Causes of allergies
Allergy is a reaction of the immune system to contact with an irritant, expressed in various external manifestations.
Insect allergy occurs upon contact with insects. It occurs in response to poison, saliva, waste products, or microparticles from the bodies of insects entering the human blood.
Bed bugs that live in houses are called bed bugs. They have a dirty yellow or brown color, a flattened body shape and sizes up to 9 mm. These parasites feed on the blood of humans and animals mainly at night, and during the day they hide in secluded places, for example, in box springs and bed frames, mattresses, inside sofas, in ventilation, under baseboards, on the back walls of cabinets and chests of drawers, and in sockets. Their bites cause an allergic reaction called chemipterosis.
An allergy to bedbugs can occur when their saliva enters the wound through a bite or inhalation of body scales, excrement, or skin particles along with dust. When biting, the parasite inserts 2 proboscis into the skin - one at a time, saliva enters the victim’s body, and the second, the insect sucks out blood. An “injection” with saliva is administered because of the analgesics it contains, thanks to which the victim does not feel pain from the bite and does not wake up, and also because of the ability of the substances included in its composition to thin the blood for more convenient suction. The allergen is a protein contained in the saliva of insects.
Causes of allergies
The cause of the allergic reaction is the saliva that the insect secretes when it bites. If an allergy is accompanied by itching, this means that the immune system has begun to intensively produce histamine to fight the foreign protein. Histamine, in turn, provokes leukocytosis, which leads to an inflammatory reaction.
Of no small importance is the patient’s poor environmental situation and sedentary lifestyle, which, combined with a complicated allergic history, can provoke a strong reaction even to long-familiar substances.
Allergens can be all biological substances contained in the saliva of insects that feed on blood, which includes bed bugs. Most often, an allergic reaction to a parasite bite occurs in preschool children. In addition, the toxin released by bedbugs when they bite infants can erase the symptomatic picture, which is why a visual examination of the baby is so important.
Common reaction to a bug bite
Bed parasites feed on human blood. When the insect is hungry, its body is flat, light brown and measures 3-8 mm in size. It is extremely difficult to kill hungry bedbugs due to their body structure. It is much easier to destroy a well-fed one when his body becomes larger, longer, and expands. It absorbs an amount of blood twice its weight. The larvae of the parasites are small, the body is transparent. The larvae also drink blood, after which a drop of blood is visible in the transparent body. Bed suckers are active at night from 1 am to 6 am.
The bedbug's jaw allows it to pierce the skin and suck blood. Having pierced the skin, he looks for a capillary and unerringly chooses the place where he feels the vibration of the blood. The upper and lower jaws look like piercing, unsegmented bristles and form two canals: a wide one for receiving blood and a narrow one for secreting saliva, which acts as an anesthetic. Bedbug bites are painful: adults secrete saliva into the wound, but larvae do not.
Domestic insect bites often cause an allergic reaction. However, the occurrence of serious complications is less than 1%. Frequent bedbug bites provoke a number of complications. In humans, nocturnal insect bites look like swelling.
Mechanism of reaction development
Bed bugs are most active between 3 and 5 a.m. when people are still sleeping, but they can sometimes be aggressive and attack during the day.
Having chosen a suitable place for a bite, the bug sticks its proboscis into the skin, injecting saliva, which contains anticoagulants, and begins to suck out blood. The average time of the sucking process takes 10–15 minutes, during which the bug can increase in size to 3 times its normal volume.
The analgesic effect is provided by one of the components of the insect's saliva, as a result of which the bug has time to get enough blood and hide safely. Often a person does not even suspect that the external symptoms that appear are due to bedbug bites and consult a dermatologist, considering such manifestations to be an infectious disease.
How bedbug bites affect us
People react completely differently to contact with these insects. Let's look at the various manifestations. So, the reaction to bedbug bites can:
- completely absent (according to studies, from 30 to 60% of people do not react to bites);
- manifest itself in the form of minor inflammation of the skin;
- cause a local allergic reaction;
- provoke a generalized allergic reaction, which can manifest itself in the form of urticaria, asthma attacks, angioedema, up to the development of anaphylactic shock (a life-threatening condition requiring immediate medical attention).
