In May, the year of insects begins, which does not give life to livestock on pastures. People also get it from flying parasites. The largest flying bloodsuckers are various types of horseflies. All short-haired dipterous insects are united under the general name “fly”. Horseflies are large flies whose females need to drink blood to reproduce. They bite painfully, which often leads to a panicked flight of livestock from the meadows to the forest or home to shelter.
Description and habitat
Horseflies are flying arthropod insects from the Diptera family. They belong to the short-whiskered suborder. The habitat is very extensive. Horseflies live on all continents except Antarctica. Only Iceland and Greenland do not have them. These flies are common:
- in Europe and Asia;
- in America;
- in Siberia;
- in Africa;
- in the Caucasus;
- on the territory of Russia and the CIS.
They are especially common in forest zones, steppes, desert areas, near rivers and lakes. But the most favorite habitats of horseflies are wetlands and cattle grazing areas. Here the activity of these flies is very high.
Currently, science knows about 4 thousand species of horseflies. About 200 live in Russia and neighboring countries.
What does a horsefly look like? At first, looking at it, it may seem that it is just a large fly about 1.5-2 cm long. But if you look at this insect up close or under a microscope, its bright features become noticeable:
- Semicircular head, quite mobile and connected to the body by a thin “neck”.
- Large eyes that shimmer in different colors.
- The oral apparatus is of a piercing-cutting type, which consists of 6 thin plates forming a fluke. He also has a special education, with the help of which horseflies lick various sweet juices or quench their thirst.
- Fleshy trunk hiding sharp stilettos.
- Barely visible small antennae resembling horns (serve for smell perception).
- Wide transparent (less often smoky or mesh) wings with barely noticeable veins.
- Flat abdomen pointed towards the tail (usually with triangular spots).
- Elongated compact body with a thin chitinous cover. Moreover, in females it is more rounded than in males.
- Miniature halteres behind the wings. Thanks to them, the insect balances during flight and makes a characteristic sound.
As you can see, the appearance of the horsefly is quite specific. At the same time, the body structure and physiological characteristics allow it to feed on both blood and plant foods. This insect does not have a sting. This fly bites with its proboscis and powerful jaws
The color of horse flies is inconspicuous: it is dominated by faded shades of gray, brown, and yellow. Thus, this blood-sucking insect easily blends in with its environment.
Many people put the emphasis on the word horsefly incorrectly. The sound emphasis should be on the last syllable. Similarly, in the plural - horseflies.
Habitats
In total, the horsefly family has slightly less than 4,500 thousand species. These insects are distributed throughout the planet. Bullflies were found even at an altitude of 2 km above sea level. They are absent only on remote islands and Antarctica. There are 200 species of horseflies in the CIS.
Insects prefer places with high humidity. Horseflies are flies whose larvae develop in an aquatic environment. Some of the larvae are predators, feeding on small inhabitants of the reservoir. Others eat rotting plant parts. For this reason, accumulations of insects are usually observed near bodies of water. Up to 20 species of horseflies can be found in the same area.
On a note!
They are all an important part of the ecosystem. Horsefly larvae living in water contribute to soil enrichment. Adult horse flies are eaten by a significant number of birds and animals.
Insect horsefly
Why is horsefly called this way?
To this day, many people argue about where the word “horsefly” itself came from. Some believe that the insect received this name as a result of the fact that it often tries to bite a person or animal in the eye. As if he wants to blind his victim.
horsefly lacewing
It is also widely believed that the horsefly began to be called so because of its striking behavior. During an attack and when biting, this insect is so obsessed with the thirst for blood that it does not notice anything. Thus, it behaves as if it sees poorly - as a result, it can be easily killed or simply removed by hand from the animal to which this parasite has attached itself.
But in fact, the horsefly has good eyesight, which helps it find food and hunt. A number of entomologists even claim that this flying bloodsucker notices prey at a distance of about 1000 meters. True, horseflies see mainly the outlines of objects and react to their movement. For this reason, horseflies often mistake their prey and go after a car, boat or train.
