- Wild animals
- >>
- Arachnids
Argiope Brünnich is often found under the name wasp spider. This is due to the bright colors, which are very reminiscent of wasps. The characteristic bright stripes also gave rise to another name - tiger spider. Most often, a bright color indicates that the insect is dangerous and poisonous.
Due to the fact that the wasp spider is quite common in some regions of Russia, you need to clearly know whether you should be wary of the insect when you encounter it. Zoologists unequivocally state that spiders are indeed considered poisonous, but their poison is not at all dangerous to humans.
Origin of the species and description
Photo: Argiope Brünnich
Argiope brunnich belongs to the arachnid arthropods, is a representative of the order of spiders, the family of orb-weaving spiders, the genus Argiope, the species of Argiope brunnich.
The spider received the name Argiope in honor of the ancient Greek nymph. About three hundred years ago, it was customary to give insects the names of ancient Greek divine creatures. Brunnich is the name of a researcher, a zoologist originally from Denmark, who wrote a large encyclopedia on insectology in 1700.
Video: Argiope Brünnich
The exact time of origin and stages of evolution of this species of arthropod is quite difficult to determine. This is due to the fact that the protective chitinous layer is destroyed quite quickly. The few remains of various parts of the body of the ancient ancestors of arachnids were most often preserved in amber or resin. It was these findings that allowed scientists and researchers to suggest that the first arachnids appeared approximately 280 - 320 million years ago.
The oldest discovery of an arthropod was discovered in the territory of the modern People's Republic of China. Judging by the body parts isolated from amber, the arthropods of that period were small in size, not exceeding five to six millimeters. Characteristically, they had a long tail, which disappeared during the process of evolution. The tail was used to make the so-called spider web. The ancient ancestors of arthropods did not know how to weave webs; they simply involuntarily secreted dense sticky threads, which they used to weave their shelters and protect cocoons.
Another characteristic feature of ancient spiders was the almost separate cephalothorax and abdomen. Zoologists suggest that the place where spiders appeared is Gondwana. With the advent of Pangea, insects began to spread almost at lightning speed throughout the entire landmass. With the onset of ice ages, insect habitats declined significantly.
Reproduction of Argiope
The lifespan of this arthropod species is about 12 months. Mating occurs only after the start of the molting period, which the male knows about in advance. The whole process goes like this:
- The male waits for the moment of mating near the site where the web is weaved, usually at its edge.
- After the start of molting, the mating process occurs, which ends with the female eating the male.
The process of the female eating the male after mating is similar to the type of reproduction in black widows - There are times when he manages to avoid this fate and escape from the nets, but this happens extremely rarely.
- If this happens, the second mating will definitely be the last for the male.
- This is due to the fact that he has only 2 legs, on which the male genital organs are located. After the first mating, one of them disappears, leaving the second. For this reason, the lifespan of a male rarely exceeds several months.
The spider is of considerable size, which can instill fear in a person.
After eating her partner, the female weaves a cocoon from the web, which will become a shelter for future offspring. As a rule, at a time she lays several hundred eggs, which are kept in a cocoon until the spiderlings hatch. The mother diligently protects the offspring and leaves them only when threatened.
In winter, the female dies , but the cocoon remains, and spiderlings appear in the spring. After this, the babies settle in different places, and the entire life cycle begins anew. If the eggs were laid in early summer, the offspring may hatch as early as early autumn. Spiders spread with the help of the wind, which carries the webs to different places.
Appearance and features
Photo: Argiope Brünnich spider
Argiope Brünnich is considered a medium-sized spider. The body size is 2.5-5 centimeters. However, adults in some regions may exceed these sizes. Individuals of this species are characterized by pronounced sexual dimorphism. Males are significantly smaller than females. Their body size rarely exceeds a centimeter. In addition to their size, they are easy to distinguish with the naked eye by their appearance and color.