What do bedbug bites usually look like?
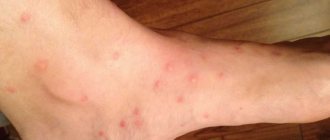
Red itchy spots from 2 to 5 mm appear on the skin around the bite sites; the skin around the bites may be swollen and painful. Usually a person discovers such formations on the skin when he wakes up in the morning. As a rule, they go away within a week. Bedbug bites can resemble mosquito bites, but they have a characteristic feature - they usually form a “path”.
How does an allergy to bedbugs manifest?
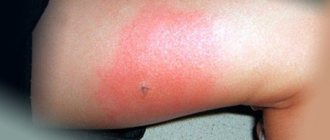
In this case, the characteristic signs of bites: redness, swelling and itching will be more pronounced. For example, swelling may spread to the entire bitten limb. The itching can become unbearable, the papules are painful, and sometimes blisters appear. In rare cases, lymph nodes may become enlarged.
Generalized/general allergic reaction
It is extremely rare, but is a very serious complication and can be life-threatening. If an allergy after bedbug bites, in addition to a local skin reaction, is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Difficulty breathing;
- Hoarseness;
- Dizziness;
- Chest pain;
- Difficulty swallowing;
- Swelling of the lips and/or tongue;
- Itchy rash all over the body;
- Spreading redness around the bite sites;
- Fever
Call an ambulance immediately. These are signs of extreme manifestations of allergies - Quincke's edema and developing anaphylactic shock. In this case, prompt medical intervention is necessary. Otherwise death may occur.
How is an allergic reaction different from a bug bite?
Not everyone can distinguish a food allergy from bedbug bites, since they have similar primary symptoms. The presence of paths of 3 or 4 redness located nearby indicates insect bites. After a couple of weeks they completely disappear. An allergic reaction to foods goes away in a shorter time.
Healthy people, after being bitten by a bug, have virtually no reaction to it. The only thing that may remind you of a parasite bite is the presence of a small red spot or a small bump. In people with a genetic predisposition to allergies to foreign substances, a reaction to bedbug bites can be expressed by the following symptoms:
- redness and swelling at the site of the bite become more and more day by day;
- the affected areas become covered with blisters;
- the appearance of minor itching.
Such symptoms do not cause much harm to a person and go away on their own after a few days. Common signs of an allergy to bedbug bites include:
- runny nose, increased tearing and sneezing;
- difficulty breathing, shortness of breath, and increased heart rate;
- swelling of the mucous membranes, the most dangerous of which is swelling of the larynx, leading to attacks of suffocation;
- in the most severe cases, the victim may lose consciousness.
Main signs of allergies
Domestic insect bites often cause an allergic reaction. The occurrence of serious complications is less than 1%. For a longer stay in the house, apartment bugs provoke a number of complications. In humans, insect bites look like swelling.
The first signs of allergic reactions in the body appear within six to twelve hours after contact with insects. Each person's reaction is purely individual. But it is an undeniable fact that for allergy sufferers, bedbugs are a serious health problem.
If you find the characteristic spots, you should carefully inspect exposed areas of the body, as bed bugs do not bite through clothing. Examine the body as quickly as possible. The appearance of the bite changes very quickly, and within a day or two the redness may spread to the entire limb.
People with allergies experience the following symptoms. Already on the second day, an allergic reaction may appear in the following form:
- itchy rash;
- bronchospasm;
- swollen eyelids and larynx;
- anaphylactic shock.
A child reacts more painfully to a beetle bite, since the parasite does not immediately dig into the body, but “tastes” every area until it finds the “tastiest” place. The delicate skin of children immediately reacts to damage with burning heat, dense tumors and unbearable itching.
The first thing to do when a child or adult is bitten by a bedbug is to prevent scratching so as not to spread an infection to the affected areas.
