Description
Despite the huge species diversity, bedbugs have similar features:
- number of limbs: adults have three pairs of limbs, they can be of different types, adapted for life on land or in water;
- oral apparatus in the form of a proboscis and bristles: the bug feeds on liquid food, it pierces the shell and sucks out the contents, be it blood or plant sap;
- glands that secrete an odorous substance that is designed to repel enemies;
- wings - most species have them, they have a certain appearance: half of the wings are leathery, the other half are membranous; There are also representatives of the family that have only elytra or have completely lost their wings as unnecessary.
Bedbugs come in different sizes - from a couple of millimeters to 15 cm. The largest representative of the family is the water bug, which grows up to 15 cm in length. The shape varies, but most of the individuals are round, with a flattened body in a chitinous shell. Round or rod-shaped forms are also found. Not all bedbugs have eyes. But the organs of touch are well developed in all varieties.
Bedbugs come in different colors. Bright colors for those who are better left alone. It is a protection and a method of intimidation. Another means of protection is a pungent, unpleasant odor, which is caused by cimicic acid. Bedbugs secrete secretions from their glands. It is this smell that animals and birds that might eat bedbugs do not like.
Types of bedbugs
Depending on their habitat, bedbugs can be terrestrial or aquatic, indoor or outdoor.
According to their feeding method, the following types of bedbugs are distinguished:
- Herbivores (phytophages) - eat cell sap, which is obtained from the fruits, seeds and leaves of various plants.
- Predators – hunt larvae, insects and invertebrates.
- Ectoparasites (hematophages) - feed on the blood of people and warm-blooded animals.
The vast majority of bedbug species are herbivores. There are insects with a mixed type of nutrition. There are frequent cases of cannibalism, that is, eating their relatives.
According to the danger and harm caused, representatives of the genus are divided into useful, harmless and pests. They are generally harmless to humans.
Beneficial bugs
Some types of bedbugs can be quite beneficial. For example, the wingless red bug, also called the soldier bug, feeds on the remains of dead invertebrates or fallen leaves, contributing to their decomposition. The blue zikron bug destroys the larvae and eggs of leaf beetles. Thanks to its activities, the number of Colorado potato beetles is reduced. Also destroying the Colorado potato beetle, including its imago, is the perillus bug. Several species of flower bugs eat aphids, mites, eggs and larvae of harmful insects, and they are even bred specifically to protect seedlings and flowers grown indoors.
Pest bugs
Pests from the class of garden bugs are well known to gardeners and gardeners:
- Cruciferous and rapeseed - destroy plantings of cabbage, rapeseed, turnips and radishes.
- The berry bug, or light green stink bug, feeds on the juice of raspberries, gooseberries and other berries and can also infect cereal crops. Berries affected by this bug acquire an unpleasant odor and cannot be eaten.
- The tortoiseshell is a pest that is difficult to notice on plants due to the color and pattern on the shell; it attacks cereal crops. Turtles lay eggs, from which larvae emerge during the ripening period of the crop. Larvae and adults damage the grain, which becomes unsuitable for processing.
Biology of predatory bugs.
Different types of reduviids are characterized by different habitats - on the ground, trees, human habitation. Eggs ranging from several tens to thousands are laid in the usual habitats of adults. Embryonic development - 2-3 weeks. There are usually five nymphal stages. Triatomine bugs are not necessarily located near a food source. Blood sucking is necessary for egg production and normal development of the nymphal stages, but adults can lay eggs without feeding if the nymphal stages have been well fed. The entire development cycle lasts from one to two years.
Water bugs
Many species of hemiptera have chosen water as their habitat. The most famous types of water bugs are:
- Water scorpion - this family includes more than 200 species of bedbugs. Their length reaches 4.5 cm. They are brown, with forelimbs that have transformed into claws. They live in shallow water and cannot swim. They breathe through the tail appendage, which is placed above the water. They hunt tadpoles and crustaceans.
- Water striders are the largest family, which includes more than 700 species. They have long limbs on which they glide through the water. They feed on insects that have fallen into the water. They overwinter in fallen leaves outside water bodies.
- Smoothies live in water, but can also fly. They feed on insects and small fish; they can bite animals or humans, but the bite is not dangerous.
- Plautus vulgaris - feeds on insects, larvae, mollusks and fry.
- Belostoma gigantica - the bug got its name for its size; adult individuals reach a length of 10 cm. They can attack not only insects, but also fish and turtles. Not found in our country.
Bedbugs and cockroaches
Many people believe that bedbugs cannot appear in an apartment where there are cockroaches. In fact, this opinion is wrong. These insects have completely different habitats and life processes. Bedbugs settle closer to a person, in his bed, furniture, clothes, and cockroaches prefer places with direct access to food (kitchen, dining room). Thus, pests can calmly coexist without intersecting or interfering with each other. Some people believe that cockroaches eat bedbugs like other organic foods, but this is not entirely true. It is impossible to say with certainty who eats bedbugs, since such insects are not included in any food chain. Such cases are not possible in laboratories and at home.
These insects simply cannot compete for resources. Organic food (crumbs, scraps, water) is suitable for cockroaches, which bedbugs are not interested in at all. And bedbugs like the blood of humans and animals, which in turn is not accepted by cockroaches.
Ground bugs
Bedbugs live in different conditions. They live in the ground, grass, bushes and trees. They can live in any climatic zones, in forests and fields, in deserts and steppes, even in the tundra. Many people choose houses or other heated structures for their existence, for example, a barn or a poultry house.
Among terrestrial species, stink bugs are the most common. They got their name because they look like they have a shield on their back. They are also called tree bugs, although they do not only live on trees. There are more than 4 thousand species of stink bugs, most of them are agricultural pests.