Females have a large, round abdomen, which is distinguished by the presence of bright black and yellow stripes. The female's long limbs also have light stripes. Males have a thin and elongated body. The color is inconspicuous, gray or sandy. The abdominal area is somewhat lighter and has light longitudinal stripes. The male also has stripes on his limbs. However, they are dim and blurry. The span of the limbs is quite large. In some individuals it reaches 10-12 centimeters.
Fun Fact: Spiders have six pairs of limbs, four of which act as legs and two as jaws!
The short pedipalps look like tentacles. The stomach, which is flat on the inside, has irregularities along the contour in the shape of teeth. If you look at the spider from below, you might think that you are looking at a squash with legs. The bright, rich color allows spiders to avoid the fate of being eaten by birds and other insect hunters.
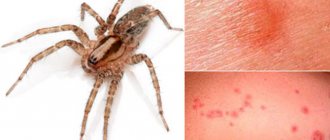
Spiders are poisonous. However, they are not capable of causing much harm to a person. The maximum that can happen when they bite is a burning sensation, redness of the bite area, a feeling of numbness, and swelling.
Photo and description of the web
Argiope with a yellow belly weaves a complex web, which consists of vertical and horizontal threads. A spider sits in the center, waiting for its victim. The predator is engaged in the production of trapping nets at night. This takes no more than an hour. The web is placed between the plants at a height of no more than 30 cm from the surface of the earth.
Interesting!
The web shimmers in the sun, attracting the attention of grasshoppers, locusts, flies, and other insects. Argiope's nets serve to scare away enemies. A large spider begins to shake its web. When oscillating, the shine from the sun's rays increases, which confuses enemies.
Where does Argiope Brünnich live?
Photo: Poisonous spider Argiope Brünnich
The habitat of this type of arachnid is quite wide. We can say with confidence that insects live in various parts of the world. Geographical regions of arthropod habitat:
- Africa;
- Europe;
- Asia Minor;
- Middle Asia;
- Japan;
- Kazakhstan;
- Eastern region of Ukraine;
- Indonesia;
- China;
- Russia (Bryansk, Lipetsk, Penza, Tula, Moscow, Oryol, Voronezh, Ulyanovsk, Tambov, and other regions).
In the 60s and 70s, most individuals of Argiope Bryukhin were concentrated within 52-53 degrees north latitude. However, already in the 2000s, information began to arrive about the discovery of the insect in a variety of regions, and, in most cases, the discovered individuals lived much further to the north of the specified region. Zoologists claim that this unusual method of settlement of arachnids was facilitated by the unusual ability to move - with the wind.
The attraction of this species of arthropod to xerophilic vegetation species was revealed. They prefer to settle on various types of meadow vegetation and shrubs. They can often be found on roadsides and forest edges.
Spiders prefer open, sunny areas. They love fresh, dry air and absolutely cannot tolerate high humidity and cold climates. Most of the time, the wasp spider tends to be in the open sun. Among all types of vegetation, they prefer to settle on low plants that grow in dry, open, sunny areas.
Now you know where Argiope Brünnich lives. Let's see what she eats.
Danger
The venom of the wasp spider is deadly to insects, but practically harmless to humans. At the same time, argiope bruennichi does not purposefully attack people. This insect can only bite accidentally if it is disturbed by picking it up. The affected area may experience:
- slight swelling;
- redness;
- burning;
- pain.
But these symptoms often go away very quickly. If after a wasp spider bite you begin to experience discomfort, then apply something cold to the affected area to speed up healing. After such a compress, the pain subsides and the swelling goes away.
In general, the venom of the wasp spider is quite weak for humans. However, sometimes, in particular with weak immunity, the body’s negative reaction can be quite intense. In such cases, anti-inflammatory ointments usually help. The poison of argiope bruennichi can be dangerous for humans only if there is an allergy to insect bites. In this situation, you should definitely seek qualified medical help.
(Latin name "Argiope lobata Pall") is a large genus of spiders belonging to the family of Orb-weaving spiders.
