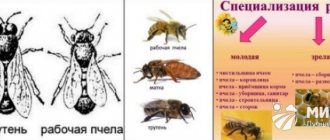
In search of sweet juice, the bee lands on flowers and honey plants, which may be inhabited by parasites. One of them is the Varroa mite, which feeds on hemolymph and causes varroatosis. Without the participation of a beekeeper who carries out the prevention and treatment of beneficial insects, the entire swarm dies. The necessary treatment of bees against mites (according to experts) is best done in the fall after honey collection before the onset of the first frost.
The well-being of bees is the main concern in beekeeping. Bee colonies are often the target of mites. Infection leads to the death of bees, weakens colonies, and reduces their quality. In this case, the productivity of the apiary decreases.
Beekeeping is experiencing great financial loss. It is the spring work of a beekeeper that will help the family maintain health and performance throughout the season.
General characteristics of the disease
Varroatosis is a dangerous pathology. It affects any bees - both adults and larvae. The danger of the disease is that at the initial stage it can rarely be detected due to the absence of obvious clinical signs.
Varroatosis is a quarantine disease, since the degree of its contagiousness is very high.
Insects affected by varroa do not form a club in the fall. They do not tolerate the winter period well. It is possible to awaken in the first half of winter.
Acarapidosis of bees
The tracheal mite is one of the two most famous bee parasites. At the same time, he is also the most dangerous for them.
It is difficult to notice with the naked eye due to the size of the individuals - the female reaches in size from 160x80 microns to 190x110 microns, the male - from 85x60 microns to 120x80 microns. Distinctive features of this species are the body of an oblong, rounded shape, almost oval, and white color.
They infect only adult bees, hard workers, while completely ignoring the larvae.
The tracheal mite causes an invasive disease called acarapidosis in bees. This parasite begins its action directly by infecting the bee’s thoracic trachea and “pumping out” the hemolymph.
These processes can be called the first stage - it lasts exactly until the tick pierces the wall of the trachea.
As soon as the female Acarapis woody gets into the trachea, she immediately lays eggs - from 6 to 10 pieces. The larvae take about 5 days to hatch, after which they gradually turn into a nymph, and then into an adult.
An individual develops from a larva to an adult in two weeks + - a couple of days. They live for about a month.
More than 130 individuals can be found in a bee infected with this parasite that is still alive.
What’s interesting is that insects can recover from this infection on their own. The cases known to science occurred in the middle of the spring period, when flowering and growth of honey production begin.
Bees die from acarapis for several reasons: firstly, they lose the ability to breathe due to the fact that their tracheal tubes are filled with dried blood and mite waste. This organ ceases to be soft and becomes completely inelastic.
Secondly, the bees lose a lot of blood and their muscles weaken. They are unable to fly and sit on the landing board, and having fallen from it, they are not able to return back.
Voodoo acarapis is especially dangerous because even in a dead bee it remains viable for a week.
Infection of a healthy bee occurs through direct contact with a sick insect - the incidence increases especially strongly at the end of the summer period, and its peak occurs in the middle of wintering. An entire apiary can become infected, either immediately after an infected family has been introduced into it, or from the moment an infected swarm arrives.
The fight for the health of bees is complicated by the fact that during the first years after infection the disease is not visible, but it appears only when half of the apiary is infected with Acarapis.
The easiest way to notice acarapidosis in your charges is by observing them during their first flight in early spring. At this time, bees weakened by parasites will not fly, but will crawl along the landing board and on the ground near the hive. Their abdomens will be noticeably larger than the abdomens of healthy insects, and their wings will “look” in different directions.
Treatment begins only at the end of spring and continues throughout the summer until September. During this period, aerosols with tedione, ethersulfonate and other chemicals become a reliable companion for the beekeeper.
Before each procedure, the outer frames with food are removed from the hive, freeing up a space of about 10 centimeters. All holes are securely sealed with available materials - for example, cotton wool.
One portion of the medicine - a strip of cardboard - is set on fire to a smoldering state and introduced into the hive through the ceiling or entrance so that the strip is located exactly in the middle between the bottom and the roof.