Allergy symptoms
An allergic reaction to a bedbug bite is identified by the following general symptoms:
- Increasing redness, pimples, blisters that increase in size and shape and spread beyond the bites;
- Swelling and pain in the affected areas of the skin;
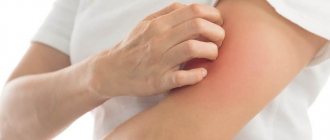
- Increasing itching;
- Severe watery eyes, runny nose, and sneezing;
- Difficulty breathing (bronchospasm), shortness of breath or tachycardia;
- Loss of consciousness.
A negative reaction in the form of an allergy to the secretion of a bug of protein origin can be severe. The patient may experience unbearable itching and bloody spots. The spread of swelling, the appearance of erosion, Quincke's edema, swelling of the upper respiratory organs, the appearance of erosion, and anaphylaxis are possible.
In children, allergies can be more severe than in adults. In most cases, their body temperature rises, which is explained by the child’s immature immune system and the sensitivity of his skin.
An allergic reaction appears under the influence of certain factors, in particular against the background of hereditary disposition and unfavorable environmental conditions. A number of factors that cause allergies also include bad habits, frequent chronic or acute diseases, uncontrolled use of medications, stress, instability of the immune system, and a tendency to allergic reactions.
Child's reaction
In children, the allergic reaction to bedbug bites is much more pronounced than in adults. This is due to the fact that the formation of their immunity has not yet been completed. That is why in children, in addition to the above symptoms, the body temperature rises, and in the most difficult situations, anaphylactic shock may occur. All these signs indicate that measures must be taken immediately to prevent further development of the disease.
Allergies in a child
Women and children are mainly attacked by bedbugs. The reason for this is their delicate skin, which is easily calcined with the help of a proboscis. Men whose blood vessels are located close to the skin are also susceptible to bedbug bites.
After a puncture for sucking, a red swelling with a mark in the center forms on the skin. The swollen area at the site of the bite is very itchy and painful. In a child with increased sensitivity to substances in the bedbug’s saliva, a swelling appears, which can reach up to 5 cm. An allergic reaction in children to the secretions secreted by a bug appears more often than in adults. The reason for this is an immature immune system.
You can distinguish bedbug bites from the bites of other insects, in particular mosquitoes, by the following distinctive features:
- Traces after mosquito bites are single, appearing only on open areas of the body. Bedbug bites can occur over the entire surface of the skin;
- Mosquito bites are single, after the bugs there are characteristic tracks of red, swollen tubercles;
- If a child has been subjected to multiple bedbug attacks, the bites may merge into a large red spot.
The child's body reacts more actively to specific enzymes in insect saliva. In some children, the bite causes a violent allergic reaction, and in some, the marks after the parasite invasion only itch and stop bothering them after a few days.
A swelling on the child’s skin appears 15 minutes after the bite and quickly begins to itch and swell. If the child is prone to allergies, the space between the punctures will be filled with red pimples, reminiscent of hives. The bite of the larvae can cause inflammation and abscesses.
Evidence of a bedbug attack is a chain of about 6 swellings that resemble red pimples. Parents should be concerned about scarlet, extensive bite marks; they indicate the development of an allergic reaction in the child’s body. This reaction can last 7-10 days; in the presence of infection, a longer period is required for complete recovery.
When there are a large number of bites and maggot attacks, symptoms of inflammation may appear. The child may have a fever of up to 39 degrees, and the lymph nodes may become painful and change in size. Also, rhinitis and cough, abdominal pain and diarrhea may appear. Such symptoms can be accepted by parents as the beginning of colds.
The presence of bedbugs in a child's room may be indicated by a strange smell reminiscent of sour berries. This is the smell of a lubricant that the females secrete when attaching the larva to surfaces. On the sheets you can find red spots of blood, which is released from wounds on the body after a bite. The secretion that bedbugs inject into the wound along with saliva affects blood clotting. Large brown spots from crushed bedbugs appear on the bed, because after feeding, the parasites become clumsy.
