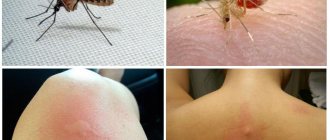
The linen louse is not an independent species, it is just a type of head louse. But they prefer fleecy clothes to their heads, where they live most of their cycle. Nature has adapted linen lice (by the way, that’s what people call them, the correct name is body louse) to live in clothes. They have devices on their paws that allow them to easily cling to fabrics.
Although this subspecies will never live on the head, it is capable of interbreeding with head lice. The place of residence of these insects is human underwear, hence their name. Their source of nutrition is human blood, and they have very good access to it while wearing underwear. It must be said that the body louse is a rather fastidious parasite, and it will only live in conditions that completely suit it. The well-being of body lice depends on the behavior of the person infected with this scourge. It is possible to get rid of this type of parasite, and this can be done quite quickly with or without the use of chemicals. But the methods of killing linen lice are somewhat different from the methods by which they get rid of other types of these parasites.
Linen lice: photo, characteristics, living conditions
An interesting fact is that linen lice are gradually evolving into an independent species, currently being a subspecies of head lice and having the ability to mate with them. They only live on certain types of fabrics, for example, they will never live in clothes made of wool, and all due to the fact that people do not wear woolen clothes directly on their bodies. Also, these insects really do not like silk and other smooth clothes, but they will feel comfortable on cotton and linen.
These insects live only on humans; animal blood is not suitable for them. They are not able to go without food for a long time; a day of hunger can become a critical time for them. In order to always have the opportunity to eat, insects are constantly near the human body in order to immediately have a snack as soon as the need arises, and it occurs about 5 times a day. By the way, one of the main methods of removing head lice is based on their fasting. If the clothes that these insects have chosen as their home are not worn within 5 days, the parasites die.
People whose wardrobe is quite diverse have reliable protection against infection by these insects, because even if a louse accidentally gets on an item of clothing, it may well die while the person is not using it. From this we can conclude that linen lice are permanent residents on the clothes of homeless people and other asocial elements. A declassed lifestyle is a guarantee of infection with linen lice.
Differences between lice bites and other insect bites
It is usually difficult to tell right away whether lice are actively biting a person or other insects. Bites of pubic and head parasites are characterized by a common difference - spots appear regularly. Other representatives are not interested in constantly returning to the hair growth zone.
This feature of pests is explained by the specific structure of the body - only lice can boast of special hook-shaped growths on their paws, which facilitate the process of moving individuals along the hair.
Body lice bites are not so easy to distinguish: their marks are approximately the same size, they are located in the area of the buttocks, abdomen, arms, etc.
The peculiarity of lice bites of this type can only be considered their chaotic arrangement.
If you compare a louse with a bug, the latter leaves behind a chain of red dots on the body of the victim.
Appearance of linen lice
In appearance they resemble head ones; they can reach 2-3 mm in length. If you look closely, the edges of the abdomen consist of folds that straighten when the insect takes the next portion of food. Still, there are signs by which a linen louse differs from a head louse: we are talking about color - body lice are almost white. But only a hungry louse has this color; when it is filled with blood, its color turns brown.
The appearance of linen lice larvae is no different from the appearance of adult individuals; they differ only in size. The nits of both types of lice also look the same, but the process of their development occurs in completely different places: if the nits of head lice are attached to the hair at a short distance from the head, then female linen nits lay their eggs in the folds of clothing. They look for the most secluded places where they will be more difficult to detect - pockets, folds. It is very difficult to detect linen louse nits without using magnifying glasses due to their very small size - 0.5 mm.
Linen lice are distinguished by their front legs - they are widely spaced and have a powerful appearance. They also differ from head lice in their manner of behavior: on clothing they prefer to stay in groups, and only when feeding on a human body can they be alone. And these parasites spend most of their time on laundry. Lice crawl onto the human body only when they want to eat. But since they live on their underwear, this journey cannot be called long.