After the cardboard has smoldered, all the holes are tightly closed.
If you are using tedione, you will need to close the hives for 5 hours, if you are using ethersulfonate, then for 2 hours.
Once the treatment is complete, all holes are opened and the hive is ventilated.
This procedure must be carried out once a week for two months.
How to determine what type of parasites your children are suffering from? The simplest option is an external inspection. Moreover, tracheal mites in bees, due to their large size, are clearly visible even with the naked eye.
To find out this type of parasite, you can study photos of tracheal mites posted on the Internet. You can do the same with other varieties of organisms that are a source of dangerous diseases for honey-winged apiary workers.
Of course, there are other, more authoritative sources of information on this topic. It turns out that dissertations are even written on it.
The authoritative author, who is a specialist on this issue, is A. I. Muravskaya. She is the author of the dissertation “Reproduction of the Varroa Jacobsoni mite in bee and drone brood.”
This paper presents effective zootechnical methods that can be used to combat varroa disease caused by the parasite species of the same name. If you wish, you can familiarize yourself with them, but there are also sources of information that are more accessible to the general public.
You can also read popular science articles posted on specialized resources on the Internet. Some thematic magazines are also available in electronic form.
And, of course, you can always turn to your hobby and business colleagues for help. They will always be able to share with you not only theoretical knowledge, but also practical methods of working to overcome the problem associated with high incidence of disease on the territory of your apiary farm.
The fact is that the characteristics and nature of the infection may also depend on the region in which your apiary is located. And the practical experience of your neighbors can be much more useful to you than universal advice that does not take into account your location and other aspects specific to you.
If you want to carry out effective treatment for tracheal mites, we advise you to use strips called “Varroades”. Its name should not mislead you: we will use it to treat the tracheal breed, and not the Varroa mite.
The basis for the manufacture of such strips is wood. A special active ingredient, namely an acaricide, is applied to such a base. This substance can rid your area of harmful organisms.
At the same time, remember that simply placing such strips in the nest will not be enough. It is necessary to carry out some preparatory measures that will help increase the effectiveness of your treatment.
Be sure to make small holes in your strip. For these purposes, you can use the most ordinary hairpin.
Placing a strip in a nest must also follow certain rules. You should not put them there just like that: on the contrary, the strips should be clearly fixed in the nest street you have chosen.
When installing strips, you must also take into account the current condition of your patients. For example, if the honey plant community has already weakened, then you should place such devices strictly between the honeycomb frames.
How long can you install such strips in the nest? Typically the recommended period is one month.
However, you must adjust this indicator yourself, focusing on the amount of brood contained in your nest. The less brood, the longer you can keep the record in your nest.
Goals of autumn processing
Autumn prevention helps reduce the risk of varroatosis, which develops throughout the winter. This procedure makes it possible to minimize the losses of the bee colony, since infected individuals are often unable to survive wintering and do not survive until its end.
Tick-borne parasites predominantly settle in the abdominal cavity of insects, between segments, remaining there until the brood develops.
Preventive actions are carried out after the end of the main honey collection.
Symptoms and diagnosis of infection
The presence of a mite in the hive is determined primarily by the behavior of the bees and their appearance. They become lethargic because they lose a lot of protein, which is sucked out by parasites. Insects are unable to fully collect and bring the required amount of honey and pollen for their livelihoods.
Only emerging young individuals may have deformed bodies and underdeveloped wings. There is no presence of brood within the framework. When affected by parasites, you can observe a large number of worker bees crawling near the flight board.
Varroa can be seen with the naked eye, and to identify other (very small) representatives of this species, it is necessary to submit dead bees to the laboratory for research.
What and why do you need to treat bees?
The bee family is treated not because they themselves cannot cope with the problem, but because of the reduction of individuals due to numerous problems.
The basis of all the troubles is the lack of proper care for the apiary on the part of its owners and, of course, a number of other equally global reasons. Prerequisites for the upcoming processing of hives:
- An apiary affected by varroa or an infestation of mites caused by a special type of parasite - Jacobson's Varroa. The pathology is dangerous both in spring and autumn, since insects are weakened during these periods. If proper treatment is carried out, it is possible to save the majority of the livestock; otherwise, the disease will begin to rapidly progress, the family will weaken, and the development of its fruits will be delayed.