If there are a large number of insects, black formations resembling poppy seeds may appear on the child’s bed - these are bedbug excrement. You can see parasites scattering if you suddenly turn on the light in the room between 2 and 4 am. To correct the situation, you need to try to remove parasites from the nursery using suitable insecticides.
If a child is found to have bedbug bites, it is necessary to ensure that the child does not scratch the bite sites. This can infect the wound and cause abscesses to develop that are difficult to heal. The affected child may complain of itching, pain and burning at the site of the bite. There is a risk of developing local inflammatory reactions on the skin. The child's sleep patterns may be disrupted, he becomes irritable, moody, and loses his appetite. A large number of bites can cause the baby to develop anemia.
The enzyme released from a bug bite into a child's blood is a powerful allergen and often causes an allergic reaction. The pathological condition is revealed by increased body temperature and fever, abdominal pain, development of swelling of the mucous membranes, irritability, itching and burning in the bite areas, and the appearance of edema.
If several symptoms appear at the same time, parents should urgently seek medical help. In some cases, the development of an allergic reaction can occur rapidly, and over a short period of time, swelling of the mucous membranes and respiratory tract, shortness of breath, swelling of facial tissues, dizziness, loss of consciousness, and shock may develop. Allergies should be treated by a specialist; self-medication can lead to irreversible consequences.
You can help your child by reducing allergies. To relieve larger lesions, you can use soda paste. To do this, baking soda is diluted with a small amount of water. The paste is applied to the affected areas of the skin. One commonly used remedy is to wash the skin at the site of the bite with soapy water.
To stabilize the child’s condition, it is necessary to relieve pain from bites and reduce itching. Eliminating these symptoms will help prevent scratching, skin trauma, infection and the development of inflammation. An infusion of medicinal herbs: a series of tripartite, chamomile and sage will help relieve itching and inflammation in severely itchy bites.
An effective remedy for eliminating symptoms after a bedbug bite is a decoction of oak bark.
Parents should take measures to eliminate parasites from the child’s room - first of all, inspect the child’s bed, change the mattress and bedding.
Among medications for the treatment of allergies, Fenistil gel, which is available in the form of drops or ointments, is effective. Drugs with similar effects are used, such as Zyrtec, Ketocin, Dermadrin, Cetirizine DS, Suprastin.
Homeopathic remedies are relatively safe for children. Apis and Ledum are used to treat the consequences of a bite. For external treatment of wounds, you can use an alcohol tincture of marigolds.
Treatment must be prescribed by a doctor; the choice of drug and dosage is also made by a specialist.
Difference from other diseases
Bed bug bites are sometimes misleading because they resemble both chicken pox and an allergic reaction. Characteristic features of the marks left by bedbugs are a clear outline, pain and swelling.
Mosquito and flea bites are usually located on different parts of the skin. A mosquito can pass its proboscis through the fabric. The bug needs to have direct contact with the body, since it has a completely different oral apparatus.
Bedbug bites are also different from tick bites. Traces of tick attacks are larger, and in the center the tick itself is found, immersed in the wound with its head. The bug does not linger on the body; once it has had its fill, the insect hides. The bites of a wasp and a bug are clearly different. The first one hurts a lot, the second one itches.
Often, numerous bedbug bites are confused with an allergic reaction or rashes characteristic of infectious diseases. Ectoparasite bites are distinguished by the presence of a microscopic wound in the center of each spot.
The main sign of bedbug bites is the time the rash appears. Bed bugs are only active at night. Daytime ones appear on the skin as a result of the activity of other insects.
Hives after bedbug bites
A bedbug bite in adults can cause local and general allergic reactions. The local reaction is expressed by the formation of swelling and redness of the skin, itching.
Local manifestations of allergies are not dangerous; after some time, the symptoms may go away on their own. To alleviate the condition, it is recommended to use cold compresses and ointments that have an antipruritic and soothing effect. The main danger with local allergic reactions is itching. Since the bite sites are very itchy, victims scratch them, damaging the skin, and through the damaged skin an infection enters the body, which causes suppuration.