Horseflies pose a great danger to humans due to the fact that they are carriers of dangerous diseases, since they feed on the blood of rodents, birds and dead animals.
Symptoms of a horsefly bite
An insect bite is very painful and sometimes has serious consequences. After all, poisonous saliva penetrates into the wound. This liquid contains anticoagulants and toxic substances:
- Toxins entering the human body lead to tissue swelling, pain, itching, burning, redness and quite often allergic reactions.
- Anticoagulants prevent the blood in the wound from clotting, which causes prolonged bleeding and promotes long healing.
In addition to skin symptoms, the following signs of a horsefly bite may be present:
- weakness,
- nausea,
- breathing disorder,
- dizziness.
The horsefly is not an insect that can quietly approach its intended victim. The approach of an aggressive large fly is impossible not to notice. However, sometimes horseflies do not hunt alone. And when one individual distracts the object, the second attacks.
But even if it was not possible to notice the one who committed the attack, this bite cannot be confused with any other. A large tumor appears at the site of the lesion, usually white with a wide red border around the edge.
Consequences: allergies, bumps and infections
Usually, serious consequences do not occur after a horsefly attack, and symptoms disappear after 2–4 days. But there are also exceptions. In addition to allergies caused by fly saliva, the following may appear:
- painful nodes and bumps, as a result of infection with a bite,
- suppuration of soft tissues due to the penetration of a secondary infection when scratching the wound,
- enlargement and inflammation of the lymph nodes due to infection of the lymph and blood.
All this threatens that the bite site may become very swollen, as well as the appearance of non-healing wounds, phlegmons and abscesses. Sometimes necrosis of the affected areas occurs.
When attacked by this blood-sucking insect, the localization of the bite site is important. The closer the large blood vessels and nerve endings are to it, the more delicate the skin, the more dangerous the consequences. However, a direct threat to human life can arise only as a last resort, for example, when:
- multiple insect bites,
- presence of allergies,
- the addition of a secondary infection.
Infections carried by horse flies
Horseflies, like many blood-sucking parasitic insects, are capable of transmitting pathogens of infectious diseases dangerous to human health and life, in particular:
- anthrax,
- tularemia,
- foot and mouth disease
- bubonic plague, etc.
Lifestyle and nutrition
Unlike the gadfly, horseflies are not parasites. This insect is classified as a midge, as it feeds on the blood of mammals. The flight of horse flies begins when the air temperature warms up to +15 °C. In central Russia this is approximately the twentieth of May. In the south - a little earlier.
As we said above, horseflies feel good in forests, fields, steppes, as well as in deserts and mountainous areas. These blood-sucking flies like to hunt closer to bodies of water, because there is moisture necessary for their life. By the way, horsefly larvae of most species develop in water. Adults spend almost their entire lives in flight.
These insects, unlike mosquitoes and midges, love sunny and hot weather, so they are often active during the daytime on summer and warm days. These flies perk up sharply before rain, but in bad weather and wind they do not fly or hunt. The exception is horse flies, which can attack even in light rainfall.
Many people wrongly believe that horseflies feed only on blood. The fact is that the males of all these flying insects are “vegetarians”. They eat plant pollen, flower nectar, worm secretions, aphids, etc. Only fertilized female horseflies bite and drink blood. They need this liquid for procreation, and more precisely, for the development of eggs.
Moreover, in one meal, each female can suck up to 200 mg. As for unfertilized females, they easily tolerate the lack of protein food and are content with a plant-based menu.
During flight, horseflies can reach speeds of up to 60 km/h. This is comparable to the speed of a car moving through the city. Moreover, the average flight range of this insect is 2-4 km.
Common types of horseflies
Approximately 200 species of horseflies are found in the CIS countries. The most common representatives of species and genera are worth considering in more detail.