- The second dangerous invasion for bees is the penetration of Euvarroa Sinha mites - they are dangerous for drones. This parasite feeds on the larva throughout the entire period of development, and the females, before closing the cells with the larvae, place them on the drone larva or on the wall.
- Affected by fungal diseases and infections. The main thing is to identify them in a timely manner in order to preserve the insect population as much as possible.
- Non-contagious pathogenic manifestations threaten the bee family due to improper care on the part of the beekeeper. Proper development involves feeding with various additives. For example, carbohydrates (otherwise the family will suffer from carbohydrate dystrophy). This problem is caused by fermentation and crystallization of the main beekeeping product - honey. Signs of suffocation are also observed in healthy bees due to poor ventilation.
Types of diseases:
- filamentovirus (a DNA-containing virus leads to lethargy and death);
- hafniosis (develops when bees are infected with enterobacteria from dirty water and low-quality feed);
- ascopherosis (can be treated with antibiotics, is fungal in nature, and forms in areas of dampness);
- nosematosis (manifested by diarrhea of individuals, spread by old bees and low-quality food);
- amoebiasis (usually manifests itself in combination with nosematosis, provoked by amoeba parasites);
- salmonellosis (weakens the inhabitants of the hive, develops in a humid environment).
When to treat
Ticks are usually located in the abdominal region between the segments. They remain in such places until the brood develops. The brooding period lasts from spring to autumn. Parasites are characterized by fairly rapid reproduction, which is why there can be up to 7 ticks per individual.
Parasitic mites are characterized by very rapid reproduction. In advanced cases, there are up to 7 mites per bee.
Ticks affect not only adults, but also brood. Therefore, means of combating varroatosis and acarapidosis must be combined. For example, it is doubtful that the plates are capable of controlling parasites on the brood.
This means that in this case, the greater effect will be from using a smoke gun or spraying acid solutions.
Preventive treatment of bees against mites is a very important measure in beekeeping, as it can significantly reduce the risk of varroatosis.
Usually this disease develops in winter. Therefore, it is recommended to treat bees in the fall, and not in the spring or summer. After all, in spring and summer insects will already be infected with parasites.
Reasons for treating bees for parasites in the fall
- at this time there are significantly fewer bees;
- in the presence of parasites in the nest, a significant weakening of the family is observed;
- the risk of developing concomitant insect diseases increases.
If you properly treat bees against mites in the fall, you can minimize the losses of the bee colony, because infected individuals most likely will not survive until spring.
If spring or summer is chosen to treat bees against mites, then such prevention will be several times less effective. Therefore, bees are not particularly disturbed in spring and summer.
Methods for treating bees against mites
Methods for controlling varroa mites are divided into 3 groups:
- physical;
- biological;
- chemical.
Treatment may include the use of purchased medications and folk remedies.
Thermal impact
Increasing the temperature inside the hive is one of the methods of combating the varroa mite. Using special chambers, the air inside the hive is heated to +48⁰C. Bees tolerate such conditions, but they are uncomfortable for mites. The hive is warmed up for 8–10 minutes, during which time the parasites leave the hosts’ bodies. The method is ineffective, requires the purchase of additional equipment, and in addition poses a danger to bees, so it is used infrequently.
Smoke treatment
One of the most popular methods of getting rid of mites is treating the hive with a smoke gun. Propolis-impregnated canvas, oak bark and leaves, and a mixture of horseradish root and wild rosemary are used as a source of smoke. The procedure lasts about half an hour. After this, dead parasites are removed from the bottom of the house.
Biological drugs
Beekeepers actively use two biological preparations to treat bees against mites:
- formic acid;
- oxalic acid.
Formic acid
Before use, the product is diluted with water, the resulting mixture is slightly heated and placed in the hive. The substance evaporates over 3 to 5 days, during which time its vapors affect the parasites. The optimal temperature for such a procedure is +15… +25⁰С.
