A skin and hair disease caused by parasites is called pediculosis. The likelihood of infection does not depend on living conditions, wealth or hygiene. Usually, for lice to be transmitted, contact between a healthy person and a carrier is sufficient.
It is often not always possible to detect insects immediately after infection. If you know what the clinical picture of the disease looks like, you can understand that you have lice from the first signs.
What to do in such a situation? To get started, we recommend reading this article. This article describes in detail methods of controlling parasites. We also recommend that you consult a specialist. Read the article >>>
Symptoms of infection
Pediculosis can be detected at an early stage by the following main signs:
- itching It gets worse after washing your hair, in the evening, during sleep.
- Insect eggs (nits) are present.
- Feeling of crawling.
- Rashes in various manifestations (ulcers, papules, minor inflammations).
- Presence of excrement (like small black dots).
- Hair gets tangled and quickly gets dirty.
If you are unable to resolve the problem on your own, you should consult a dermatologist.
Symptoms of body lice
The body louse chose clothing and bedding as its habitat. It is simply not capable of attaching itself to the head. An adult may not be aware of its existence, and may perceive itchy spots as an allergy.
Symptoms of this type of lice are as follows:
- bluish spots appear all over the body;
- It was possible to recognize lice in the folds of clothing.
A linen louse bite causes:
- papules;
- age spots;
- blisters.
In advanced stages, body lice can cause fever, nausea, headaches and insomnia.
This type of lice is rare and it is almost impossible to find it in your home. A body louse cannot grow in a clean room.
How can you tell if you have lice on your own?
Localization of parasites. Typically, detecting parasites in the head is not difficult if the head of an adult or child is regularly examined as a preventive measure.
There are certain areas where insect development occurs most intensively. It is from these places that they spread throughout the entire head, so they need to be examined immediately if pediculosis is suspected. These include the occipital region and temples.
So how do you know if you have lice? Pay attention to the back of the head and temple area, as well as behind the ears and on the neck.
Nits. Just a couple of days after infection, nits become noticeable, but adult individuals are not always visible.
They do not have the ability to quickly move from visible areas. Parasites are characterized by a special attachment of nits - one larva on each hair. A small number of larvae are not immediately noticeable, especially with head lice in children with blond hair.
Sometimes they can be confused with dandruff at the initial stage, but when squeezed, the capsule with the larva makes a popping sound, which is not typical for keratinized skin particles. Nits have an oblong, spindle-shaped shape, not exceeding 0.8 mm. There is a small seal at the end of the formation.
Lice. How to recognize head lice? The adult insect is sometimes difficult to identify. The light gray color and small size are almost invisible, so parasites are often identified by the presence of nits. The average size of a louse is 2-3 mm, but can reach 4 mm.
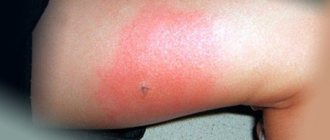
Bites. How do you know if you have lice? Slight redness appears in areas where insects are active. They can be single at the initial stage and multiple if pediculosis is advanced.
Constant skin irritation causes severe itching, which leads to hyperemia at the bite sites and even swelling. In some cases, an allergic reaction may develop.
Help with inspection for lice. Sometimes self-identification of lice when suspected becomes difficult. Then this can be done with the help of another family member.
Parents should also regularly conduct preventive head examinations of children who have contact with peers in kindergarten or school.
Using a comb. How to tell if lice are in your head using a comb? A tool with fine teeth will allow you to quickly identify nits and subsequently comb them out.
But a comb alone will not be enough to remove adult parasites. The louse easily hides between the cloves and then ends up back on the hair.
Detecting and combing out lice on a damp head. Before you realize that lice have appeared, are infested and happily live on your hair, we recommend that you wet your hair. It is easy to identify lice with wet hair, since they remain motionless when exposed to water.
When combing, the teeth should reach the roots of the hair and lightly touch the skin. The comb is drawn from the skin along its entire length, and then examined for the presence of nits and lice.
If at least one individual is noticed, then the person is sick with pediculosis. After each stroke through the hair, the teeth are thoroughly wiped with a napkin or rinsed with water.
What lice and nits look like
Due to their appearance, parasites are very easy to camouflage. The louse has an oblong body, it reaches 5 mm in length. The color of the body depends on whether it is full or hungry. When hungry, they have a gray body color; as they become saturated, it changes to brown.