Rainflies or hemorrhages (Haematopota)
A very common genus of horseflies, including approximately 400 species of insects with a characteristic appearance.
These are ash-gray flies, 6 to 13 mm long, with marbled wing patterns. They hunt silently and attack in both clear and rainy weather. Rainflies live in Eurasia and Africa.
Horsefly of the species Haematopota pseudolusitanica related to hemorrhages.
Bullfly (Tabanus bovinus)
This is a large fly, 1-2.4 cm long. The body of the insects is brown, the chest, dotted with yellow hairs, is crossed by dark stripes. A yellowish-brown border runs along the edges of the abdomen. The middle part of the abdomen is decorated with a stripe of ashy or yellow triangular spots.
Bullflies live throughout Europe, northern Asia and northwest Africa.
Bullfly (Tabanus bovinus).
Bullfly: male
Bullfly: female
Great gray horsefly (Tabanus autumnalis)
Large dark gray flies, growing from 1.6 to 2.3 cm. They are distinguished from other horseflies by their black abdomen, decorated with patterns of light triangular spots in the center and a diamond-shaped border on the sides.
Heat-loving insects can be found in the central and southern regions of Eurasia, as well as in North Africa.
Horsefly of the species Tabanus autumnalis.
Forest lacewing (Chrysops caecutiens)
A fly, measuring from 7.5 to 10 mm with amazingly beautiful eyes, shimmering in emerald-golden color. And the lacewing is brightly colored, its abdomen is yellow with black spots. Between the thoracic region and the abdomen of the insect there is a well-defined V-shaped inverted pattern.
The range of forest lacewings covers European countries, the Caucasus, northern Kazakhstan and Mongolia.
Forest lacewing horsefly.
Forest lacewing (Chrysops caecutiens)
A fly, measuring from 7.5 to 10 mm with amazingly beautiful eyes, shimmering in emerald-golden color. And the lacewing is brightly colored, its abdomen is yellow with black spots. Between the thoracic region and the abdomen of the insect there is a well-defined V-shaped inverted pattern.
The range of forest lacewings covers European countries, the Caucasus, northern Kazakhstan and Mongolia.
Forest lacewing horsefly.
Common lacewing (Chrysops relictus)
A bright fly with golden-green eyes, a glossy black chest and brownish pubescence. The abdomen of insects is spotted, black and yellow. The wings are mosaic marble with brown splashes. Due to their chaotic coloration, these horseflies received a second name - common pieds. The growth of insects is 9-14 mm.
Residents of Europe and the Western Siberian region become victims of the common lacewing.
Horsefly of the species common moth (common lacewing, lat. Chrysops relictus).
Detailed description: common pied.
Reproduction
Caring for procreation and breeding offspring in horse flies begins in the warm season. The exact timing and duration of the breeding season is determined by the species of insects and the climatic conditions of the habitat.
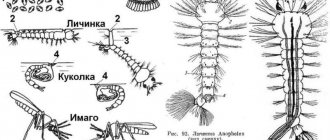
The life cycle of horse flies consists of four phases:
- Egg. One female lays from 400 to 1000 pieces.
- Larva. It has a spindle-shaped shape. No limbs.
- Doll. Resembles the pupa of an ordinary butterfly.
- Imago (adult). Their life expectancy is short. Usually this is one month. In rare cases - summer.
horsefly larva
That is, horsefly is an insect with complete transformation. The total life expectancy from the moment of laying eggs until the death of the imago is 4 years. That's quite a lot. Many insects live an order of magnitude shorter.
The very method of their reproduction is identical to the type of reproduction in other dipterans. Under favorable circumstances, opposite-sex individuals mate, and after some time the female lays a clutch. At the same time, pregnant horseflies need to feed on the blood of humans and warm-blooded animals.