Chemicals
Chemical preparations for treating bees against mites are available in various forms. It can be:
- emulsions;
- concentrates for preparing solutions;
- strips impregnated with acaricide;
- plates with applied drug;
- powders.
The greatest demand is:
- Bipin;
- Polisan;
- Aqua-Flo;
- Varroades;
- Bivarool.
Such drugs are indicated in case of a rapid increase in the number of ticks and weakening of the swarm. They can only be used following all precautions and at a time when the risk of toxic substances getting into beekeeping products is minimal.
Traditional methods
Medicines for bees against mites, prepared according to folk recipes, can reduce the number of parasites and increase the immunity of insects. The most popular means:
- infusion of pine needles (you can add a little chopped garlic);
- top dressing with hot pepper;
- thyme (the plant is crushed and placed in a gauze bag and placed in the hive);
- alcohol vapor with lavender oil.
You can enhance the effect by combining several options at once.
How to determine if bees are infected with mites
The occurrence of parasites that appear on bees can be a serious problem for beekeepers.
Infected insects very often leave their homes, and the remaining bees die. When mites land on a bee's body, they begin to feed on insects and gradually lead to their death.
Parasites can also be carriers of various diseases that affect the insect and can be transmitted by a bite.
Signs of tick infestation
- insects become lethargic and may not fly out of the hive for a long time;
- the amount of honey decreases;
- very often the insect’s body becomes deformed, young bees have damaged or undeveloped wings;
- the number of young insects decreases; with a large number of mites, further reproduction of bees stops.
Female mites are slightly larger than a millimeter in size, brown in color, and visible on the bee’s body. Life expectancy is two to three months in summer and up to five in winter. At the same time, the individual is very hardy and, even without direct contact with bees, is capable of surviving up to 18 days inside the hive and up to five days outside.
The male mite is slightly smaller, the color of the shell is white and it can only survive inside the hive. Ticks are ready to reproduce immediately after hatching, and the male quickly dies. The female lays eggs on brood and adults, and a week later a new generation of mites appears. It is very difficult to destroy it, especially since the parasite is now rapidly becoming accustomed to insecticides.
How to determine whether bees have mites?
If the flight speed of bees has decreased significantly, and the amount of honey produced is rapidly falling, it is worth examining bee colonies for the following signs:
- The shape of the bees' body changes noticeably.
- The brood gradually disappears or disappears completely.
- Insects stop collecting nectar and dust and become lethargic.
The mite feeds on the protein parts of the body of bees, so if the disease affects the hive in the fall, the insects will not be able to survive the winter. Effective control of Varroa mites begins with determining the stage of the disease.
Instructions:
- Take several glass jars, according to the number of hives available on the farm. Then place two dozen insects in each of them. Close with lids with holes for ventilation.
- Pour half a liter of liquid into a low water container, such as a basin, and place it on the stove.
- Lower the jars into the basin so that water is drawn through the ventilation holes. Shake the jars to wet the bees. This way they will not be able to fly, and the temperature will affect the parasites and bees at the same time.
- Heat the liquid to 50 degrees. After which the mites will fall off the bees.
- To make it easier to count ticks, you can heat the water to a boil. Insects are not able to withstand high temperatures and will therefore die.
- Pour the original liquid with the mites into a porcelain or clay plate, preferably a light one.
- Recount the number of ticks.
- Repeat the procedure for the remaining jars of bees.
Be sure to read:
Processing bees with a smoke gun: principle of operation, when to use, how to do it yourself
If the number of harmful insects exceeds 0.5%, treatment against varroa is required
Use of Thymol
A not very popular method of treating honey insects against mites is the use of Timol. This is due to the fact that this substance is moderately toxic to bees.
The drug is sold in powder or crystal form. This drug is placed in special bags and placed at the top of the frame bars. Timol can also be poured into bags and hung on top of the honeycomb. Approximately 10–15 g of substance is poured into one such bag.
After spring treatment with Timol, good survival of insects is shown.
Heat treatment
For this type of “disinfection”, special cassettes are required. The whole family is placed in these small containers and heated to +48 degrees. At this temperature, bees become incredibly active and can begin to sting each other. Heat treatment allows you to get results instantly, but at a high cost.
