But you shouldn’t lose your vigilance, insects are different - harmless and aggressive, with an intelligent nature and a bandit. The former fly past a person and do not pay any attention to him, the latter simply consider it their duty to glare at the first person they come across, relaxing in the spring sun. Bees and bumblebees can be classified as intelligent - they never attack a person without reason. But hornets and wasps are real aggressors, stinging just like that, depending on their mood.
The reason for such aggression has not been clarified by science, but interesting facts have been established. Bees' stings have tiny serrations, making it impossible to remove them from human skin. Therefore, having stung, a bee loses not only its sting, but also part of its stomach, which is incompatible with life - after a sting, it inevitably dies. Wasps and hornets have a smooth, sharp sting that easily penetrates the skin and back, so these insects can bite repeatedly, each time injecting a certain dose of poison into the victim.
And one more inexplicable, but experimentally confirmed fact: angry bees and wasps are more likely to attack those who are allergic to their stings. How they recognize this is a mystery to scientists.
Wasp venom and its specifics
The composition of wasp venom is in many ways similar to the venoms of other Hymenoptera - bees, hornets, bumblebees, some tropical ants - but it also has its own characteristics.
Here are some active components of wasp venom:
- phospholipases, which cause destruction of cell walls, swelling and inflammation;
- melitin is a component that promotes hemolysis (destruction) of mast cells;
- apamin is a toxin that has a strong effect on the nervous system, including motor nerves;
- acetylcholine, which has a direct effect on the conduction of nerve impulses;
- histamine, the main function of which is to trigger the mechanism of an allergic reaction (the action of anti-allergenic drugs, which are called antihistamines, is aimed at neutralizing histamine);
- MCD-peptide, which destroys mast cells and causes an avalanche-like increase in the amount of histamine in the blood (as a result, the development of an allergic reaction accelerates);
and some others.
Partly due to the destruction of cell walls is the fact that a wasp sting often hurts for a long time and goes away rather slowly: inflammation develops in the affected area, which disappears as the cells recover. When the walls of small blood vessels are destroyed, hemorrhage occurs - this is especially pronounced with hornet bites.
People's reactions to the effects of wasp venom are largely individual. On average, for a healthy person, a wasp sting hurts for several days, and its consequences completely disappear within a week and a half.
Different species of wasps have different venom compositions. For example, the bite of the so-called road wasp, long and slender, is considered one of the most painful among all insects known in the world (the bite of a tropical bullet ant is even more painful). But the bites of wild wasps (paper wasps, whose nests can be found, for example, on trees in the forest) are not much different from the bites of the same insects, but building their nests, for example, in summer cottages.
There are very large predatory phylant wasps that feed on bees. Their bite is generally insensitive, and beekeepers catch and crush them with their bare hands. On the contrary, open spaces are inhabited by small wasps, the size of a house ant, which bite about as painfully as ordinary paper wasps. Therefore, the bite of some forest wasp that is not quite familiar in appearance may be difficult to predict in its consequences.
Consequences of a bite for a person
An encounter with this insect will go unnoticed unless you try to destroy the nest or accidentally press it with your bare foot or hand. But as soon as you disturb her, she uses her weapon - a sting. Moreover, unlike a bee, it is capable of delivering several blows at a time, each time introducing a new portion of wasp venom into your body. And although its composition is very close to that of bees, it is still more allergenic and therefore can lead to various reactions, including anaphylactic shock.
However, do not console yourself with the idea that a honey bee sting is completely safe. It can also cause allergic reactions, but the likelihood of their occurrence is less high. So that you can be convinced of the high danger of communicating with this insect, let’s consider what components are contained in the toxic substance they secrete and how they affect the human body.
A wasp bite in the eye, tongue, neck, mouth and chin is dangerous for any person, which can cause swelling of the tongue, larynx and lead to suffocation.
Composition of wasp venom
It contains a variety of substances, but most of them are capable of influencing nerve endings, leading to an immune response in the body of the bitten person.
Its main components are:
- Acetylcholine
- Histamine
- Phospholipase enzymes
- Hyaluronidase.
The first is a neurotransmitter. A high concentration of this element leads to disruption of the nervous system.