In the oral cavity of insects there are peculiar protrusions with which they make injections and suck blood. At the same time, to prevent blood clotting, when they bite, they inject a special substance, which is the cause of allergies to bites in some people. At the sites of bites on the human body, spots with a bluish tint form.
Linen lice are hardy insects, since the temperature range in which they can feel comfortable is wide - from 0 to 45 degrees Celsius. Young insects, the so-called nymphs, are not so hardy; they can exist at temperatures of 0-40 degrees Celsius. But both nymphs and adult insects feel most comfortable at 31-32 degrees Celsius. The activity of parasites slows down noticeably if the items of clothing on which they live are not worn for some time. It should be borne in mind that linen lice love humidity, and they will breed most actively where the humidity is high.
The life cycle of body lice reaches 45 days. They can live longer if the air temperature is slightly lower than what is optimal for them. Then their life processes begin to occur more slowly, and the size of the insects also becomes smaller.
Food intake for linen lice is not regulated, but they feed up to 5 times a day, consuming up to 0.5 ml of blood each time.
Lice will not necessarily be on the underwear of an infected person; with advanced lice, they crawl in different directions.
Body lice appear where there is unsanitary conditions, since then excellent conditions are created for their reproduction. Homeless people and other people leading a corresponding lifestyle meet these conditions.
Regular washing will not help destroy lice, because they can remain in water for 2 days. Systematic change of underwear will also not help to destroy these insects, because if a piece of clothing is worn at least once every few days, there may well remain insects whose life processes have slowed down, but they are still alive, only slightly reduced in size. They will very quickly return to their previous form if they feed on blood for at least 1 day.
Here are the signs by which linen lice are distinguished from other parasites:
- They are distinguished from fleas by their color. Fleas are much darker.
- Bedbugs are also much darker than lice, and they are much larger in size. And bugs feed only at night, while lice bite at any time of the day.
- Lice also differ from ticks in their lighter color and the number of limbs - lice have 6, and ticks have 8.
- As already mentioned, linen lice are very similar to head lice, and they are also very different from pubic lice. The pubic louse resembles a crab due to its wide abdomen.
Nymphs of body lice are not much different from adult individuals; the differences concern only the reproductive system, which in nymphs is in an underdeveloped state. Nymphs also feed only on human blood; they behave in the same way as adults. During her life cycle, the female is capable of laying up to 150 eggs. Every day she lays 3-4 nits. If external conditions meet the standards (30-35 degrees Celsius), then the incubation period will last no more than 5 days. Nits are very tenacious, and it is not so easy to destroy them. If the clothes on which they are deposited are not worn for some time, then the process of their development is preserved; the preservation period can last up to 2 months.
When the larva emerges from the egg, it immediately begins to feed, after which its first molt occurs. There will be 3 molts in total over 9 days. Then the nymph will completely transform into an adult. If measures are not taken in time, then within 20 days the number of lice can increase many times over, so after the first signs of head lice appear, it is necessary to immediately take the necessary measures.
How dangerous is a linen louse?
The parasitic insect must receive a portion of fresh human blood in order to continue its vital activity. The mouthparts are adapted for piercing the skin; it is strong and functional enough to quickly penetrate and inject saliva for pain relief, so the victim does not immediately sense the danger and the louse has time to suck in the blood until completely saturated.
The maximum that a person feels at this moment is a slight tingling sensation. A little later, burning and severe itching begins, which are difficult to tolerate and there is a need to scratch the inflamed area. This is what happens most often. At the same time, the likelihood of infection of the bite site increases significantly, which threatens complications, infection from the outside, and deterioration of general well-being. The reaction to body louse bites largely depends on the sensitivity of the person and his tendency to allergies.
Those who have unwittingly encountered a parasite and know how linen lice bite are unlikely to want to encounter them again. This is not only pain, an unpleasant feeling of disgust, but also the danger of contracting serious diseases. Are linen lice bites dangerous? Yes, and not only because the wounds from its bites serve as “entry gates” for infection. Scratching areas can lead to pyoderma, a condition in which ulcers, irritation, and suppuration form on the skin.