The most severe manifestations of allergies involve the development of general reactions of the body. The condition is fraught with the development of urticaria, that is, the formation of a rash outside the location of the bites. An allergic reaction can lead to lacrimation, runny nose, provoke bronchospasm, Quincke's edema and even anaphylactic shock.
How to distinguish a bug bite from an allergy
About once a week, bedbugs feed by making a small hole in the skin. The saliva residue causes an allergic reaction in most people.
Traces appear 1-3 days after the bite. For most people, these are small red spots that are flat or raised. They are very itchy.
Because bed bug bites vary greatly in appearance, people often confuse them with hives.
How to diagnose
Only a doctor can professionally diagnose allergies. You can independently identify the nature of the rash based on a number of signs:
- the bite sites look like very swollen red bumps;
- there are several bites, they are located nearby or lined up;
- the spots are very itchy;
- additional ailments arose in the form of fever, runny nose, dizziness, nausea, etc.
It is more difficult to independently diagnose the disease in children, because if there are only rashes on the body and no other symptoms are felt, then bedbug bites can be confused with damage from mosquitoes, ants, fleas, dermatitis, prickly heat, respiratory or food allergies . The latter especially concerns children who are introduced to complementary foods or new foods.
Take into account indirect signs indicating the presence of bedbugs in your bed: new bites appear in the morning after sleep, there is a cognac or almond aroma in the room (that’s what enzymes secreted by insects smell like), there are blood stains on the bed linen, and near the bed – dark colored particles (parasite excrement).
It is important to differentiate bedbug bites from bites of other insects.
First aid
First aid for numerous bedbug bites consists of relieving symptoms and preventing infection of the damaged skin.
Necessary:
- Wash affected areas of skin with cool water and antibacterial soap, alcohol or antiseptic lotion;
- Apply a cold compress or ice to the problem area;
- Wipe the bite areas with a baking soda solution;
- Rinse skin with warm running water.
Medicines you can use:
- Hormonal ointments against inflammation;
- Antihistamines against allergic reactions;
- Antibiotics against infection.
For further treatment of bed bug bites, traditional methods are effective to help reduce itching and stimulate skin healing.
Effective:
- Alcohol tinctures based on calendula, St. John's wort or plantain. The healing infusion is applied to the skin. The alcohol in the tincture helps to disinfect the wound, and the herbal composition activates regeneration.
- Aloe juice squeezed from fresh leaves. The product fights inflammation, relieves swelling, and relieves itching.
- Baking soda solution prepared as follows: 1 tsp. soda per 170 ml of water. The solution helps reduce itching and speed up the recovery of damaged skin.
If the allergy caused by bed bug bites is not too severe, it goes away on its own within 2-3 days. If you have a severe allergic reaction, you should consult a doctor.
Drugs for treatment
For allergies, antihistamines are effective, which are aimed at suppressing excessive histamine production. A cold compress is placed on the site of the bites or balms and ointments are used to relieve skin itching. These include, for example, Fenistil or Psilo-balm. Tablet medications also relieve itching: Suprastin, Loratalin, Tavegil, Cetrin.
Pregnant women who have become victims of sting allergies are not recommended to take antihistamines. Therefore, expectant mothers should especially take care of themselves and it is better to immediately seek advice from a doctor if suspicious redness is detected on the body. Children under three years of age should be given the drug in accordance with the doses indicated in the instructions.
Treatment tactics
If a person discovers primary symptoms of bedbug bites on his skin, it is recommended to take the following measures:
- It is recommended to take a warm shower or bath, which can significantly reduce itching and irritation;
- Allergy treatment can be carried out using antihistamines (Tavegil, Loratadine, Aleron, etc.). In addition, hormonal external agents (Prednisolone, Hydrocortisone, etc.) can be used to relieve itching and swelling;
- in case of severe pain, it is recommended to use painkillers (Analgin, Spazgan, etc.).
In case of severe development of allergies, treatment with infusion therapy in a hospital setting is recommended. Traditional medicine methods are often used, but it must be remembered that in any case a consultation with the attending physician is required.