What does it look like
Argiope is a fairly large spider. The average body length of an adult female is 3 centimeters, but larger specimens are also found. Males are much smaller in size - on average, body length does not exceed five millimeters. The female Argiope is quite easy to recognize by her bright coloring. The head is black in color, the cephalothorax is covered with thick ash-colored hairs, the abdomen is striped (bright yellow and black stripes alternate). The females' legs are very long and black with pale yellow rings. Due to the presence of stripes, female Argiopes have been called "zebra spiders". Males do not have such bright colors; their bodies are either black or gray.
Lifestyle
Argiope live in small colonies, the number of which does not exceed 20 individuals. Spiders prefer to settle in forests, fields and meadows where there is a lot of vegetation. They stretch their networks between several plants, attaching the main threads to the stems. Argiope's catching webs are distinguished by very small cells and incredibly beautiful patterns (like many other orb-weaving spiders). The spider spends all the time sitting in the center on its lower side. Argiope mainly hunts, and, but does not refuse other insects caught in the net. Spiders paralyze their prey in a matter of seconds with poison, wrap them in cobwebs, and then just as quickly eat them.
Where does he live?
Argiope spiders inhabit southern and central Europe. In total, scientists identify over 150 species (from the genus Argiope), which are found in almost all corners of the planet, excluding the polar zones. Only a few species can be found in the European part of Eurasia.
Danger!!!
Argiope spiders do not pose a great danger to humans, since their venom is quite weak. Only the female of this spider can bite a person, and only if you pick her up. The bite itself is quite painful, since the spider inserts its stinging organs very deeply under the skin. A few seconds after the bite, the area around the wound begins to redden and swell, and a feeling of numbness appears. After a few hours, the pain begins to subside, and the swelling goes away after two to three days. Argiope bites are a real danger only for people who are allergic to insect bites.
Although this creature is cute, it inspires inner anxiety. Some kind of unreasonable fear. It is especially creepy to watch how a spider with yellow stripes, also called a wasp, deals with defenseless grasshoppers and flies. He sets out a trapping net, sits half asleep, and waits. But as soon as the careless insect comes into view, it immediately transforms - it quickly pounces, paralyzes the victim with poison and deftly packs its “lunch” into a cocoon of cobwebs. Is it dangerous for humans?
At first glance, a very cute spider... until you find out that it is poisonous
What does Argiope Brunnich eat?
Photo: Argiope Brünnich, or spider wasp
Wasp spiders are considered omnivorous arthropods. The main food source is insects. Spiders get them using their webs. It is worth noting that they have practically no equal in the skill of weaving webs. The network is quite large and has a wheel-shaped shape. A distinctive feature of the web of these arthropods is the presence of zigzag lines. Such a network is a reliable assistant in the process of obtaining food. Spiders happily eat any insects that may fall into it.
What is the food supply of Argiope:
- flies;
- mosquitoes;
- grasshoppers;
- beetles.
The specific shape of the web allows spiders to catch a fairly large number of insects. Tiger spiders synthesize venom with which they paralyze the prey, preventing it from being released from the web. Sensing vibrations in the nets, the arthropod instantly approaches its victim, bites it, injecting poison inside and sedately waits.
Interesting fact: Most often, after several insects become entangled in a network at the same time, they look for another place and weave a new network. This is explained by the caution of spiders, who are afraid of scaring off potential new victims.
After some time, the poison begins to act. It paralyzes the victim and helps melt the insides of the insect. After this, the spiders simply drink the internal contents, leaving the outer shell. Often after mating, the female eats her partner if she is very hungry.
General information
The yellow-black Argiope spider was named after the famous Danish zoologist Morten Brunnich. The cephalothorax and abdomen of the animal are connected by a thin septum and are very mobile. The body length of the wasp spider reaches 2.5 cm if we are talking about females. Males do not exceed 1 cm in length.
A distinctive feature of this species is the clear difference between representatives of different sexes. Females are always significantly larger than males, their abdomen is round and oblong. In males, the body is a solid elongated oval without clear distinctions between the head and abdomen.
The arthropod received its unofficial name and comparison with known insects thanks to the transverse stripes on its back. The color of the stripes is black, and they are located on a bright yellow background, which ensures the similarity. The animal's legs are light in color and have black tips. The female always looks brighter than the male.