With prolonged contact with parasites, to which some segments of the population are exposed (homeless people, displaced persons, refugees and disaster victims), changes occur on the skin. They are expressed by its coarsening, the appearance of pigmentation and the formation of scars. The linen louse can carry typhus, intestinal infections, and trench fever.
What are bites? What they look like
The symptoms of linen lice lesions differ only slightly from the bites of other blood-sucking lice, but some features are still present. Basically, the specificity of their bites is expressed in the sensations of the one they bite. A linen louse can bite any part of the body that comes into contact with clothing - it could be arms, legs, back, etc. Other varieties of these parasites are not capable of this.
Symptoms and appearance of the bite
A person begins to suspect the presence of insects after lesions resembling insect bites appear on the body. It is very important to immediately determine which insect caused these lesions. After this, a decision should be made regarding measures to remove parasites. It is necessary to be able to distinguish the symptoms of lesions caused by lice in order to accurately determine the fact of their presence.
The bites of linen parasites are not much different from the bites of other insects - they are a red swelling that constantly itches and is located at some distance from other affected areas of the skin. Each swelling is crowned with a black dot - this is, in fact, a wound left by an insect when it punctures the skin. Through this hole the louse sucked blood.
A person will not immediately feel the bite, as the insect introduces a special enzyme for pain relief. At first, the bite is felt as a slight tingling sensation; it begins to itch only after a while, when the louse has already crawled to a safe distance.
The localization of bite sites is in the folds of clothing - armpits, lower back, etc. But this does not mean that these parasites do not bite other parts of the body; bite sites can be found anywhere. It must be said that the bites are very painful and very itchy. At the same time, the desire to scratch seems natural, but you need to control yourself in order to avoid the appearance of characteristic scratches on the body.
And now about the symptoms of linen lice in more detail:
- There is a red rash all over the body. This also applies to those areas where no bites were found. The whole body itches and hurts after scratching.
- Since the desire to scratch with head lice is inevitable, scars will eventually appear on the body; they can be deep.
- Pigment spots may form at the affected sites, indicating the presence of an allergic reaction in the infected person.
- In advanced cases, ulcers may well form on the body, which will certainly develop into pyoderma if a course of treatment is not carried out.
- Very advanced cases (happens to homeless people and other non-social elements) are characterized by thickening of the skin and its excessive pigmentation.
Usually people get rid of parasites at their first signs, but when proper measures are not taken for years, pediculosis goes into a neglected state, and this already threatens with serious consequences.
Characteristic signs of body lice bites
Of course, body lice bites are very similar to the bites of any other blood-sucking insect, but they still have their own characteristic signs:
- If there is a whole path on the body consisting of bite sites, then this is a clear sign of the presence of bedbugs. These insects try to make as many punctures as possible. There is no sequence in the bites of linen lice; they bite only in one place.
- Lice bites differ from flea bites in that they are much less painful. The fact is that nature did not take care of the secrecy of fleas, because they are very difficult to catch, but lice inject an anesthetic substance, since they are clumsy, and it is much more difficult for them to hide from persecution. In addition, flea bites, like bedbugs, are also located in the form of paths.
- Wounds caused by lice differ from tick bites by being slightly painful. After a tick, significant swelling remains on the body. In addition, the tick, having attached itself to the human body, remains in one place for a very long time, while the time the lice eat does not exceed several minutes.
- Lice bites can be confused with wounds left by mosquitoes, but mosquito bites do not have a black dot in the middle. And mosquitoes don’t bite under clothes, which, of course, cannot be said about linen lice.
- If the body is very itchy, but there are no signs of punctures, then the cause is not lice, but most likely scabies mites.
What dangers do parasite bites pose?
We have already talked about the possibility of pyoderma, but this is not the only danger that lice bites can cause. Lice may well be carriers of fever and even typhoid. In ancient times, these diseases were a real disaster for all peoples, but today they remain only in undeveloped countries.
