quality of wintering. A bad wintering means either a weakening of the family or its death.
This is interesting Keeping bee colonies in double-hull hives
If a beekeeper is attentive to his bees, he may be able to spot mites with the naked eye. They resemble tiny - 1 x 1.5 mm - brown tubercles on the body of a bee. On the brood, adult mites look the same, while young ones are lighter in color.
To determine how infected a colony is, you need to make a percentage calculation of the number of mites in relation to the number of bees. The most common method is sampling. It is done in the fall. One hundred bees need to be placed in a container and filled with either boiling water or a solution of washing powder. Then visually count the mites that have fallen off the bees. This is where you will make a diagnosis - the degree of damage, according to which the most effective method of treating varrotasis will be selected.
A situation requiring preventive measures is considered when there are no more than 10 mites per hundred bees. If there are 20 of them, then this is already a serious infection. When the number is 20 or more, we can talk about an epidemic.
Folk remedies for varroa mites
Along with chemicals, folk remedies are successfully used in the fight against varroa mites. The most popular herbal preparation is Varrabraulin. This environmentally friendly and safe product is used at the rate of 4 g per frame.
In addition, the following recipes are widely used:
Pine flour
The recipe is prepared and used as follows:
- take any needles;
- dry the material;
- grind the needles into powder;
- sprinkle the beehives with powder three times, at intervals of a week, at the rate of 50 g per family;
- After contact with the powder, the varroa mite will no longer be able to attach itself to the victim.
Dill oil for varroa mites
The recipe is prepared according to the following algorithm:
- take 2 cups of crushed dill seeds;
- mix the powder with 100 g of sunflower oil;
- the composition is heated in a water bath for 2 hours;
- leave the composition for 22 hours;
- squeeze out the composition and spread it on a piece of plastic film measuring 30 by 20 cm;
- the film with the smeared side is placed on the frame, and on top of it is placed the same piece of film with the smeared side facing up;
- after a week this procedure should be repeated.
Horseradish
Dried horseradish roots are placed in a smoker along with other flammable material. Then the hives affected by the mite are thoroughly treated with smoke.
Attention! Despite the fact that folk remedies are harmless to humans, it is still advisable to complete the last treatment with them 7 days before pumping out the honey.
Treatment of varroatosis
Varroatosis is treated with chemicals:
- pyrethroids (apistan, apifit, bayvorol, fumisan);
- formamines (bipin, anitraz, tactin);
- bromopropylates (folbex);
- organic acids (formic, oxalic);
- essential oils and infusions of medicinal plants.
It is worth knowing that varroa mites quickly become accustomed to one product; those that survive after treatment produce offspring that are more adapted to the drug. And after a couple of years, a stable population of ticks emerges. Therefore, medications need to be changed periodically.
In spring, Apifit is used. One plate is placed per 3 combs, for 3 days, when there is no sealed brood yet.
You can use formic acid in early spring. Formic acid vapors kill mites even in sealed brood; in addition, the causative agents of ascospherosis, acarapidosis, nosematosis and various foulbroods die. Wax moths also die. But formic acid must be used carefully; high concentrations are also harmful to bees.
In the summer, tick reproduction is suppressed with a mixture of dill oil and petroleum jelly. Take 90 grams of Vaseline and 10 grams of dill oil, this mixture is applied to paper in a layer of 3 millimeters. One bee colony requires two sheets of paper 20 by 30 centimeters. One sheet is placed on the bottom of the hive, the second sheet is placed on the frames with the greased side down.
There is another good folk remedy against varroatosis - take a tampon, moisten it with pine essential oil and place it on the upper bars of the frames. This treatment should be carried out every 5 days for 2-3 weeks. It is important to clean the bottom of the hive, since mites generally do not die, but fall off the bees to the bottom of the hive and become immobilized for some time.
In the fall, final treatment against varroa is carried out. I use bipin. I treat bees against mites when there is no longer any brood in the hives and mites are sitting on the bees between the chitinous plates. It should be cold outside, with temperatures above 2-3 degrees. Then the bees form a club and the drug is well transferred from bee to bee.
This is how you need to breed Bipin. Pour warm water into a jar and break the ampoule at the rate of 1 ml of the drug per 2 liters of water. Mix and treat the bees at the rate of 10 ml per street. I draw the drug into a 20 ml syringe and spray it on the bees sitting between the frames. So that the bees don’t worry, I work with two canvases, open 1-2 streets, process them and close them. I draw Bipin into the syringe and repeat everything with other tricks. It is more convenient to work with an assistant. One takes the product and processes the bees, the other works with the canvases. Hands should be wearing rubber gloves and a gauze bandage on the face. After treatment, wash your hands thoroughly. Requires 2-fold treatment with a break of 7-10 days.
Preventative measures for the appearance of varroa mites
To protect your bees from varroa, you need to plan and implement a range of preventive measures. Here is a list of the most important of them:
- if you have purchased a bee family or caught a swarm of bees, treat them with pericin;
- regularly inspect the hive tray and drone brood, trying to detect the parasite at the earliest stage of infection;
- It is advisable to carry out anti-mite treatments simultaneously with beekeepers who have their hives nearby;
- Clean and disinfect hives regularly.
The varroa mite is one of the most insidious parasites that can significantly reduce honey production in an apiary. Nowadays, the beekeeper has many methods and options for its destruction.
You just need to develop your own strategy to combat the parasite, which would be combined with the design of the hives, climatic conditions, food supply and technology for keeping bees.
Development of the disease
The varroa mite has four limbs, which can be easily observed on the body of bees, as well as against the background of pupae. Males are white in color.