In this video you will learn about the wasp spider:
A male can also be distinguished by the presence of 2-3 stripes, which are not so bright and are located on a pale yellow background. It was the females who were nicknamed the wasp spider, since the male bears little resemblance to this insect.
Habitats
The Argiope spider is a fairly common species. It can be found in many countries of North and South Africa, America, Korea and China. Argiope Brünnich is found in Indonesia and Central Asia. Southern and Central Europe, Crimea, and Kazakhstan are also rich in this type of arachnid.
You can meet a spider in the CIS countries only in the southern regions
The arthropod is widespread throughout Russia and the eastern part of Ukraine. It prefers a mild climate and does not tolerate cold well, so it is extremely rare in that part of our country where a damp and cold climate prevails.
The wasp spider prefers to be in the sun most of the time. That is why its favorite habitats are open meadows, lawns and places along highways. The animal prefers to place its web on low plants growing in particularly dry areas.
An interesting feature of the striped animal is that, thanks to its long and strong web, it can move quite long distances and easily adapts to new conditions. Quite often, southern varieties can be found in areas with colder climates.
Lifestyle Features
The black-and-yellow arthropod does not like loneliness, so it settles with its close relatives in groups of 15-20 individuals. This helps them hunt prey together and raise offspring. After the main female in the flock chooses a place to settle, weaving a web to catch insects begins.
The essence of the wasp spider's hunt is to wait for prey to fall onto the web.
Each member of the flock weaves an extensive web, distinguished by its strength and beautiful pattern, in about 60 minutes. Its peculiarity is that even the smallest hole will not let in prey that has already been caught in the net.
The web is also distinguished by its variety of patterns and multi-layered nature. According to research, individuals weave it in several layers so that it reflects ultraviolet rays. The shine attracts insects of different species, providing the colony with a constant supply of food. Weaving usually begins at sunset.
If this process is interrupted, the arthropod abandons its work, hurries to shelter and, after the threat disappears, begins weaving in another place. After finishing the work, the animal is placed in the center of its network and waits for prey, remaining motionless for several hours.
Wasp spider feeding
The striped spider prefers to feed on grasshoppers, various types of locusts, and its diet also includes mosquitoes, flies and other common insects. They get caught in the web, after which the animal begins a ritual of eating, which is almost indistinguishable from the feeding habits of other spiders:
- When caught in a net, an insect tries to free itself.
- To prevent the prey from tearing the net, the argiope bites it. When bitten, the venom and digestive enzymes of the arthropod enter the insect.
The introduction of enzymes into the victim’s body activates the process of digestion of the entrails inside it - The poison immobilizes the victim, and he stops trying to free himself.
- Next, Argiope Brünnich waits for some time until the enzymes make the food suitable for consumption. They actually dissolve the insides of the insect, and after a certain period of time, the wasp spider simply drinks the liquid, leaving a chitinous shell.
It is worth noting that the unique and multi-layered pattern of the web allows the arthropod not to be left without food, since it attracts a large number of different insects during the day. As a rule, after several insects become entangled in a web, the animal leaves this place and weaves a new one. This avoids scaring potential victims away from beautiful networks.
Features of character and lifestyle
Photo: Argiope Brünnich
Argiope Brünnich is not a solitary insect. Spiders of this species tend to gather in groups, the number of which can reach two dozen individuals. This is necessary to more effectively provide oneself with a food supply, as well as for breeding and raising offspring. In this group, the leading position is occupied by a female individual. It determines the place where the group will settle. After settlement, the process of weaving a trapping net begins.
Arthropods tend to lead a terrestrial lifestyle. To provide themselves with a source of food, spiders weave webs. They belong to the orb-weaving spiders. This means that the web weaved by it has a beautiful pattern in the form of small cells.
Argiopes weave their webs in the dark. It takes approximately 60-80 minutes to make a web. During the period of weaving their nets, female individuals are most often located in the center of the trapping net with their limbs outstretched. The web is most often placed on twigs, blades of grass, or other places where there is a high probability of catching insects. After everything is ready, the spider lurks below and simply waits for its prey.