In addition, lice may well be carriers of rickettsia - these are very dangerous bacteria that can cause several diseases similar to each other. And in the tropics, lice carry many more diseases that are unknown in temperate countries. Therefore, there are a lot of diseases that can be caused by lice. Be sure to consult a doctor if you experience nausea, fever, or increased temperature while having lice; these may well be symptoms of diseases caused by lice bites.
Where can you “catch” the infection?
- Linen lice can change hosts during close contact between people.
- There is a high probability of infection in crowded places.
- If people share the same items of clothing, this can also cause infection.
- In places where used clothing is sold, the presence of parasites is also possible.
- Lice can stay in water for up to 2 days, so they can be “picked up” in public bathing areas, for example, in swimming pools.
Types of lice and what their bites look like, symptoms
It is not surprising that when associating the word pediculosis with head parasites, few people remember the existence of pubic or bed lice. The fact is that these varieties of multi-legged “bloodsuckers” are found much less frequently.
However, it’s still not worth relaxing, because no one is immune from the danger of “picking up” a rare parasite while trying on something in a store, in a sauna, or at a doctor’s appointment. Therefore, remembering the proverb: forewarned is forearmed, it is necessary to study the symptoms of the presence of lice and learn methods for eliminating insects.
Attention! In people predisposed to developing allergic reactions, the condition may become more complicated due to insect bites. If the bitten areas begin to swell, the victim has difficulty breathing - he needs qualified medical assistance. Otherwise, there is a possibility that an anaphylactic reaction will develop and the person will die from suffocation.
Linen bed lice
The linen (bed, clothes) louse is an almost invisible insect, at first glance resembling a small bug. The parasite lives in bedding, seams of blankets, pillows or items of clothing. Moreover, preference is given to contaminated products made from natural fibers.
Finding themselves in a blanket that has not been washed for a long time, the 5-mm bloodsuckers begin to lay eggs (nits). Only one female is capable of laying about 300 eggs in just one month. The stimulus for the development of hatched babies is the heat generated by a person during sleep or wearing a dress/shirt with nits attached to the seams.
Single bites of linen lice are indistinguishable from traces left by mosquitoes, midges, and bedbugs. The following symptoms appear at the site of puncture and injection of saliva:
- barely noticeable swelling with a diameter of 2–4 mm;
- redness (even where there are no bites);
- in the center of the red spot there is a drop of dark, dried blood;
- unbearable itching and pain (after some time);
- in people prone to allergies, pigment spots appear at the sites of bites;
- in advanced cases, ulcers form at the sites of scratching, and then purulent, difficult-to-heal wounds.
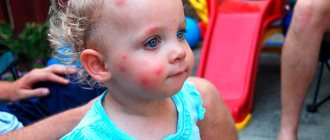
With a large-scale infection, numerous randomly located bites resemble a rash or merge into one huge spot.
Attention! If you feel an unbearable itch under your clothes, “like someone bit you,” it is better to undress and carefully examine every seam of your clothing with a magnifying glass. This precaution will allow you to detect parasites immediately after they “populate”.
Body lice bite up to four times a day, in places where blood vessels are located as close as possible to the surface. As a rule, these are the shoulders, back, neck, stomach, buttocks. In young children - a face. Unlike their head counterparts, bed lice do not live and do not “feed” on the scalp.
How long does it take for bed lice bites to go away?
After removing the insects, the wounds take the same amount of time to heal as regular skin lesions (rarely it takes more than four days). However, if body lice have bitten large areas of the body, the recovery process is unlikely to take less than a week.
Pubic lice
In America and European countries, lice pubis has reached epidemic proportions, affecting mainly people under 35 years of age. According to recent statistics, among citizens of the Russian Federation, no more than 8% of residents of megacities suffer from “intimate” parasites.
Contrary to popular belief, this is not a sexually transmitted disease, because you can “catch” pubic lice not only from a sexual partner, but also after a number of health procedures: swimming pool, solarium, sauna, massage, etc.
The favorite place for pubic lice is at the base of the hairs surrounding the perineum. The fact is that it is the groin area that contains the maximum number of apocrine glands, which secrete sweat with a characteristic odor.