As a result, having pumped up the blood, the female after some time begins to lay eggs in groups:
- on the lower surface of the leaves;
- on plant stems;
- in water;
- into damp ground;
- along the banks of flowing rivers, streams, ponds or lakes;
The horsefly larva hatches after 3-8 or more days. Then it leads an aquatic or semi-aquatic lifestyle, eating small mollusks, insects, worms or organic debris. Some larvae even practice cannibalism.
At the same time, I would like to dispel one popular “myth” among the people. It concerns the fact that horseflies can supposedly lay their eggs and larvae under the skin of humans or animals. Actually this is not true. Only a gadfly can do something like that. And horseflies lay eggs in water, grass, soil saturated with moisture and other places protected from direct sunlight.
As for the larval stage, it lasts about a year. Moreover, the larvae even manage to survive the winter. In the spring, pupation begins. They crawl to drier places, where they turn into pupae. The stage itself lasts from five days to several weeks. After which an adult insect appears.
The difference between horsefly larvae and gadfly larvae, why people confuse these insects
The only harm caused by these insects is the painful bites of females. Horseflies lay eggs on plants, so the question of how to remove a horsefly larva is incorrect. We are most likely talking about gadfly larvae.
Many gardeners, while gardening in the summer, repeatedly experience bites from various blood-sucking insects, among which the most intrusive are horseflies and gadflies: the differences between insects are subtle, and an uninitiated person is unlikely to be able to distinguish them from each other in real conditions.
Nutrition and maturation
It is believed that this insect got its name because of its excessive intrusiveness. Females do not see any purpose in their existence other than to drink blood; it is for this reason that they often hang around people and animals, without thinking about danger. Males are calmer, their life cycle is shorter, so they do not need blood, while females can drink 0.2 g of blood at a time, which is a huge dose for such a small insect. Livestock suffer the most from these bloodsuckers: cows begin to give less milk, get sick and literally go crazy from their annoying neighbors.
Horseflies need blood not only as food, but also as a substance that allows them to reproduce. One female is capable of hatching more than 2 thousand eggs laid in the ground per season. Often the laying sites are plant leaves or moss.
The larvae mature for 2 weeks in the shell, then hatch and remain in an underdeveloped state for another six months and feed on the remains of plant food. Only in spring does the process of final ripening begin, which lasts more than a month.
Due to the fact that animal carcasses are also a favorite delicacy, they are carriers of dangerous diseases, including polio, ulcers, etc.
Appearance
The horsefly does not even reach 3 cm in length. Its body is more elongated, unlike an ordinary fly. They have a large head, with disproportionately large eyes, allowing them to observe and attack moving subjects.
The wings are transparent or gray, single, like those of a fly. The body can be monochromatic: brown, gray, almost black, or beige with dark splashes.
Features of the gadfly
Nutrition and maturation
Very often there is confusion between horseflies and gadflies. The difference between them is nutrition. The latter practically do not feed and pester people and animals simply by their nature, imposing themselves like flies.
After hatching, females look for a mate, lay larvae and die immediately. Their life cycle lasts very short; they reserve strength for this time while still in the egg.
Adults are more intrusive than horseflies, since their goal is to lay eggs in the folds of the animal's body.
Mating of the male and female occurs a few days after hatching. They can live another month to have time to lay offspring. One individual is capable of laying about 700 eggs on the body of one animal.
The most common places for laying are:
- groin area,
- stomach,
- hips.
Due to the fact that the animal’s body temperature exceeds the ambient temperature, after 3-5 days the bloodsucker larva hatches from the egg and moves under the host’s skin to the spine. There she bites a hole in the skin for breathing. After maturation, it falls out of the hole, remains for some time in the animal’s place of residence (stall, barn) and flies away.
The appearance of the gadfly is practically no different from the appearance of an ordinary fly. It does not exceed 1.5 cm in length. It has small transparent wings, large eyes and a black or brown body.
It does not attack humans directly; even the human gadfly uses bloodsuckers in contact with humans to implant eggs under a person’s skin. Eggs are often carried by mosquitoes.
Conclusion
Horseflies and gadflies differ not only in size, but also in their feeding habits and lifestyle.