When an arthropod senses an approaching threat, it immediately descends to the surface of the earth and turns over with its belly up, hiding its cephalothorax. In some situations, argiopes begin to swing on the web for self-defense. The threads have the property of reflecting the sun's rays, forming a large shiny spot, scaring away potential enemies.
Spiders are naturally endowed with a calm disposition; they are not inclined to show aggression. If a person encounters such a spider in natural conditions, he can, without fear, photograph it or carefully examine it at close range. During the period of darkness or drop in temperature, spiders are not too active and rather inactive.
Danger to humans
According to scientists, the poison released by a spider during a bite cannot harm a person. It acts as a defense mechanism and poses a danger only to insects that Argiope Brünnich preys on.
The bite of this spider is not life-threatening, but causes prolonged pain.
But this does not mean that the arthropod will not bite a person who intentionally or accidentally tries to pick it up and gets into the web. The bite is comparable to that of an aspen in terms of the nature of the pain due to the strong jaws of the arachnid and the penetration of poison under the human skin. In most cases, the pain goes away within 1-2 hours.
A hyperemic spot and swelling may form at the site of the bite. The body's reaction depends on the predisposition to an allergic reaction and the state of the immune system. Such bites are especially dangerous for people with allergies to insect venom , as well as for young children with weak immune systems.
A spider cannot cause the death of a person, but if severe itching, burning, swelling and hyperemia occur at the site of the bite, it is recommended to consult a specialist. This is especially necessary if the symptoms are accompanied by dizziness, weakness, nausea or a critical decrease in blood pressure.
Argiope Brünnich is an arachnid with a unique color and lifestyle.
If you keep a distance from its webs and do not try to harm, the spider is not dangerous to human life and health. This is interesting: what kind of spiders are there?
Social structure and reproduction
Photo: Argiope Brünnich spider
Females are ready to enter into mating relationships after molting. Most often this happens with the onset of the autumn season. It is after the end of molting that the female’s mouthparts remain soft for some time, which leaves the males a chance to survive after mating. However, this does not always help males survive. To lay eggs, females vitally need protein, the source of which can be a partner.
Before mating, males look closely for a long time and choose the female they like. They have been nearby for some time. When the male approaches the potential partner he likes, the threads of the trapping net do not vibrate, as when prey hits them, and the female understands that the time has come for mating. Males tend to “clog” the chosen female so that no other contenders can fertilize her.
About a month after mating, the spider lays eggs. Before this, she weaves one or several cocoons, in each of which she lays about four hundred eggs. After the cocoons are filled, the female fixes them near her web using reliable, strong threads.
Interesting fact: After the eggs are hidden in cocoons and securely fixed on twigs or other types of vegetation, the female dies.
The eggs survive the winter in these cocoons. Spiders hatch from eggs only in spring. From childhood, individuals of this species experience fierce competition for survival. The lack of food in the limited space of the cocoon encourages stronger spiders to eat weaker and smaller ones. Those who survive get out of the cocoon and climb higher onto various types of vegetation. They lift their abdomen up and release a web. Along with the wind, cobwebs and spiders are carried in a variety of directions. The full life cycle of a spider averages 12 months.
Spider Wasp: Lifestyle
This arachnid rarely lives more than 1 year. A distinctive feature of the species is its group lifestyle. Spiders can weave webs and hunt together. There are usually up to 20 individuals in a group. This lifestyle helps the argiope protect itself from natural enemies.
The arthropod belongs to the family of orb-weaving spiders, so it has a characteristic large wheel-shaped web. Argiope Brunnich is especially active in the evening. At the same time, the spider weaves its web. During the day it may hide in dense vegetation or bark. It should be noted that the wasp spider has a calm disposition. In addition, he is inactive at night.
Each group has a dominant female. Her place is most often taken by the strongest female. She determines the place of residence, the time of weaving webs and hunting, and is also responsible for the protection of offspring.