They have paws with claws, thanks to which they grip well on any surface. They have no vision, and small antennae are responsible for the process of smell.
The oral apparatus has something like needles that pierce the skin. Next, they insert a proboscis into the wound and suck out the blood. Nits are round in shape and white. Their size reaches 1 mm.
How to correctly diagnose parasitic skin disease?
The human louse is a blood-sucking parasite. It can live in the scalp, in the folds of clothes and the pubic area. These are different types of head lice. The insect does not exceed 4 mm in length. It is light brown in color and can be transparent.
When bitten, the parasite secretes saliva, which contains a substance that causes severe itching of human skin. For this reason, scratching occurs, which becomes covered with crusts as it heals.
The period when a person discovers signs of head lice can reach 30 days. This is considered the incubation period for head lice. The second stage of the disease is its identification. It is better to entrust the diagnosis of pediculosis to a doctor.
The initial location of lice on the human head is the occipital and temporal zones. Over time, the parasites spread throughout the entire scalp. In this case, the head type of lice is diagnosed.
The maturation of eggs in the female’s body occurs on days 9-10 and depends on the warmth of human skin. If the temperature is less than 22 degrees, nits do not ripen. In this state (on objects or things) they can remain for about a year. A nymph (larva) emerges from a mature egg on days 20-22, which differs from the adult in the following characteristics:
- body dimensions;
- absence of genitals;
- color;
- little activity.
We suggest you read: How to find out if you have lice on your head: symptoms and signs of lice Over the course of two weeks, nymphs grow and develop, turning into sexually mature individuals. Oviposition of parasites continues without interruption, with additional matings occurring. The female lays nits throughout her life (38 days), and stops 24 hours before death.
Pubic lice (pubic lice) belong to the order of blood-sucking lice and live on the hairy parts of the human body. The disease in humans is called phthiriasis. Parasites often live in the genital area, around the anus, in the armpits, in the hairy parts of the chest and abdomen.
In some cases, pubic lice have been found in the beard and eyebrows. They feed on human blood, and without food they die within 24 hours. In addition, being outside the habitat, the insect is able to fall into a state of suspended animation, that is, slow down life processes. A pubic louse can remain in this form for several months.
The disease must be treated by a doctor. Preventive measures for pediculosis (disinfection, personal hygiene, ironing) will help avoid infection.
The pathogen lives on clothing and deposits nits there. It feeds on blood, and for this purpose it moves onto the human body. Body lice occurs in people with an asocial lifestyle who ignore the rules of personal hygiene, as well as in people without a fixed place of residence.
The clothes parasite weighs no more than one gram, and sucks out quite a lot of blood (1-3 μl) due to the ability of its stomach to stretch. Females are larger than males and therefore eat more.
A distinctive feature of the parasite is the presence of a proboscis on its muzzle, with which it sucks blood. The organ works like a pump, while the insect secretes a special substrate that prevents blood clotting.
To identify the first symptoms of head lice, just part the hair on your head and examine it in good lighting. A visual inspection will determine the presence of nits and parasites.
Secondary symptoms of the disease are scratching on the skin and matted hair. If during examination only a single individual without nits is found, a diagnosis of pediculosis is still made.
The very first sign of pediculosis is the appearance of small wounds - traces of parasite bites. In particular, they can often be seen in the occipital and temporal regions, as well as near the ears.
In some cases, the bitten area becomes infected, which is accompanied not only by deviations in the condition of the skin surface, but also by the appearance of a new sign of lice in humans - swelling of the lymph nodes.
In addition, if a person neglects the rules of personal hygiene, lice eggs and secretions cause a rather unpleasant odor and tangled hair. This causes greater deposition of nits and, consequently, accelerated reproduction of parasites.
Also, you should not start the treatment process - the disease can spread quite quickly, both in the family circle and among other people.
Lice are special types of parasitic insects that live on the hairy parts of the human body or in his clothing. If the infestation is recent, they may be difficult to detect by visual inspection. The size of an adult insect is only 2-3 mm, and its protective coloring makes it inconspicuous.
When moving in search of food, they crawl along the skin, but the structure of their paws allows them to hold firmly on the hair shaft. In clothing, parasites at rest become lodged in seams and folds of linen.