Important! Bees are treated with temperature exclusively in the early stages of varroatosis, so that the parasites die within two to three minutes. If there are a lot of ticks in a club, then prolonged exposure to high temperature will almost completely destroy the colony.
This type of “disinfection”, coupled with chemical treatment, will give maximum results.
- The bees are placed in cassettes and processed.
- A plate with Mavrik or any other preparation is placed in an empty hive and set on fire.
In fact, everything is very simple, but due to the high risk of being left without honey insects, beekeepers avoid heat treatment.
Against acarosis and varroatosis
Let's consider those products that kill all ticks equally well - both tracheal and Varroa mites:
- Bipin-T - an emulsion is prepared from a liquid medicine by taking two liters of warm water per 1 ml of the medicine. The bees are sprayed with the emulsion from a syringe - only 10-20 ml is needed per frame. Bipin treatment is carried out twice: once - after honey collection, the second - before the start of wintering.
- Phenothiazine – treatment is carried out after the main pumping of honey or 30 days before it. It is necessary to perform three treatments at intervals of a day, then, after a week, the course is repeated again. How to work with Phenothiazine correctly, read below.
- Fumagillin is a drug mixed with sugar syrup in a ratio of 2 to 1000. It is used after pumping out honey. Feeding is carried out 4-5 times with an interval of three days. One family needs about a glass of syrup per day.
The drug Phenothiazine must be purchased in tablet form. Before treatment, a puff of smoke is let into the hive, and after 60 seconds a smoldering tablet is introduced. The entrance is immediately closed.
Processing procedure
First, give a few puffs of smoke into the entrance, thus stirring up the bees. Quickly but carefully remove the frames with the bees and the queen one by one, shaking all the bees into the cassette through the funnel.
Then let the bees calm down for 10-15 minutes. Then take the tape to the heated television camera. Place white paper (newspaper) under it. Having started the countdown, begin processing, turning the cassette and shaking it periodically, without allowing the bees to twist.
After finishing the treatment, give the bees the opportunity to calm down and come to their senses near the hive. Then pour the bees into the hive on top of the frames and carefully close them.
When the family calms down, take the hive to its place. This process is somewhat labor-intensive, but very effective. Mainly used in small apiaries.
How to spray hives
Spraying of hives is carried out using special preparations. The optimal ambient temperature is 15 0 . At this temperature, all drugs evaporate quickly. The choice of dosage and medication for ticks depends on the degree of damage.
Treatment of bee varroatosis
Currently, all apiaries in Eurasia are considered a priori to be infected with varroa. Every year it is necessary to carry out therapeutic and preventive treatment. There are no biological methods to control varroa. The varroa mite has no diseases or natural enemies - at least, they have not been identified so far. The only option for regulating the number of parasites is to remove mite-ridden drone brood. Varroa can be combated using chemical, physical, zootechnical and folk methods.
Treatment
It is precisely because of this negative influence of the parasite that it is necessary to combat it with special care. Therefore, the beekeeper must know how and when to handle bees.
It is also necessary to take into account the intensity of infection of the bee colony. If mite infestation is about 0.5% or less, then preventive measures are taken. Otherwise, it is necessary to carry out intensive treatment of the bees.
In summer
In beekeeping, they try to get rid of the varroa mite in the spring. This is what will contribute to the full functioning of the hive and will not harm the honey collection process and the health of insects. But, if suddenly the moment was missed or not noticed due to an insufficiently thorough examination, the treatment is carried out on bees in the summer, preferably in June.
in spring
Full control of the varroa mite should begin in early spring, in March, when a small amount of honey remains in the bee houses. Spring treatment allows you to:
- Avoid reducing the number of individuals.
- Start full-time work in the summer and protect the brood in the future.
- By the way, additional treatment for protection against ticks is also carried out in the fall. This way the insects will be able to overwinter without negative consequences.
Tool
The main tool that can be used to combat ticks is a smoker. With its help, parasites are removed from smoke. The basis of the device is a cylindrical body equipped with a cone-shaped lid to which the bellows are attached.