Wasp spider or Agryope Brünnich with prey, photo
Spider wasp or Agryope Brünnich on the hand, photo
Spider wasp or Agryope Brünnich on a leaf, photo
Reproduction
Females are ready to mate immediately after molting. At this point, the female's chelicerae (jaws) are soft, which gives the male a chance to survive. Males do not immediately mate with females. They stay close for some time, choosing the best partner. At the same time, females do not show aggression.
During mating, the female wraps a web around the male. For the proper development of the offspring, she needs a lot of protein. If the male fails to escape, the female eats him. Females rarely mate again. Males can mate with several females, but in most cases they become the prey of the first partner. Among those who observed the reproductive process in this species, no one has ever noted that a male individual managed to fertilize more than two females.
Females weave a large cocoon in which they lay about 400 eggs. One female can have several clutches. Such cocoons are always located close to the web. The female protects her offspring. At the end of summer or early autumn, young spiderlings emerge from the cocoon and leave the nest, flying through the air on their webs.
The full life cycle of a wasp spider is one year.
It happens that the female lays eggs only at the end of autumn. In this case, she does not live until spring, but dies. However, the eggs are most often guarded by other members of the group.
At the egg stage, the arachnid overwinters. Once born, the young are locked inside a cocoon. At this moment, strict natural selection occurs. Due to a serious lack of food, the offspring begin to eat each other. By the time the spiders have enough strength to destroy the cocoon, only the strongest individuals remain. Then they climb to higher ground and are carried by the wind. Later, the arachnids form groups and the cycle repeats.
Diet and hunting habits
Argiope Brünnich feeds on small insects and arachnids. Most often its prey is:
- grasshoppers;
- crickets;
- locusts;
- mosquitoes;
- flies;
- midges.
The arachnid's diet also includes small flying beetles. Unlike many other spiders, Argiope Brünnich does not hunt from ambush. The arthropod is located in the center of the web, waiting for prey. This behavior is justified by the fact that in the center of the web there are thick zigzag threads, such a thickened pattern is called “stabilimentum”. Many insects are guided by light during migration, so they are attracted to such webs.
Having entangled the victim in a web, the predator injects poison, which paralyzes and liquefies the tissues of the insect. After this, the wasp spider drinks the juices, leaving only the shell. As necessary, the argiope leaves its web and looks for a new place of residence. This often happens when a large number of insects are caught in the net, as they scare off future prey.
Natural enemies
Wasp spider, what does it look like?
Argiope Brünnich scares off many birds with its bright colors. Spiders also never fight among themselves. The web and group lifestyle further protect the wasp spider from almost all predatory insects and arachnids.
The main threats to Argiope are frogs and lizards. They are often attacked by rodents. Sometimes the wasp spider gets into a fight with wasps or bees, to which it most often loses. In self-defense measures, an arthropod can swing its web to scare off a predator with its bright shine. In extreme cases, the arachnid simply breaks off the web and falls to the ground, quickly hiding in the grass.
Natural enemies of Argiope Brünnich
Photo: Poisonous Argiope Brunnich
Argiope brunnich, like any other insect species, has a number of enemies. Nature has endowed them with a bright, unusual coloring for spiders, thanks to which they manage to avoid attacks by many species of birds. Birds perceive bright color as a signal and a sign that the insect is poisonous and eating it is dangerous to life.
Spider relatives do not pose any danger to each other. They do not wage war over territory, borders, or females. Small spiders hatched from eggs tend to eat each other while still in the cocoon. This slightly reduces the number of insects. It is worth noting that spiders tend to avoid insectivorous plant species, and they are reliably protected from predatory insects by a strong web.
Rodents, frogs, and lizards pose a danger to the spider. However, in some cases, spiders manage to outwit these dangerous creatures. They tend to defend themselves. To do this, they loosen the web, the threads of which glisten in the sun and scare away those who are about to feast on arthropods. If this does not help, the spiders break off the web and simply fall into the grass. It's hard to find them there. In addition to rodents and lizards, the enemies of Argiope Brünnich are considered to be wasps and bees, whose venom is fatal to spiders.