The horsefly matures over a period of more than 9 months, but the gadfly hatches in a matter of days and goes to the mating sites. Despite the fact that the latter do not drink blood, they bring more unpleasant sensations when they get under the skin of an animal or person.
The horsefly, being a blood-sucking insect, causes inconvenience to both animals and people in the warm season. Many people are familiar with its obsessive buzzing and painful bites. In hot weather, far from cities, horseflies stage real attacks, interfering with comfortable outdoor recreation or work in the garden. They also annoy livestock. What kind of insect is this and why does it attack?
Why are horse flies dangerous?
First of all, by the fact that when bitten they release substances that can cause a negative reaction in the body:
- allergies;
- itching;
- inflammation;
- irritation;
- elevated temperature, etc.
In young children and sensitive people, swelling, additional rash and severe redness quite often appear, accompanied by a deterioration in well-being and enlargement of regional lymph nodes. In this case, the bite site is almost always itchy and itchy. Sometimes a hard, painful nodule forms in its place, which goes away only after a couple of weeks.
But bites and unpleasant consequences from them are far from the only problem due to which horseflies can be dangerous. Some of these insects are carriers of infections and diseases. Among them:
- anthrax;
- tularemia;
- polio;
- filariasis;
- trypanosomiasis, etc.
Therefore, if after a horsefly attack you have a fever or other symptoms, you should consult a doctor.
Horseflies cause enormous harm to agriculture and livestock. Due to their activity, attacks and bites, cattle suffer. As a result, horses' endurance decreases, cows' milk yield decreases, and pigs may even begin to lose weight or slowly gain it.
Are there any benefits to horse flies? As you know, there is nothing superfluous in nature. These insects are food for many birds and fish. Therefore, a reduction in their numbers can lead to a significant imbalance in the surrounding world.
Many people ask, is it possible to get AIDS from a horsefly bite? Fortunately, no. HIV is completely unviable in other environments, that is, outside the human body. Therefore, even if a horsefly first bites an HIV-infected person and then a healthy person, the virus will not be transmitted. He simply cannot survive in these conditions.
Is horsefly harmful to humans?
Horseflies often bite people. The insect's saliva causes a painful reaction on the skin. Some suffer from an allergy to the bites of blood-sucking flies, and then the affected area swells greatly. Together with saliva, toxic substances that cause pain and swelling, and anticoagulants that prevent blood clotting enter the wound. Horseflies pose a particular danger as carriers of infectious diseases. Therefore, if you have a fever after the attack, you should seek medical help.
Knowing what a horsefly looks like, you can distinguish it from other insects. It is difficult to avoid meeting him on summer days with clear weather. During the period when female flies are bearing offspring, they are extremely aggressive and often attack people. To repel horseflies, insecticides are used in the form of a spray or aerosol, and special traps are built in the areas.
Are horseflies and gadflies the same thing?
Of course not. These are different insects that also belong to different families. Gadflies and horse flies differ:
- structure;
- appearance;
- behavior;
- characteristics of reproduction;
- nutrition (for example, adult gadflies, unlike horseflies, do not need food at all and do not drink blood);
Therefore, those people who call horse flies gadflies are greatly mistaken. Although both of these insects are unpleasant and dangerous. They must be fought. Moreover, every farmer, gardener, fisherman, hunter and traveler should know how to protect themselves from such blood-sucking reptiles.
Features of the external structure
This insect in appearance resembles a large fly, whose body reaches three centimeters in length. The insect has two large wings of a slightly smoky color.
The head of a horsefly has a large diameter; in its front part a pair of processes are visible, thanks to which those very painful bites are carried out. Two pairs of large iridescent eyes help the insect to see its prey from afar.
Female horse flies have more distance between their eyes than males. They also have a more rounded body and a pair of larger processes. Photos of horseflies will help you become better acquainted with the structural features of this insect.
What harm do they cause?