Some models have a metal glass with a lattice bottom installed inside the case. In this case, between the bottom of the glass and the body there is a special space intended for ash. Materials for burning and rags soaked in a composition for killing ticks are placed in a glass.
Traditional recipes for treating bees against varroatosis
CAS-81
Recently, in the practice of combating varroa, the drug CAS-81, prepared from plant materials - pine buds and wormwood, harvested in two periods: before and after flowering, has become widely popular. In addition to the systemic effect on the Varroa mite, this drug has stimulating properties during the spring development of bee colonies. In addition, its use with sugar syrup in the autumn feeding of bees technologically fits into the system of beekeeping on an industrial basis. Preparation of the drug is available to every beekeeper. The dried raw materials are crushed to particles no larger than 4 cm in size and a mixture is prepared in the following ratio: 50 g of pine buds, 50 g of wormwood during the growing season and 900 g during the flowering period. The mixture is poured into 10 liters of water and boiled over low heat for 2-3 hours, and then left for up to 8 hours in a warm place and filtered through 2-3 layers of gauze. Add sugar syrup (1.5 kg of sugar per 1 liter of water) to the resulting liquid, 30-35 ml (or grams) per liter. It is used in the fall when feeding bees for winter maintenance; families are given up to 6 liters in 3-4 doses. Wormwood is harvested at two times due to the fact that at different stages of development it contains various ingredients that have a detrimental effect on mites and have a positive effect on bees. The recommended dose of the drug can be doubled, which will not affect the general condition of the bee colony. At the same time, they note that with increasing dosage of the drug, bees take the syrup worse. When harvesting pine buds, needles are not removed from the shoots; the buds are used together with young shoots. The decoction is prepared in a sealed container; the amount of liquid that has evaporated during the boiling period should not be replenished. You can use a decoction of pine buds and wormwood with syrup in the spring after the bees have flown around. After this, there is an active growth of young bees. KAS-81 can be added to candy and used for spring feeding. The remaining broth cannot be used. The drug should be prepared immediately before use. During storage, essential oils, phytoncides and other active plant substances evaporate from it. The amount of decoction prepared at a time depends on the size of the apiary. The drug KAS-81 acts on the mite for a long time, throughout the winter period, until the bees use up the carbohydrate food they processed.
HORSERASH ROOT
To combat varroatosis, you can use the roots of ordinary horseradish. Dried horseradish trimmings, small roots, and husks from the roots are poured into a smoker on top of burning rotten things when fumigating hives with bees.
RED PEPPER INFUSION
An infusion of red capsicum showed good effectiveness in treating bees against varroatosis; it is not recommended to use other types of pepper. To prepare the infusion, the dried pods are cut with scissors into 1 cm pieces. 40-60 g are placed in a thermos, pour 1 liter of boiling water and seal hermetically. The infusion is kept for 10-20 hours, then filtered without squeezing, for which nylon fabric is used. A properly prepared infusion burns the skin and irritates breathing during treatment. Bees are treated with pepper infusion during any period of the active season at a temperature not lower than 15°C. For this purpose, the frames with bees, drones, brood and queen are removed or moved apart in the hive, sprayed on them, as well as the bottom, walls and ceilings. Spray with “Rosinka” or a spray gun. Spraying is carried out three times: in early spring three to four times with an interval of 6-8 days, after pumping out honey and at the beginning of the emergence of young bees from the autumn (last) brood. As a result of the treatment, young bees will go into wintering disinfected.