The second one is an activator of its own. Entering the body from wasp venom, it leads to the development of an inflammatory process and allergic reactions. People sensitive to this element may suffer from fever, urticaria, and Quincke's edema.
Phospholipases promote the destruction of cell walls, which is accompanied by pain and inflammation at the site of the bite. The toxin hyaduronidase has similar properties.
How does a wasp sting, how does its sting differ from a bee sting?
These are quite aggressive insects, always ready to attack. However, they will not sting a person peacefully passing by. Wasps attack if they are in danger or the threat of ruin hangs over the nest. When biting, the insect pierces the skin of the victim with its sting, injecting poison. Having bitten once, it strives to do it again.
The wasps do not die after the attack. They can sting repeatedly. The number of bites depends on the type of insect, its age and the amount of toxic substance that its body is capable of producing. Wasps usually bite at least 5 times.
Bees, unlike wasps, leave a sting in the wound, dying some time after losing it. The bee is considered the most harmless stinging insect. Wasp venom is much more toxic, so the consequences of their stings are more pronounced than the reaction to bee venom
How to kill stinging insects
No matter how great the benefits of wasps in nature are, in some cases people have to take extreme measures and destroy dangerous neighbors. To reduce the number of insects, special traps are used. These are homemade or purchased containers with sweet bait. Individuals that fly into them cannot get out. You can get rid of the nest using modern insecticidal preparations. Aerosol products - Dr. Klaus, Mosquitoll. Dichlorvos allows you to quickly and effectively destroy stinging insects. An effective way is to burn the nest. But you won’t be able to use it under the roof of a house or on a tree.
Everything created by nature has its purpose. Beneficial insects, wasps, should not be underestimated. Without these tireless hunters, cities would have to fight off hordes of flies. In gardens, predators destroy harmful insects, allowing you to use chemicals less often.
Why does the skin at the site of the bite become red, swollen and itchy?
If bitten by a wasp, the skin at the site of the lesion quickly swells, turns red and becomes hot. During an insect attack, the victim feels acute pain, which turns into severe itching. Why does the area where the wasp sting occurs itch, swell and turn red?
The self-defense weapon of these insects is a sting, which is connected to a paired gland that secretes a toxic substance. Their poison is stored in a special tank. By thrusting its stinger into the skin, the wasp injects a certain amount of toxic substance. The natural reaction of a healthy body to interaction with it is redness, swelling and irritation.
For allergy sufferers and people with weak immune systems, symptoms may be more pronounced. An allergy to a wasp sting is manifested by the following symptoms:
- increased body temperature;
- dizziness;
- attacks of nausea and vomiting;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- fainting;
- clouding of consciousness;
- diarrhea;
- deterioration in vision clarity;
- increased heart rate;
- blood pressure disorders;
- skin rashes;
- swelling of the eyelids and soft tissues;
- swelling of the larynx;
- feeling of suffocation;
- anaphylactic shock;
- pallor of the skin.
Signs of a wasp sting
The main symptoms of a wasp sting:
- burning pain in the affected area;
- skin redness;
- edema.
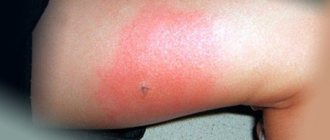
Bite
These signs appear in everyone, but sometimes an allergy occurs, which manifests itself as follows:
- severe swelling spreading far beyond the bitten area;
- itching;
- rash;
- labored breathing;
- too fast or slow pulse;
- dizziness, weakness;
- high temperature, fever, chills;
- nausea, vomiting.
In a healthy person, symptoms disappear 1 to 3 days after he was attacked by wasps. But it also happens that recovery takes several weeks.
Bite symptoms
Externally, the manifestations are practically no different. It is difficult to assess the degree of pain, if a wasp or bee stings for the first time, a person has nothing to compare with. The bite looks like this:
- edema;
- redness;
- swelling;
- pain;
- in the center is a dot with a small depression;
- itching
A photo of a bee or wasp sting is shown below. You can carefully examine all the features of the traces of an attack by striped insects.
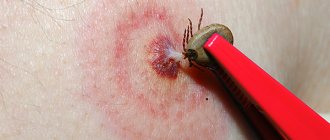
Wasp sting
On a note!