Parasites feed on the blood of the host, piercing the skin with piercing-sucking mouthparts adapted for this purpose. It is often possible to determine the presence of insects in a child or adult by the unpleasant sensations that lice cause when bitten.
Lice that parasitize humans.
A saturated louse becomes a brighter, reddish-brown or orange color. It is easy to see during examination, and in rare light hair (for example, in a child) it can be noticed by accident.
In such cases, the insect resembles a miniature bug.
An adult female lays 7-14 eggs daily. During her life (about 49 days), she alone can leave abundant offspring. Eggs (nits) resemble small whitish balls firmly glued to the hair.
Depending on their habitat, there are 3 types of human lice:
- cephalic, lives only on the head, not found in underwear or on other parts of the body;
- pubis, or flatum, lives on the pubis and in the genital area, anus, in the armpits, sometimes on the eyebrows and eyelashes;
- clothes, settles on linen and clothing, feeds on the body in places where clothing fits tightly to the skin.
The first signs and symptoms of the appearance of lice and nits in an adult, depending on their type
One louse in the hair is not lice. Pediculosis is understood as a complex of symptoms characteristic of the numerous presence of parasites with their vigorous activity:
- Itching, rashes, possible allergic reactions.
- It is almost impossible to know the moment of infection , although parasites that get on the hair immediately begin to take root and act. The initial bites are not noticeable to the victim. When the skin is punctured, the louse injects a special enzyme into the wound to digest blood. It acts as a pronounced allergen and causes itching. When bitten by several lice, a person may not pay attention to this and associate the itching with something else. But when there are already dozens of lice, the itching begins to get annoying.
- In addition to feeding, the louse reproduces in parallel . Nymphs are voracious and bite more often. These bites in the form of pinpoint redness with a small protracted hole in the middle are easily detected on the skin. When there are many of them, they can merge into reddened areas. Multiple bites force a person to literally not take his hands out of his hair.
- At the sites of scratching, excoriation forms characteristic scratches in the upper layer of the skin, which quickly become covered with crusts. Then they are more noticeable.
Head lice show the following symptoms:
- Unreasonable itching on the head, especially on the back of the head, neck and behind the ears.
- Sensation of moving hair.
- Detection of insects in hair, even dead ones.
- Bite points.
- Sudden “dandruff” that does not shake off (nits).
- The itching does not go away after washing your hair and gets worse at night.
- If pediculosis is accompanied by the inability to wash your hair (hiking conditions, vagrancy and military operations), tangles appear. This occurs due to the fact that when the female attaches the eggs to the hair, she envelops it with a sticky secretion. If the insect holds on to several hairs, they all stick together and tangles form. The skin underneath itches not only because of the bites, but there is no ventilation and dandruff and dirt accumulate.
The main signs of body lice:
- Scratching on any part of the body, not necessarily where the hair is.
- Lice come out at night to search for food. The nutrient medium for them is blood and sweat fluid. Having eaten, the louse returns to the seams of clothing and lays eggs. In the morning, small unbearably itchy dots appear at the site of the bites.
- Pests can be detected by inspecting clothing: they usually get stuck in the seams.
Body louse requires, first of all, maximum treatment of clothing - exposure to high or very low temperatures: boiling, frying clothes in the sun or taking clothes out into the cold. An additional measure is to iron the seams on both sides.
The patches settle on the pubis and regularly manifest themselves as itching . From here they can move on to eyelashes and eyebrows, and a beard.
Do you treat clothes when head lice appear?
Not really
Symptoms of flat spots in women:
- Itching in the pubic area after infection through sexual contact.
- Rash, irritation.
- Itchy spots with a bluish tint, which are especially bothersome at night.
- Detection of the parasites themselves and their larvae on pubic hair.
- When shaving the groin, you can see dark spots in the pores with a bluish rim around (the bite site).
- Pubic lice leave their waste products in the form of black dots on underwear.
The only cause of infection is sexual contact with a carrier of the disease.
How to detect nits
Adults cannot always be seen without aids. They cling tenaciously to the hair and can be immobile. These insects are brown or gray-brown in color and darken when saturated with blood. So sometimes they are indistinguishable against the background of hair.