The varroa mite has the following stages of development:
- female mites penetrate between the abdomens of bees, where they remain during wintering;
- before laying eggs, females eat larvae belonging to the open bee brood;
- Having had enough, the female is at the bottom of the bee cell, where she does not move for a long time;
- after the cells are sealed, the larvae eat food with the tick, the disease actively grows in the spring;
- the tick weaves a cocoon to enter the prepupal stage, where the laying of white eggs begins;
- Males emerge from unfertilized eggs, and females from fertilized eggs.
Varroatosis of bees is a fatal disease that can occur in spring and autumn, causing complications in the apiary if treatment is not started in a timely manner. Eighty percent of the mites are in the brood. At the end of spring, the winter tick is replaced by a new one. The reproduction of this pest is influenced by climate, weather, humidity and temperature in the hives. An important role for mites is played by the breed of bees, the health and strength of the family, as well as the ratio of bee and drone brood.
Spreading
Varroatosis is common in autumn, spring and summer. Infection occurs due to the fault of the sick family. Many parasites live in drones, less often in workers, as they often fly away.
There are the following ways of transmitting the disease among bees:
- from one family of bees to another;
- the source of the disease may be a drone that takes off on mating flights;
- contact between sick and healthy insects;
- installation of affected brood into a healthy colony;
- replanting the mother with varroa mites;
- infection of brood with drones.
It is important to detect the disease in a timely manner in order to prevent dire consequences for the apiary. Treating bees for varroa requires compliance with certain rules.
How to assess the level of infection
If a beekeeper suspects that a mite has spread inside the hive, he needs to assess the level of infestation. You can do this in a laboratory, but most often beekeepers do it themselves. First you need to catch 100 insects. Dilute washing powder in a glass container with hot water. Place the bees in a glass and wait 20 minutes. The mites will precipitate.
As a rule, about 2-3 ticks fall from one insect, in some cases - 5-7. Based on this assessment, the beekeeper decides whether he will treat the hive with special preparations or dispose of it.
Prevention of infection
To minimize the number of mites, the first and last sealed broods are destroyed in autumn and spring. It is necessary to install retractable trays in the hives, which should be cleaned and disinfected once every 7 days, removing any shed parasites. As soon as the bees gather in the hive, you should remove the tray and place cardboard soaked in Vaseline or dill oil on it, this will prevent re-infection from the fallen mite.
Basic preventive measures that will help keep bee colonies in good condition:
- When purchasing a new family, check it for varroa.
- It is necessary to install hives in the apiary at a considerable distance from each other in order to prevent bee theft.
- Carry out treatment together with nearby apiaries.
- Individuals that accompany the purchased queen must be destroyed.
- Install the hives 30 cm above ground level.
- Change brood combs once a year.
- Treat in the fall, even if the level of mite infestation is less than 4%.
- The apiary should be located in a sunny, dry clearing;
- Comply with all sanitary standards for breeding and keeping bees.
Drugs
There are a lot of medications for treating bees against mites; we will consider only the most effective and in demand.
Bipin
The active component of this medicine for bees is the acaricide amitraz, a very powerful chemical. There is a type of drug called Bipin T, a mixture of thymol and amitraz that acts on ticks and pathogenic microbes.
The drug is sold in ampoules - it is an emulsion that should be diluted strictly according to the instructions.
The solution is very volatile, so treatment is carried out immediately after preparing the composition. The method of application is as follows:
- Draw up the acaricide solution into a syringe.
- Drip between the frames in several places of the hive.
- Repeat treatment after a week.
The drug has no side effects, it does not affect the bees and the quality of honey, but if the swarm is weak, then it is better to choose another method of treatment.
Apitak
This drug is used only in the fall, after the honey has been collected and the bees are preparing for winter.
The medicine itself is a very strong acaricide, sold in ampoules in the form of an oil suspension. The drug must be diluted strictly according to the instructions; the result will be an opaque, milky liquid.
Treatment is carried out by pouring the streets into the hive from a syringe. Treatment is carried out twice with an interval of 7 days.
Bivarool
A very effective, toxic drug for the treatment of varroatosis. Treatment is carried out in the spring before the start of honey collection, approximately 2 weeks. In the fall - after pumping.
The packaging is opened immediately before processing. The drug must be diluted strictly according to the instructions in compliance with the dosages. There are cases where non-compliance with recommendations led to mass death of bees.
The parasite very quickly gets used to chemicals, so methods and methods of treatment have to be changed frequently. Some beekeepers have found a new use for Bivarool - treating bees and houses from the parasite using a smoke gun.
It will be possible to determine how effective the treatment was only after a day, by pulling out and inspecting the pallet.
Plates and strips
Preparations applied to veneer plates or strips have proven themselves to be effective in treating bees against mites. They are very simple to use - the plates are simply placed in the hive for a long time, and the pieces of paper are set on fire and placed in a tray.
The most effective are strips impregnated with formicide. These are Apimol-T, Vetfor and Varrosan. Apifit and Varroades are also popular.
Smoke
The most progressive and simplest way to get rid of varroa is the use of a smoke gun. It is used everywhere by both experienced beekeepers and beginners. The first step is to clean and fumigate the hive. Then a canvas moistened with propolis is placed in a smoke gun and exposed to the bees for 30 minutes.
It is good to change fumigation using oak bark in summer or autumn. The drug is natural and does not cause harm. Some professional beekeepers use tansy herb mixed with dried horseradish or wild rosemary root for fumigation.
The Varomor smoke gun, which can be bought in specialized beekeeping stores, has proven itself to be excellent. A modern device with precise direction and dosed consumption of the drug.