If a wasp or bee stings in the leg, injects poison into the arm, the entire limb swells. If you are bitten on the neck, face, or tongue, the likelihood of swelling of the larynx increases. In severe cases, Quincke's edema develops. In the absence of qualified help, a person risks dying. If you are bitten by bees or attacked by a swarm of wasps, the dose of poison in the blood increases significantly and anaphylactic shock may occur.
A severe allergic reaction provokes:
- dizziness;
- headache;
- nausea;
- vomiting;
- diarrhea;
- violation of movement coordination;
- clouding of consciousness;
- fainting;
- blurred vision;
- decreased blood pressure;
- pale skin;
- constriction of the pupil;
- difficulty breathing, shortness of breath;
- arrhythmia;
- increased sweating;
- chills.
At home, it is allowed to treat a wasp or bee sting in case of a local allergic reaction. If you experience deterioration in your health, difficulty breathing, or swelling of the larynx, you should immediately call an ambulance or go to a sanitary checkpoint accompanied by other people.
First aid for a bee or wasp sting
After an insect attack, you need to take certain actions to avoid complications and reduce allergies.
- Rinse the wound with clean cold water. The procedure will help wash away any remaining poison and remove dirt. At home, use laundry soap.
- Disinfect. They use ammonia, medical alcohol, and boric alcohol. And also hydrogen peroxide, a medicinal herbal tincture of medicinal herbs.
- Neutralize the effect of the poison. Use vinegar and citric acid. To prepare the solution, add 1 teaspoon of vinegar or 0.5 teaspoon of acid to a glass of water. They wipe the sore spot, make lotions and compresses. If it is not possible to prepare a solution, apply a piece of sugar for 5 minutes.
- Don't let the poison spread. Ice cubes or cold objects are applied to the bite site for 5 minutes - a bottle of water, meat from the freezer, a heating pad. Cold constricts blood vessels, prevents the spread of poison, and also relieves swelling and eliminates pain.
- Reduce inflammation. You can treat the bite with a decoction or tincture of calendula, chamomile, or valerian. Or they use pharmaceutical drugs.
First aid for insect bites
If you have a severe allergic reaction, you need to take an antihistamine as quickly as possible. Be sure to take medicine for multiple bites, if a wasp or bee stings you on the neck or face.
Bees
They are most aggressive in the spring, when there are still few flowers and poor honey yield. They attack people when they are located on the path of their flight, next to an apiary or at a honey collection site. The anger of bees can be caused by strong odors of perfume or deodorant, sudden movements and waves of hands, as well as active games with throwing objects.
When a bee stings, it leaves a sting in the wound, to which a sac of poison is attached. Thus, the entire dose of poison enters the wound at once. The bee dies after being stung, but new bees immediately arrive at the smell of poison and also try to sting the victim. A bee sting is very painful and dangerous. If left untreated, an allergic reaction of varying severity may develop.
✔ The sting should be removed from the wound as quickly as possible using tweezers. You should not try to squeeze out the poison, as this contributes to its spread throughout the body.
The wound from a bee sting should be treated with hydrogen peroxide, chlorhexidine or an alcohol-containing solution.
✔ Products containing acid will help relieve pain and partially neutralize the poison in an open wound. This could be a slice of lemon, orange or apple. If you don't have these products on hand. plants should be used. Fresh parsley or plantain leaves will do. Take a few leaves and chew them, apply the resulting pulp to the bite site.
✔ A cold compress will help remove swelling. Ice should be applied to the bite. You can take frozen meat or a bag of vegetables out of the freezer and apply it to the sore spot.
✔ An alcohol compress can stop the spread of poison throughout the body. You should dilute medical alcohol with water, you can take vodka, soak a piece of bandage or cloth in it and apply it to the bite for half an hour.
Young children can apply a warm bag of freshly brewed tea to the bite site to help relieve pain and swelling.
How to help at home?
If there are no medicines at hand, folk remedies that can be found in every home can help. By the way, natural remedies will also come in handy if a wasp has bitten a pregnant woman, for whom the list of approved medications is very limited. More often than others, the following are used to treat the bite site:
- aloe juice or pulp;
- a slurry of soda mixed with water;
- sour fruit (lemon, sour blocks);
- diluted apple cider vinegar;
- tomato pulp (both ripe and green);
- grated fresh potatoes.