CONIFEROUS LIQUID EXTRACT
They also use a method that consists in improving the health of the bees themselves with the help of a coniferous liquid extract, which is produced by the Tikhvin LHZ in the Leningrad region. This is an aqueous extract of pine needles (40-50% pine or spruce, evaporated to a viscous liquid). Coniferous extract is produced for medical purposes. Other types of extracts are not recommended. In the absence of pine extract, an infusion of the tops of young pines and fir trees, collected during flowering in May-June, is used. 2 kg of finely chopped pine needles are brewed with 10 liters of boiling water and infused in a closed, well-insulated enamel container for about 8 hours. Add 200 g of infusion per 1 liter of syrup to the fertilizer with a concentration of 1.2 kg of sugar per 1 liter of water. Under normal conditions, pine infusion is stored for no more than 3 days. In the spring, after the exhibition of bees and a friendly flight, when the bees cannot yet bring nectar and pollen to the hive, they are given fertilizer with pine extract - 1 liter of syrup every other day. Periodically, on dry days, they are fed until the raspberries bloom. Prepare the syrup immediately before distribution at the rate of 1 teaspoon of pine extract, previously dissolved in 5 glasses of warm water, pour in 1 liter of syrup and stir. Bees take this syrup well. At the same time, bee colonies develop quickly, grow 2-3 times more brood, and mite infestation decreases. In mid-August, when the harvest in nature is reduced and marketable honey is selected from the families, fertilizing is done to build up the strength of the family going into winter. To 2 liters of sugar syrup (1.2 kg of sugar per 1 liter of water) add 1 teaspoon (3 g) of pine extract, after dissolving it in 0.5 liters of warm water. Feeding is given at night. Recently it has become known that when pine extract is fed, its biologically active substances pass through the hemolymph of bees into overwintering mites. As a result, infertile male mites appear in the spring and its reproduction is interrupted. For the same purpose, you can add a decoction of herbs - cumin, hops, carrot tops.
Fighting fungus
Varroatosis is dangerous because a specific virus is introduced into the hive with the Varroa mite. And it is not a mite or even a virus that kills bees, but a combination of a virus and a parasitic fungus. And the most important thing is added to the treatment of bees against mites in the fall: you must try to defeat the fungus.
Spores of a fungus that attacks bees
The drug Unisan, from which a mixture for spraying is prepared, will help fight the fungus:
- You need a syrup containing 4 parts water and one part sugar;
- Add 2 ml of medicine to a liter of warm syrup;
- The mixture is sprayed onto frames with bees, using 10-12 ml per frame.
At low temperatures, it is better to make a top dressing out of the medicine. But the benefit from it will be less than from spraying.
So, the recipe for healing nutrition:
- For a liter of sugar syrup prepared in a 1 to 1 ratio, take 1 ml of Unisan;
- The consumption rate of the mixture is 250 ml for each hive.
Bees need to be fed 3-4 times, maintaining an interval of 7 days. The same applies to spraying. Do not use the product 10 days before honey collection. No other restrictions were identified.
Preparations and processing methods
Today, beekeeping uses several methods for treating bees against mites at different times of the year:
- Physical impact using elevated temperatures, the so-called heat treatment.
- Biological effects. In this case, acids are used.
- Chemicals that are quite aggressive. That is why they are used only when other methods of control have not given an effective result.
To choose a method for treating bees against mites, you need to imagine the advantages of each of them.
Tick stripes
Anti-parasite strips are suitable for long-term installation in bee hives. They are also quite effective to use as a prophylactic agent. Among the advantages it is worth highlighting:
- Completely harmless to the honey insects themselves.
- Suitable for both treatment and prevention.
- Convenient to use as it requires minimal effort. All you need to do is hang it inside the hive.
But despite these advantages, anti-varroades strips also have their own disadvantages. And the main one is the correct calculation of the time of use. This is the question that most often arises among beekeepers – when is the most effective time to place strips of evidence. The fact is that it is necessary to understand the principle of the action of the insecticide contained in this drug. An individual, in contact with the material, spreads the drug throughout the hive. This way the tick is destroyed. When the temperature drops below +10°C, the bees huddle into a ball and move minimally around the house. Therefore, installing strips in evidence in the autumn does not make any sense. The effectiveness of the drug will be practically zero.
Experienced beekeepers recommend placing strips in the houses around mid-August, when the honey has already been pumped out.
Bipin
Bipin shows high efficiency due to the active component - amitrase. In addition to varroa, the remedy also has a detrimental effect on other parasites. It is used as an emulsion, treating the space between the frames by adding a few drops (from 1 to 2). One treatment is carried out, and the second is repeated after 1 week.
Bipin does not affect the quality of honey, nor does it negatively affect insects. But still, beekeepers who use this drug do not recommend treatment with bipin in cases where the bee colony is weakened.
Amitraz
Amitraz is used in the autumn. But it makes no sense to treat hives with it in spring or summer.