Argiope Brünnich: keeping in the house
Thanks to the spectacular appearance of the female, the spider attracts the attention of lovers of exotic pets. Some people keep such a spider as their pet.
To keep Argiope at home, you need an aquarium in which the lid and one of the walls are covered with a fine mesh. Dry grape branches can be placed inside. They need to be sprayed only on the hottest days.
It is better to keep one spider in the aquarium, because if there are several of them, they will begin to attack each other, which will lead to the death of one of them.
You need to feed the spider once every 2 days. Various insects are suitable as food; they can be bought at a pet store.
Danger
The venom of the wasp spider is deadly to insects, but practically harmless to humans. At the same time, argiope bruennichi does not purposefully attack people. This insect can only bite accidentally if it is disturbed by picking it up. The affected area may experience:
- slight swelling;
- redness;
- burning;
- pain.
But these symptoms often go away very quickly. If after a wasp spider bite you begin to experience discomfort, then apply something cold to the affected area to speed up healing. After such a compress, the pain subsides and the swelling goes away.
In general, the venom of the wasp spider is quite weak for humans. However, sometimes, in particular with weak immunity, the body’s negative reaction can be quite intense. In such cases, anti-inflammatory ointments usually help. The poison of argiope bruennichi can be dangerous for humans only if there is an allergy to insect bites. In this situation, you should definitely seek qualified medical help.
Argiope Brünnich spider
belongs to the araneomorphic species. This is a rather large insect, males are smaller than females. The body of an adult female can reach from 3 to 6 centimeters, although there are larger exceptions.
Argiope males
, on the contrary, are small in size - no more than 5 millimeters; in addition, the boy’s narrow little body is usually painted in a nondescript, monochromatic gray or black color with a light belly and two dark stripes on it located along the sides. On light legs there are faint, vague rings of a dark shade. The pedipalps crown the male genital organs, otherwise called bulbs.
The photo shows a male Argiope spider
The female differs not only in size, but also in general appearance. Female Argiope black and yellow
striped, with a black head, there are small light hairs on the rounded-oblong body. If you count starting from the cephalothorax, then the 4th stripe differs from the others by two small tubercles in the middle.
Some scientists describe the legs of females as long, thin, black with beige or light yellow rings, others believe the opposite: the legs of the spider are light, and the ringing stripes are black. The span of the limbs can reach 10 centimeters. In total, the spider has 6 pairs of limbs: 4 pairs are considered legs and 2 are considered jaws.
The photo shows a female Argiope spider
The pedipalps are quite short, more like tentacles. It is because of the combination of black and yellow colors, expressed in stripes on both the body and legs, that Argiope is called the “wasp spider.”
. The beautiful color of the spider also helps it not to become dinner for, because in the animal world bright colors indicate the presence of strong poison.
Another fairly common variety is Argiope lobata,
or otherwise -
argiope lobata
.
The spider received its first name because of the unusual shape of its body - its flat belly is crowned with sharp teeth along the edges. Argiope lobata in the photo
resembles a small squash with long thin legs.
The photo shows the spider Argiope lobata (lobed agriope)
Representatives of the species are widespread throughout the world. They are found in Europe, Asia Minor and Central Asia, in most regions of the Russian Federation, Japan,. The preferred place of life is meadows, forest edges, and any other well-lit places.
The question often asked is “ is the Argiope spider poisonous or not?
“, the answer to which is definitely yes.
Like most spiders, argiope is poisonous
, but it poses absolutely no danger to humans - its poison is too weak.
The insect does not express aggressiveness towards people;
only a female
Argiope
bite and only if you pick her up.
However, despite the weakness of the venom, the bite itself can cause pain, as the stings penetrate deep into the skin. The bite site almost immediately turns red, swells slightly, and becomes numb.
The pain subsides only after a couple of hours, but the swelling from the bite of the Argiope spider
may last for several days. Only people with allergies to this kind of bites should be seriously afraid. Argiope thrives in captivity, which is why (and because of its spectacular color) representatives of the species can often be seen in terrariums.