If you have lice on your head, there will definitely be nits - parasite eggs. They are attached at the base of the hair, and only one nit can be attached to one hair. But females lay eggs in a crowded pattern - on adjacent hairs. Therefore, when heavily infested, they are arranged in clusters. Nits are often confused with dandruff. They are as small and white as flaking scales on the scalp. But the difference is that dandruff is located directly on the skin, and nits are located on the hair.
When examining your head to determine whether you have lice and nits, you need to pay attention to the hair at the back of the head and temples. This is where a large number of nits are usually found. They sit tightly on a hair, as the female secretes a special secretion that glues them. When trying to remove nits, you have to make an effort. When treating head lice with folk remedies, a vinegar rinse is used, which corrodes this adhesive composition. While dandruff can be brushed off your head with your hand, this cannot be done with nits.
Appearance of parasites
In order to determine if you have lice, of course, you need to imagine what they look like. Adults are small insects with a slightly flattened body of an inconspicuous yellow-gray hue. As it becomes saturated, the abdomen fills with blood and the parasite becomes darker.
The body length is 3-4 mm, the head appears very small against the background of the abdomen. Insects have three pairs of legs ending in claws. But given the miniature size of lice, these details can only be seen under a microscope. Due to their nondescript coloring, it is quite difficult to detect adult insects; in addition, they move quite quickly along hair and skin.
Louse
With nits (lice eggs), the situation is different. They are easily found on the hair at the roots of the hair. These are translucent, whitish capsules, 0.7 - 1 mm long. Sometimes eggs can be mistaken for dandruff, but it is easy to distinguish them - dandruff can be shaken off, but to get rid of nits firmly attached to the hair with a special adhesive, you will have to try.
Mechanical method of diagnosis and treatment
The most important assistant for detecting lice is a comb, or rather a comb with very densely spaced long teeth. They comb their hair to remove lice and nits. This must be done subject to the following rules:
- It is better to comb wet hair;
- It is advisable that it is not the person who has picked up lice who does the combing, but his assistant;
- cover your shoulders with a white towel so that the combed parasites fall on it;
- Combing is best done indoors, which can then be treated with pediculicides, for example, in the bathroom.
You need to spread white paper or cloth, tilt your head in its direction and start combing your hair from the back of your head forward. The teeth of the comb should go through the hair and touch the scalp. Parasites will comb out onto the paper and get stuck between the teeth of the comb.
Please note that combing is a way to detect parasites and reduce their numbers, but not to get rid of them completely. This method of control is suitable for very small numbers of insects and nits, if the infection has occurred recently. Combing is also used to remove lice and nits from a child, for whom pediculicides cannot be used. In this case, you can not resort to special means, but try to simply comb out the parasites. The procedure must be carried out several times, combing the entire head and trying not to leave a single adult or nit on the head.
If pests are found, you can’t just leave them. Pediculosis does not go away on its own. You can get rid of them using special pediculicides, for example, produced by MediLIS Laboratory LLC: Malathion, Permifen, Super, Bio. They destroy parasites and nits. Instructions for use are included with each product; they are easy to use and effective.
Prevention of head lice
The most common type of infection is not only neglect of hygiene, but also the use of other people's hygiene items. This is especially true for combs; for girls, these are hairpins and elastic bands. You should not change clothes, which children and teenagers also like to do.
When traveling, you should be careful when choosing an overnight stay ; no one guarantees that the linen in hotels and hostels is disinfected, and that there are no parasites in the pillow.
A special topic is pubic lice. They can only be infected through sexual contact. Therefore, the choice of a partner must be balanced. You should give up the habit of trying on other people's hats, even in stores.
Important! The best prevention is regular visual inspection.
Any person can face the problem of lice, and not always a slob . The situation is complicated by the small size of the parasites. It is very difficult to notice their penetration. For this reason, you should be attentive to the sensations on your head and regularly examine your hair.
- about the author
- VK profile
It is possible to defeat parasites!
Antiparasitic Complex® - Reliable and safe removal of parasites in 21 days!
- The composition includes only natural ingredients;
- Does not cause side effects;
- Absolutely safe;
- Protects the liver, heart, lungs, stomach, skin from parasites;
- Removes waste products of parasites from the body.
- Effectively destroys most types of helminths in 21 days.
There is now a preferential program for free packaging. Read expert opinion.