Lined scale insect has a red-black color, it is striped and very bright, it eats the inflorescences of carrots, parsley and dill.
The berry shield bug is red-brown in color and eats berries, leaves and buds of oilseeds and fruit crops.
Shield bug – more than 50 species of bugs are known by this name. Destroy cereal crops.
Marbled bugs feed on different types of plants. They are highly fertile and have almost no natural enemies. They winter in houses.
Family Reduviidae (Predators).
Most reduviids are predators that feed on other insects and are called “killer bugs.” Many of them can, but usually do not, bite people. The bites are quite painful. Extraintestinal digestion. One subfamily, Triatominae, is of great medical importance because its species act as a vector for Trypanosoma cruzi. Unlike assassin bug bites, triatomine bug bites are virtually painless to the host, as would be expected for a species that needs to suck blood and remain undetected for several minutes. They are also called kissing bugs, as they often bite a sleeping person on the lips.
House bugs
Blood-sucking bedbugs are dangerous to humans. There are several dozen species of domestic ectoparasites. They are all small and flat. When saturated with blood they increase several times. They don't have wings, but they have running legs. House bugs have a flattened oval body and are yellowish or brown in color. There are no eyes, the sense of touch and smell are well developed. The size of the larva is from 1 to 4 mm, the adult is up to 6 mm.
Insects hide inside furniture, in cracks and crevices. They can migrate from apartment to apartment or to neighboring buildings. They are active at night.
Although such bugs are called bed bugs, they live not only in human homes and feed not only on human blood. Species are known that settle in caves where bats live. There are also so-called swallow bugs. They parasitize birds, but can also migrate to humans.
Bed bugs live everywhere, in all countries. Their distribution does not depend on social status, level or lifestyle.
There are types of bed bugs that are not so common and do not live in our country at all:
- stinging bug - its bite causes severe allergic reactions;
- triatomine bug - after a bite, anaphylactic shock can develop, and these parasites also carry Chagas disease, which is fatal.
These types of bedbugs live in countries with hot climates and do not pose a danger to us, but we must remember them when traveling.
There are three types of house bugs in Russia:
- Cimex lexctularius is the most common, common blood-sucking bug with a specific odor, feeds on human blood, and prefers to bite children due to the close proximity of the blood vessels to the skin; can fast for a whole year; the development cycle from egg to adult takes from 30 to 100 days;
- Cimex pipistrelli – parasitize bats;
- Oeciacus hirundinis is the same swallow bug mentioned above; parasitizes birds, can attack humans, and is a carrier of diseases.
Bed bug sizes
The smallest bugs are about 1 mm in size, and the largest species reaches 15 cm in length. Belostoma giants live in fresh water bodies. Synanthropic parasites are small in size. The size of bedbugs depends on age and amount of food. Hungry adults are 4.3-5 mm long; after sucking blood they increase to 6.5-8.5 mm. Males are smaller. The natural color of the insect is from dark yellow to brown. After the blood is sucked out, the swollen body takes on a red tint. The flat shape of the parasite is replaced by a spherical one. Gradually the color of the bug changes from scarlet to black. This occurs as a result of blood clotting.
The size of a bedbug egg is 0.8-1 mm. The female lays them in 5-12 pieces, gluing them to the surface with a special secretion. After 4-15 days (depending on temperature), first instar nymphs appear. Their length is only 1 mm. After a week, molting occurs and the insect doubles in size. Before reaching sexual maturity, the larva will change through 5 instars. The size of a house bug at the last stage is 4 mm. To carry out the next molt, the nymph must drink blood.
Harm from bed bugs
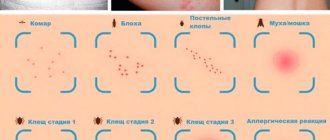
A domestic bug lives on average 12 – 14 months. Eats once a week. A bug nymph can suck up to 0.5 ml of blood at a time, and an adult can suck up to 7 ml. All bed bug bites cause itching, redness of the skin, and a rash. Moreover, a person may not notice the moment of the bite, since the parasite injects an anesthetic substance during the bite.
The danger with bed bugs is that they are difficult to get rid of. They settle in large colonies in an apartment or house and plague residents with constant bites. This leads to severe psychological discomfort. In terms of health, there is no great harm from bedbug bites. But they can cause allergic reactions. Bedbugs can also act as carriers of diseases if they migrate between rooms. In addition, blisters from bites are very itchy, scratching them can introduce an infection into the wounds, which leads to skin diseases.
Domestic bugs are sensitive to changes in living conditions. The most comfortable temperature for them is 25 – 30 degrees. With a sharp increase (more than 45 degrees) or decrease (freezing), they die. But at the same time, these insects are becoming increasingly resistant to the means used to combat them. People have to invent new compounds to chemically kill bedbugs.
Morphology of bedbugs of the family Cimicidae.
Tsimicides are red-brown bugs, up to 8 mm long. Flattened dorsoventrally. Their limbs do not have special devices for clinging to the host, but they allow the bedbugs to run quite quickly; bedbugs do not stay on the host for longer than 5-10 minutes. They absorb about 7 mg of blood at a time. Adults do not have wings, although nymphs develop rudimentary wings. Tsimicids have conspicuous compound eyes, but they do not have ocelli. The first thoracic segment forms a rim around the back of the head. The width of the tergite of the first somite of the chest exceeds its length. On the ventral side of the third somite of the chest, odorous glands open, secreting an oily secretion with an unpleasant odor characteristic of bed bugs. The smell probably serves as protection against predators.