Horseflies attack mainly large animals - elk, deer, roe deer and, first of all, livestock. But they also bite small animals - rodents, birds.
Horseflies do not disdain even fresh corpses, which makes them especially dangerous carriers of infections.
Horsefly bites are very painful, and sometimes, due to the insect's saliva getting into the wound, their bites cause severe swelling. In one bloodsucking female horsefly can consume up to 200 mg
blood. 70 mosquitoes drink this amount at one time!
In addition, horseflies can carry polio, anthrax and some other serious diseases. Since horseflies live near bodies of water, where the best pastures are located, livestock farming suffers greatly from these insects.
Cows, even with a moderate number of horseflies, quickly lose weight, and milk yield decreases by 10–15%. In humans, horsefly saliva sometimes causes an allergic reaction, and wounds from bites sometimes fester.
Gadfly bite consequences
Many doctors associate a person’s allergic reaction with the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. When the intestines are unstable, large protein molecules – allergens – enter the bloodstream. And therefore, when toxins enter the blood from the external environment, a strong reaction immediately occurs, sometimes with a fatal outcome. In cases of complications after a bite, in addition to the symptoms described above, blisters appear on the skin, the skin becomes numb, and a rash and black scab form over a large area of the body. And sometimes necrosis of the affected area of skin occurs. The consequences for the body may be different. In any case, if the temperature rises, hospitalization in a medical institution is required. Since this is the first sign of swelling of the internal organs.
In case of chronic diseases, in combination with a toxic bite of a gadfly, nausea, wheezing and shortness of breath may develop. If the area near the eyes is affected, there is a decrease or complete loss of vision, and a bite to the tongue area will cause swelling of the larynx, which can lead to asphyxia.
Where do horseflies live?
The habitat of horseflies includes almost all countries, with the only exceptions being Iceland, Greenland, the territory of Antarctica and some islands of Oceania. Horseflies live in Europe and Asia, the Caucasus and Siberia, Mongolia and North Africa, Russia and the former CIS countries. The largest populations of horseflies are found in places near water bodies or in swamps, because the lack of moisture is destructive for most species of these insects.
Horseflies are most active in hot weather, from morning until sunset, annoyingly attacking herds of domestic animals that come to a pond to drink, attacking birds, rodents and even lizards. The most common victims of painful horsefly bites are cows, horses, deer, elk and roe deer. Often, female horseflies do not disdain the corpses of animals, satiating themselves with their blood in the first two or three days after death. This fact makes horse flies carriers of very dangerous infections. Horseflies will not refuse to feast on human blood: everyone who has ever rested on the banks of a river or lake has felt the bites of these insects. When choosing a victim, insects rely on their vision: horseflies see the outlines of objects and react to their movement. This is why horseflies sometimes mistake their prey, chase moving cars and river boats, and fly into open train windows.
Types of insects
Commonly encountered species of the described insect include:
- Bullfly - considered the largest species of the described family, reaching a length of about 20 mm. The bullfly is a two-winged insect belonging to the horsefly family. This species of horsefly lives in Europe, colored brown, with dark stripes located along the body and yellowish hairs.
- Lacewings or moths - about 250 species of horseflies are equated to the described genus. The most common horsefly is the common lacewing, reaching a length of 14 mm and having a rather bright color of its body. The chest of this insect has a blackish color, while the abdomen is complemented by original yellow spots. The wings of the lacewing have a mosaic color, the top of which is completed by brown spots located on them. The huge faceted eyes cast an emerald-golden color;
- An ordinary raincoat - with a modest color and wings with a complex smoky pattern. The described type of insect can produce, so to speak, a real horsefly bite, even in gloomy and cloudy weather.
First aid if bitten by a horsefly
How to react to gadfly bites?
- It is necessary to treat the affected area of the body as quickly as possible, rinsing it with clean water (or with soap). After all, it is worth remembering that these insects are carriers of infection (they do not disdain corpses and feces).