If we consider the drug, it becomes clear that it belongs to the group of acaricides and is of organic synthetic origin. In terms of toxicity, it has a hazard class of 3, so processing must be carried out strictly according to the instructions.
Acaricide
The acaricide is most often used in the form of a preparation applied to plates. With its help you can organize effective protection against ticks. To do this, just hang the strips between the frame spaces.
Individuals will spread the drug throughout the house, as a result of which the parasites die from paralysis. For treatment, it is enough to hang acaricidal plates in the hives for 1 day.
Thymol
Thymol is an effective means of combating not only varroatosis, but also tracheal mites and foulbrood. But with all this, thymol does not harm the honey workers themselves and their products. But you must stop using the drug 7 days before pumping out honey or collecting other bee products.
If we talk about the complex effects of thymol, it provides the following effect:
- Bactericidal.
- Fungicidal.
- Acaricidal.
- Nosemacidal.
It is most effective to use in the spring, when the flight ends. But in the fall, before they go to winter, in order to increase the strength of the family, Timol should also be used.
Treat with the drug 2 times with an interval of 7 days when painting according to the outer frames.
When exposed to each frame, completely planted with individuals, it is necessary to act 3 to 4 times with an interval of 3-4 days.
Oxalic acid
I use oxalic acid for treatment, you can get the following effects:
- Speed of impact on parasites.
- Simplicity and speed of processing in the hive, which is quite convenient for beekeepers.
- High level of effectiveness of treatment with oxalic acid against ticks in the spring, which is approximately 83%.
- The parasites disappear approximately on the 10th day.
In order to treat the hives, this anti-parasite preparation must be diluted with prepared clean water in such a way as to obtain a solution with a concentration of 2%.
Please note that the water should be as clean and warm as possible, only in this way can the long-term preservation of oxalic acid on the body of insects be ensured, which will increase the effectiveness of the fight against parasites. Therefore, it is best to take boiled or bottled.
It is also necessary to take into account that before treating bees with oxalic acid, it is recommended to use a smoke cannon. Thanks to this, you can calm the insects.
Formic acid
Formic acid can be used to provide protection against varroa. This is a compound familiar to the body, which in the right concentration can get rid of not only varroa, but also microbes.
But, the beekeeper needs to take into account, in order to effectively get rid of parasites using this product, it is necessary to take into account the temperature factor. The fact is that methanoic acid simply hardens when the air temperature is lower than +8°C. And in too intense heat, the acid, on the contrary, begins to evaporate intensively. And this can have a toxic effect on bees.
Therefore, it should be used in the warm season - best when the temperature ranges from +12 to +25°C.
Beginning beekeepers need to pay attention to the fact that effective protection of bees from mites using formic acid is only possible if all hives are treated. Otherwise cross contamination may occur.
Horseradish
Another option for treating bees against mites in the spring is horseradish leaves. But before using them, it is important to dry them properly. To do this, use a place with low humidity and no direct sunlight. Because if drying is improper, some of the active ingredients simply disappear. After this, the dried plant material is placed in a smoker and four shakes are made in each house.
The main effect of horseradish is that the leaves contain oxalic and formic acids. It is this that has a detrimental effect on ticks.
Smoke cannon
If the owner is concerned about protecting bees from mites, he will purchase a smoke cannon for his farm in a specialized store. True, you can do it yourself with little effort.
This processing is carried out as follows:
- First, the hives are cleaned.
- An old canvas, previously soaked with propolis, is placed in a smoker (or smoke cannon).
- Smoke will be generated from the leaves or bark of the oak tree.
- After the smoke is released into the hive, I close the entrances for 20 minutes.
- This treatment must be carried out 3-4 times. Allow about 3 days between each procedure.
Kerosene
The numerous substances that were given as examples above are not the only ones that can be used to treat insects. Protection against ticks will also be effective if you use kerosene.
But, it is mixed with Bipin, the concentration will be as follows - for 4 ml of Bipin take 100 ml of kerosene (of any type - purified or regular). They load the cannon and process the hives. This amount of solution is enough for approximately 50 bee colonies.