Much less often, insects occupy the armpits, thighs, beard, mustache, eyebrows or eyelashes - depending on the hairiness of the person. It is not easy to examine blood-sucking lice, because they are the smallest lice, rarely growing up to 3 mm. Symptoms of bites:
- severe itching caused by the parasite's saliva containing an anesthetic;
- chaotically located, quickly disappearing spots of a bluish tint with a diameter of about 1 cm;
- tiny dark spots on the inside of your underwear;
- rashes in the form of reddish swellings, blisters or eczema, provoked by scratching the bitten areas;
- nits become noticeable, rising above the skin level as the hair grows back. Moreover, their height allows you to determine how much time has passed since the lice infestation.
Pubic lice are so small that their proboscis does not leave marks in the form of a brown dot, which is characteristic of head or linen insects.
Head louse
Now, when it comes to lice, most people frown with disgust, imagining disgusting insects occupying human hair. At the same time, many remember their childhood, and more specifically, the “lousy periods” that almost always ended diving in village stakes.
But the worst thing happened when the lice bites were discovered by the mother, who developed vigorous activity and generously smeared her head with disgusting smelling kerosene or dust soap.
Immediately after infection, it is almost impossible to notice a head louse or its bites. But after a month, a single female is able to flood the victim’s head with insects and bite marks extend beyond the hairy area. The following manifestations should be a cause for concern:
- itchy scalp, mainly on the temples, back of the head, behind the ears;
- rashes in the form of red spots, “scattered” over the entire area of the scalp and neck, appearing 3–5 days after infection by insects;
- In an attempt to cope with the itching, the bitten person scratches the bite sites, causing scratches to appear on the skin. Later, the scratches become covered with purulent crusts;
- tiny, only 2–3 mm silver-gray bubbles, located first in the root zone and then along the entire length of the hair. Nits are the most accurate symptom of lice;
- if the head is infested with insects, secretory secretions stick together the hair, tangles form in the hair, which are not easy to comb. As a result, a nauseating odor emanates from the head.
This is interesting! If a person dies or gets sick with a fever, lice that experience discomfort at temperatures below 33 C° leave the person on their own.
How to get rid of laundry parasites
Almost all options for combating lice are based on their poisoning. Before treating clothes, you need to wash yourself using special shampoos - Medifox, Veda-2 or Lauri. This measure will ensure that no lice remain on the body.
Then you need to process the laundry using the following methods:
- Infected items are boiled for 20 minutes. Boiling should be done in water with the addition of special insecticidal preparations containing Permethrin - this is the most effective substance that can destroy linen parasites.
- If you have any suspicions about one of the items of clothing, you should hang it on the balcony. It is desirable that the weather be sunny, but since this is not always possible, you can hang out the laundry in any weather, the main thing is not to take it off for a week, during which time the insects in the clothes will die. Lice cannot go long without food, and hunger will certainly destroy them.
- If the infection is not in the first stage, the clothes should be treated in a special formaldehyde chamber. Of course, it is difficult for the average person to find an opportunity to do this, then dry cleaning can help.
The fight against body lice is not as troublesome as the destruction of head lice, but it can also be associated with a number of difficulties. In former times, body lice were most often gotten rid of using kerosene. This, of course, is an effective remedy, and after soaking the contaminated laundry in kerosene, the lice will definitely disappear, but the smell will remain, which will be more difficult to get rid of than lice.
Today, special preparations are used to combat lice, which we will discuss below, but now the basic principles for treating contaminated clothing:
- Infected clothing is soaked using regular powder and a special insecticide for 45 minutes.
- During this time, the owner of contaminated clothing should wash himself using insecticidal preparations.
- After this, you need to put on clothes that have not been used for a long time, since the possibility of the presence of linen parasites on them is almost zero.
- Now the contaminated items should be washed in a washing machine, also using special products. It's better if the water is hot.
- Washed clothes should be boiled or, if it is frosty outside, frozen.
- Underwear treated in this way should be worn after a week.
- Be sure to treat your bedding in the same way, as parasites could easily live in them.
What to do if bites are detected?