Traditional medicine recipes for bedbug bites
Symptoms of a bug bite can be neutralized using folk remedies.
- The irritated area can be treated with a mint leaf. This will help relieve pain and irritation;
- a good effect is observed when using dandelion, which must be kneaded and the resulting mass applied to the affected area;
- It is recommended to apply a tampon moistened with freshly squeezed garlic juice to the site of swelling, which helps relieve irritation and pain;
- You can apply a plantain leaf to the bite site for 2 hours, then treat the skin area with the prepared solution with baking soda.
Particular attention should be paid to children, as they, despite the measures taken, may scratch their wounds. In this case, the child's skin must be washed with warm soapy water. This will prevent the development of secondary infection.
Treatment
Includes varieties such as:
- elimination methods;
- antiallergic therapy.
Elimination complex
This definition refers to measures designed to stop contact with an allergen. Primarily applied:
- Disinsection (destruction of bedbugs using special means).
- Thorough cleaning of the room, cleaning carpets, curtains, mattresses using brushes and a vacuum cleaner (the contents of the dust bag must be removed into a tight sealed bag and immediately taken to a trash container outside).
- Wash bed linen and clothes in hot water.
- Putting zippered covers on mattresses (marked “from bedbugs”, “anti-allergy”), they should not be removed earlier than after 12 months.
- Removing and reapplying new wallpaper, filling gaps and cracks with silicone, throwing away old drawers and other objects where bedbugs may be hiding.
It is better to entrust pest control to specialists who will develop optimal methods for eliminating insects. If you decide to fight the parasites yourself, choose a product designed specifically for killing bedbugs, remember to ensure the safety of small children playing in the treated area and pets, who may also be exposed to the poison. When there are a lot of pests and/or it is not possible to use covers, it is better to throw away the mattresses. The same should be done with things that cannot be completely cleaned or washed.
Even after completely getting rid of bedbugs, stick to the following algorithm:
- vacuuming (preferably with a filter) at least once a week;
- using a damp cloth to remove dust on smooth surfaces;
- storing clean clothes and linen in hermetically sealed bags and trays.
The folk method for expelling bedbugs is simple: put fresh wormwood everywhere and spray water with vinegar (you can add wormwood infusion to it).
Unfortunately, home methods are often ineffective or give only temporary results; they can be dangerous not only for insects, but also for people and animals living in an infected room (if you use, for example, ammonia or kerosene).
Antiallergic therapy
It is used if an allergy from bedbug bites has already occurred. It cannot cure sensitivity, but it can stop the symptoms of the reaction or reduce their severity. It is permissible to use drugs from different groups in combination to achieve the best effect.
Antihistamines
Their action is based on suppressing the activity of histamine, the release of which causes unfavorable symptoms (swelling, itching, etc.). There are several generations of drugs in this group; the newest ones do not cause drowsiness and dry mucous membranes, and have a prolonged (long-lasting) effect, which allows you to avoid frequent use during the day. They are produced not only in tablets, but also in the form of ointments and sprays for application to affected areas of the skin. Popular:
- Claritin.
- Zyrtec.
- Cetrin.
- Telfast.
- Eden.
- Erius.
You can treat allergies with their help, but it is better to do this under the supervision of a doctor. Firstly, to select the correct dose and version of the drug, and secondly, to clarify the diagnosis. Perhaps the patient also has sensitivity to food or household chemicals, without eliminating the causes of which he will unsuccessfully use even the most expensive pharmaceutical products.
Glucocorticosteroids
These are medications containing topical (local) forms of adrenal hormones that have a powerful antiallergic effect. These include:
- Methylprednisolone (Advantan);
- Betamethasone (Celestoderm);
- Budesonide (Pulmicort);
- Hydrocortisone, etc.
Available in the form of ointments, lotions, sprays, suspensions for inhalation, etc. Help cope with itching, nasal congestion, bronchospasm; are able to remove even persistent allergic symptoms that have not responded to treatment with antihistamines. At the same time, they are used for a limited period of time and are used only on the recommendation of a doctor, as they have many contraindications and side effects.