Grated potatoes
Some housewives advise adding chopped onion or garlic, but the juice of these plants is very caustic, so the method is not suitable for everyone. In particular, such lotions are not recommended for treating wasp stings during pregnancy
What to do
The first thing a person who is stung by a wasp feels is pain. Often this happens at a time when the insect has not yet pulled out its sting. After this, the bite site turns red and swelling develops. The size of the edema may depend on the individual reaction of the body. The person begins to experience severe itching, even if the pain has passed. This is how wasp venom works when it enters the body. In the absence of allergies, the stung area ceases to bother the victim after a few hours . And yet, after a bite, you can take steps to minimize the consequences of the poison.
You should not kill the insect right where it stings. This can only increase the effect of the poison. It is better to carefully brush the wasp away. It is advisable to treat the bite site with an antiseptic solution or simply rinse thoroughly with water. To prevent the poison from spreading throughout the body, a tourniquet can be applied to the stung limb.
To remove toxins, the victim needs to drink plenty of fluids. To ease the pain, you can put ice on the bite site.
There are also folk remedies that are used to relieve pain and swelling. The pain goes away if you put apple pulp on the affected area. You can add half an onion or tomato .
To eliminate swelling, compresses with dandelion juice, parsley, mint, Kalanchoe leaves, golden mustache tincture, pharmaceutical clay, and so on are used. An aqueous solution of salt or soda and antiallergic ointments can help relieve swelling.
In rare cases, a wasp sting may remain in the skin. This is possible if the insect was killed right at the site of the bite. The sting can be removed using clean tweezers. Under no circumstances should you cut the wound or squeeze the sting out of the skin.
What to do depending on the location of the bite?
A wasp can sting any part of the body. First aid will vary slightly depending on where the affected area is:
- the wasp has bitten the lip or tongue - the victim should take an antihistamine, you can let him suck on ice;
- if a wasp stings your eye, you should apply a napkin moistened with cold water, but it is better not to use ice, so as not to chill the facial nerve;
- If you are bitten on the neck, you should immediately take an antihistamine.
The most dangerous are wasp bites to the eye, neck, and tongue. In this case, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Other bite hazards
Allergy to wasp venom is a common, but not the only consequence of the bite of these insects. Even a healthy person can be in serious danger in certain cases. First of all, this concerns the place where the wasp stung:
- the head (tongue, nose) or neck after a wasp sting may swell so much that the airways become blocked, leading to suffocation;
- if a wasp has bitten the genitals, urination becomes impossible due to swelling;
- After a bite to the eye, it is possible to develop iris atrophy, glaucoma or cataracts.
No less dangerous is the case of multiple bites resulting from repeated dives of a wasp or attack by a swarm. The strength of the poison in these cases is correlated with the number of bites, but with normal tolerance to wasp venom, several bites will not lead to death. If wasps attack a healthy person in “safe” places, the consequences will only be very severe pain and extensive swelling.
As a result of a wasp sting, the following reactions can occur in the body:
- acceleration of heart function;
- rapid breathing;
- a jump in blood sugar (very dangerous for those suffering from diabetes).
In the context of a severe allergic reaction, these symptoms are often not too obvious to the victim due to the worsening condition.
Signs of an inappropriate reaction
The human body contains special immunoglobulins that neutralize the effect of the poison and prevent a difficult situation. Immunoglobulin is produced the first or second time the poison enters the blood. This substance is absent in infants, people with pathologically weak immunity, or a genetic predisposition to allergies.
On a note!
You can determine whether there is an allergic reaction to a wasp sting by external manifestations and internal sensations. In a normal situation, the affected area turns red and swells with a diameter of 10 mm. If this indicator is exceeded, an allergy to wasps can be judged.
How further symptoms will develop depends on the individual characteristics of the body and the strength of the immune system.
Minor wasp allergy symptoms
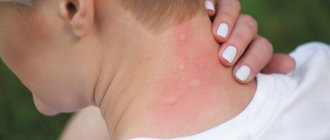
Allergic reaction to a wasp sting
Characterized by an increased local reaction on the skin.