If traces of linen louse bites are detected, sanitary and hygienic measures are necessary, first of all. Be sure to take a shower and thoroughly wash your body with soap. All clothing must be disinfected. If possible, it is better to burn it or dispose of it in a special service. At home, wash at high temperatures and iron for a long time on both sides.
- Important! Is it worth using kerosene to fight lice?
It deserves more attention than how to treat linen lice bites. Single damages that do not cause concern can be simply wiped with alcohol.
If the skin damage is significant, proceed as follows:
- Fresh wounds, swollen or bleeding , are wiped with hydrogen peroxide
- To relieve itching and improve general condition, it is good to use antihistamines that will help cope with burning and swelling. Drops and anti-allergy tablets are taken orally, and ointment (Hydrocartisone, Rescuer, etc.) is applied topically. After this, inflammation, redness and itching decrease.
- You should definitely consult a doctor . A specialist will examine the lesions on the skin and help you choose the best medications for treatment.
Effective means to combat linen lice
And now directly about the products that should be used when processing laundry:
A-par
This is perhaps the most effective drug. Its developers claim that it can get rid of not only lice, but also nits. Sold in aerosol form. It consists of two active components - Piperonibutoxide and Esdepalletrin. Before using the drug, things should be washed in the manner indicated above, after which the drug is sprayed over the entire surface of the clothing.
Akromed
The main active substance of this drug is Permethrin. It also contains kerosene, but there is no need to worry about the appearance of a characteristic odor. The drug is sold in the form of an emulsion, four liters of which is enough to treat 1 kilogram of things.
Forsyth
It is also a very effective drug, the main active ingredients of which are Permethrin and Fenthion. Sold in the form of an emulsion that requires preliminary preparation. 20 ml of the drug is diluted in a liter of water. To process a kilogram of things you will need 4 liters of ready-made solution. The treatment procedure requires repeating after a week.
Avicin
Active substance – Permethrin. To prepare the solution, take 1 part emulsion and 100 parts water. Soaking time for contaminated items is 25 minutes.
Celandine
The active substance of this drug is the same Permethrin. The drug is sold in the form of an emulsion, ready for use.
Folk remedies
There are also some folk methods for removing lice that are worth mentioning here:
Dust soap
A wonderful pediculicide, actively used by people. First, the soap is grated. The resulting shavings are dissolved in water and beaten. To completely remove lice, one treatment is sufficient. Remember that you need to carry out the processing procedure while wearing rubber gloves. Contact of dust soap with the skin is extremely undesirable. After the procedure, the laundry should be rinsed thoroughly. Do not neglect safety tips, as dust soap is a toxic substance.
Tar soap
This drug should be used like dust soap. Unlike the latter, tar soap does not pose a danger to human health. But the effectiveness of this remedy is much less.
Some herbs are also used against body lice, but it must be said that they are even less effective than tar soap, and they are used more as a prophylactic agent or for low degrees of infection.
You can wash infected laundry in mint decoction; the smell is simply disgusting to lice, but this remedy, of course, cannot be called effective. Lemon juice is also used to remove parasites; it is added in large quantities to the water in which contaminated laundry is washed. Also for this purpose, use an alcoholic infusion of angelica or a mint decoction.
Prevention of linen lice
Of course, it is impossible to insure yourself against infestation with linen lice, but it is still worth taking a set of measures that will help prevent the appearance of parasites.
- First, don't wear items that other people use, especially items that come into contact with your body. If you happen to spend some time in places where it is quite possible to find people infected with lice, be sure to carry out personal disinfection upon arrival home.
- Try not to communicate with antisocial elements. Experts highly recommend dry cleaning bedding at least once every 6 months. Upholstered furniture should also be treated with special products. And of course, maintain cleanliness, as this is the main condition for ensuring that you and your loved ones will not be infected with linen lice.
Getting rid of body lice is easier than getting rid of head lice, but you need to start doing this as soon as the first signs of infection appear, because the sooner you begin to destroy the parasites, the greater the likelihood that they will disappear quickly and completely.