Interesting to know:
Pediculosis. How to determine and what to do.
On the eve of the start of the school year, an experienced recommendation))
Over the 7 years of school, this “happiness” visited us 7 times. Sometimes it seems to me that this cannot happen in the modern world, but different schools and even cities, but the result is the same. True, the last time was last September, although the epidemic subsided in the area only in the spring. This means I learned not only to treat, but also to carry out prevention. I think now I can tell you WHAT to do and how to be.
About lice, where to look and are they lice?
To begin with, the view
It all starts with one bug and ends with a massive breeding ground for nits and endless head scratching. Finding a lice is easy, tilt your head over a bath or paper and carefully comb your head, if even one falls... it's time to take action.
Nits are small white lice eggs that are firmly attached to the hair. A living nit (this is the testicle itself) can be from black to light gray. Only the WHITE nit is dead.
The louse bites about 5 times a day, leaving a small red spot at the site of the bite that itches. The louse reaches sexual maturity in 5-7 days and also lays about 5 offspring per day. The louse lives in the head for about 4 weeks. Calculate how many nits she has time to lay. A louse does not live outside a person; by the way, it does not jump or fly. Accordingly, if a nit has attached itself to a pillow or collar of clothing, then after hatching it has a day to find food, i.e. bite, otherwise she will die. But if this adult louse is “lost” in the vastness of the apartment, then it suffers hunger for up to 10 days! The nit turns into a louse at an average temperature in the apartment of 27 degrees in about 8 days.
If the louse is not found, look carefully at the head for nits and/or bites. The bulk of both are localized on the side of the head above the ears, the second favorite place is the back of the head.
The bites are very itchy. One bite itches for about 3 days.
There are nits in the picture.
So: if a child scratches his head (mainly the back of the head and above the ears), and you find several red spots on the head and/or something attached to the hair, you need to take action.
How to get rid of lice.
There is an official way. Free. You go to the pediatrician, get a referral for etching, go to a special service and come out clean.
At the same time, your educational institution receives a certificate confirming that. If you have lice, the school/kindergarten will be required to check all children.
Minus. What if it’s just you? Why so much noise? When checking, the nurse looks superficially, so the fate of other children is still in the hands of their parents.
Home method. I won't talk about the options. I’ll tell you what helped us 100%.
1. I collect all the clothes that the child wears (even those that were washed yesterday, even street clothes, especially everything that has collars) + bed linen + toys that the child sleeps with. I put it all in large garbage bags and spray A-steam into these bags!
A lot of! I put it on the balcony for an hour (so that the house doesn’t smell). Then I wash EVERYTHING. If it is possible to wash these items at temperatures above 40 degrees, then that’s absolutely ideal!
2. I wash my hair with Nyx. Exactly according to the instructions! Then I comb my hair with the comb provided. When my head is dry, I carefully examine (while simultaneously removing from my hair) the nits. If you find at least one that is not white (or it seemed to you that at least one is not white), then after 5 days the procedure with Nyx must be repeated!
3. Nix works for 2 weeks. If I know that there is a head lice epidemic at school, then in any case I wash my hair with Nix again after 14 days. This way I get protection for another 2 weeks. After that, for 3 months, I wash it once a week with preventive shampoo (sold at the pharmacy).
From what has been tested. A-steam on the head stings VERY! DDT soap is super, a hundred thousand times super, but where can you get it? We found a small piece in grandma's bins. So they took me out in one go. Kerosene - it couldn’t stand it for even 5 minutes, so I had to wash it off urgently.
Frying clothes in a bathhouse at 90 degrees is excellent, but you need your own bathhouse.
Frying it yourself in the bathhouse did not give any results; the lice did not go away.
Still from practice. The dog is not a carrier of lice, verified. They are also not found on carpets and curtains, but you can find them in beds.
And further. The bites itch for 3 days! if all the nits are white and there are no more lice, and the child is on the next level. You've been scratching your head for a day, don't rush to do the whole procedure again, the bites should heal.
As soon as there is a rumor that lice is nearby, it is better to be safe. Tidy up hair, warn the child that a comb, hat, scarf and sweaters cannot be given or taken! If in a class or in a group, then it is better for prevention to wash your hair at least once every two weeks with preventative shampoo against lice.