- You can then gently squeeze the liquid out from the bite site. This will help localize the spread of toxic saliva under the skin.
- After removing the dirt, you need to treat the wound:
- hydrogen peroxide solution,
- Chlorhexidine,
- potassium permanganate solution,
- Streptocide,
- propolis tincture,
- Furacilin,
- vodka.
- After treatment, it is better to cover the bite site with a band-aid.
- Regardless of whether the victim is allergic to insect bites, it is worth using some kind of antihistamine that will help reduce swelling and stop itching:
- Tsetrin,
- Claritin,
- Loratadine,
- Suprastin,
- Parlazin et al.
- If severe pain is present, the use of analgesics will be very helpful. Recommended for use as an analgesic and antipyretic:
- Ibuprofen,
- Paracetamol.
- If a horsefly bite does not cause a deterioration in the general condition of the victim, then it is enough to use local remedies for 2-3 days to speed up wound healing:
- Panthenol,
- Fenistil-gel,
- Rescuer.
If suppuration, nodes or lumps appear after a horsefly bite, you should urgently consult an infectious disease doctor. Particular attention should be paid to:
- fever,
- nausea,
- vomit.
All this may indicate an infection of the body, which must be treated under the guidance of a doctor.
Medicines that can be applied to tumors to alleviate the condition after bites, gallery
Bepanten will help heal the wound. Nimesulide and its analogues will relieve fever and eliminate pain.
Treatment with traditional methods
Of course, the necessary medications and protective equipment may not always be at hand, so you need to know what you can use from available means to alleviate the condition of the victim.
- A lotion made from a bandage or any clean cloth soaked in:
- soda solution,
- Corvalbreaker,
- gruel of garlic or onion,
- juice of raw potatoes (you can grate them),
- tomato puree,
- sour cream.
- Regular ice from the refrigerator, previously placed in a plastic bag, will help reduce swelling.
- The juice of an ordinary dandelion will help to disinfect the bite site, which is recommended to treat the affected area. After manipulations, you should wash your hands to prevent milky juice from getting into your eyes.
- A lotion of salt and soda will help clean the wound from insect saliva. To do this, dilute 1 teaspoon of each ingredient in 1 glass of warm boiled water. After the crystals are completely dissolved, a bandage is dipped into the liquid, soaking it completely. Then, the fabric is wrung out and applied to the bite site.
- A paste of fresh plantain leaves can relieve itching and stop bleeding. You can use dry plant materials, previously soaked in warm water. The wet mass is applied to the damaged area and secured with a bandage.
- A compress with a mixture of natural products will help relieve swelling and redness. To do this, you need to take 2 cloves of garlic, ½ medium-sized potato and ¼ onion. All this is ground on a grater or in a meat grinder. The resulting mixture is applied to the bite site, covered with film and secured with a bandage.
Folk remedies that will help with a horsefly bite, photo
Onions are effective as a decongestant
In the composition of the compress, which relieves inflammation and redness, ordinary garlic plays an important role.
Sour cream will relieve itching after a horsefly bite. Tomato paste will relieve the condition.
Milky dandelion juice perfectly disinfects the wound and relieves intoxication Plantain juice has hemostatic properties Raw potato gruel relieves itching after a bite A solution of soda and salt will help speed up wound healing
Description of the insect
According to the biological classification, horseflies are an insect from the order Diptera and the suborder Tabanidae. This is a whole family, whose representatives around the globe number approximately 4,400 species, classified into 200 genera. The habitat of 200 species has been recorded in the CIS.
Horseflies attract attention, first of all, as one of the components of midges, because pregnant females need to eat blood. Substances released during a bite cause a negative reaction in the body: allergies, inflammation, irritation.
Midges are called species of insects from the order Diptera that suck blood from mammals. In addition to horseflies, it includes ordinary mosquitoes, the exotic tsetse fly, etc.
The horsefly's body is very compact. The length of individuals depends on the species: from 0.6 cm in Haematopota koryoensis to 3 cm in Tabanus chrysurus. These large horseflies received the popular nickname “Black Flying Horse” in the West for their impressive dimensions. The body is neatly flattened in the abdominal area. The insect's flight ability is provided by 2 wide wings.
The horsefly's body is protected by a thin covering of chitin. Its layer is thicker on the chest and head. The degree of pubescence of an insect depends on its species. Biologists have identified a pattern according to which the inhabitants of steppes and deserts have shorter villi than those living in mountainous areas. The color of horseflies does not attract attention: it is dominated by muted shades of gray, brown, yellow, so the horsefly blends in with its environment.
The thoracic region is wide and massive. Its surface is covered with microscopic villi of small thickness, sitting close to each other, due to which dense pubescence is formed. Wide wings are attached to the middle part of the horsefly's chest. In some specimens they are completely transparent, while in others they are painted with veins that create a mesh pattern, or are decorated with light gray spots. The hind pair of wings is now a vestige. It is transformed into special halteres, shaped like round-headed pins intended for sewing.
Thanks to the halteres, the fly balances during flight and makes a characteristic sound that certainly accompanies its appearance.
Horseflies have a fairly large armed proboscis that hides sharp stilettos inside. The oral apparatus is equipped with palps, antennae, and mandibles; and its structure allows it to both feed on plant foods and drink blood from large animals.
Interesting facts related to the lifestyle of the bullfly
Adult insects of this species do not feed. Adults spend most of their time in flight, guided by vision.
Female horse flies react to large moving objects. Therefore, they often choose cars or boats as their victims and begin to chase them. The speed of a moving object can reach 40 kilometers per hour. Moreover, horseflies will pursue a boat that has sailed several hundred kilometers from the shore!
Experiments have proven that horseflies do not attack striped objects. Apparently, this is due to the structure of their visual organs. What confuses them especially is the fact that the stripes are not parallel. Zebras that have exactly this color practically do not suffer from horsefly attacks.
Source: fb.ru
animals, nature
First aid for a gadfly bite
If the human body reacts without complications, then after a gadfly bite it will be sufficient to wash the affected area generously, without much rubbing, with soapy water. After washing, apply a small amount of hydrogen peroxide to the bite site, then treat the wound halo with fucorcion or brilliant green. If several gadflies are stung at once, the victim must take antipyretic and analgesic medications. In the absence of medications, it should be borne in mind that the juice from the stems of chamomile, dandelion, field onion, mint, aloe, black nightshade or plantain has anti-inflammatory properties. These plants disinfect the bitten area, reduce pain and speed up healing. And children need to be given antihistamine tablets - this will reduce the risk of further infection and relieve itching.
If complications are not observed, then until complete healing it will be enough to treat the wound for several days with an anti-inflammatory and if these simple rules for caring for the bite are not followed, suppuration of the skin occurs, and sometimes phlegmon or an abscess forms.
Dream Interpretation, Bite, bite
If in a dream you bit someone, this speaks of a dream living in the depths of your soul to subjugate some person. The obsession with this idea is such that you can literally do anything to achieve it. It is still unknown whether you will be able to achieve your goal or not, but now we can say that even for good purposes, enslaving someone else’s will is a bad step that will lead to suffering for both the enslaved and the enslaver. You were bitten in a dream - in this case you risk finding yourself completely dependent on the will of another person. The bites were not too painful and did not even attract much attention to themselves - such a dream suggests that forcing you to deviate from the right path is a rather difficult undertaking. Most likely, you will remain in your positions. If the bites greatly annoyed you and caused unbearable pain, all your attempts to weaken someone else’s influence will be useless. So you will have to submit to this state of affairs for some time, waiting for a favorable moment for liberation from captivity (possibly love). Some kind of passion may push you to recklessness and unnecessary sacrifices, but later, having assessed the object of your feelings impartially, you will be very disappointed in both him and your behavior.