- increased redness;
- severe swelling;
- rash;
- pain;
- increase in local temperature;
- burning;
- itching
Hives after a wasp sting cover only the affected area or manifestations are observed throughout the body. In most cases, it develops in small children under 2 years of age, adults with weak immunity, during the first insect attack. A photo of an allergy to a wasp sting is presented below.
Moderate symptoms
In addition to skin rashes, severe swelling, redness, there is a change in general health:
- headache;
- dizziness;
- weakness;
- nausea;
- decreased blood pressure;
- increased heart rate;
- dry cough;
- difficulty breathing;
- vomit;
- slight increase in temperature;
- muscle spasm;
- diarrhea;
- painful sensations in the stomach, intestines;
- violation of movement coordination;
- pale skin.
An allergic reaction to a wasp sting begins to appear within 20 minutes after the insect attack.
Severe symptoms
A wasp sting with a strong allergic reaction within 5 minutes causes difficulty breathing and swelling of the larynx. Anaphylactic shock may occur. The situation requires immediate emergency medical care.
The victim is given a dose of Prednisolone, Adrenaline, and a tourniquet is applied above the bite site to prevent further penetration of the poison into the blood. Further therapy is carried out in a hospital.
Without proper medical care, death from a wasp sting can occur. The situation becomes more complicated when several insects attack a person at once. ICD code 10 bite or sting by non-venomous insects, arthropods belongs to section W57.
Important!
Immediately after an insect attack, you need to provide first aid to the victim or yourself. The bite site must be disinfected, the effect of the poison must be neutralized, and the concentration of the toxic substance in the blood must be reduced. If you have complex symptoms, see a doctor immediately. If you were bitten by several insects at once, you will need emergency help.
Why is a bite dangerous?
Wasp venom contains a large number of toxins that can affect the human body in different ways:
- Acetylcholine;
- Histamine;
- Phospholipase enzymes;
- Cytotoxin;
- Glycemic index.
The first substance irritates the nerve endings, which is why the bitten person feels severe pain at the moment when the insect has not yet pulled its sting out of his skin. Histamine provokes an allergic reaction to the bite, resulting in swelling at the site of the bite.
Phospholipase triggers an inflammatory process in the body , which tries to get rid of damaged cells and toxins. In addition, phospholipase provokes a secondary allergy due to the fact that some cells begin to release their histamine, which enters the blood. This is the main danger of a wasp sting.
Cytoxin destroys the walls of small blood vessels, resulting in hemorrhage. Usually after a bite there is a slight bruise on the skin. If a person is attacked by several wasps at once, the consequences can be more serious, including internal hemorrhage.
Wasp stings lead to increased blood sugar. Shortness of breath, interruptions in heart function, and decreased blood pressure may also occur.
In addition to the poison that enters the human body through a bite, a wasp attack is also dangerous because these insects like to look for food where garbage or carrion lies. Therefore, the wasp is capable of causing an infection, which can cause a focus of purulent processes to appear in the affected area .
The last, but most serious danger to the human body from wasp stings is an allergic reaction. It can be of varying degrees of severity: from mild malaise to anaphylactic shock.
The severity of the bite depends on which insect attacked the victim. Usually there are three predators:
- Paper wasp;
- Hornet;
- Road wasp.
Fortunately, people usually encounter the first type of wasp, the consequences of whose bites are not so severe compared to the attacks of hornets and road wasps.
Folk remedies
Symptoms disappear completely within a week. All this time the sore spot hurts and itches. To speed up tissue regeneration, folk remedies are used. They are also used if it is not possible to treat the wound with professional antiseptics.
- Baking soda. Making pasta. Add a little water, mix, apply to the bite area until dry.
- Laundry soap. Foam should be applied to the bite. Leave for 5 minutes.
- Plant juices. Celandine, dandelion, plantain, and aloe vera are used.
- Toothpaste. For medicinal purposes, a hygiene product with menthol is used. Leave on skin for 5 minutes. Instead of paste, use shaving foam.
- Onion. Squeeze out the juice or apply the paste to the sore spot. The product neutralizes poison and prevents infection.
On a note!
The juices of potatoes, carrots, beets, lemon, and grapefruit have anti-inflammatory properties. They make compresses, lotions, and simply wipe the wound.
Lotions to relieve puffiness
The bite site can be treated with parsley juice to relieve inflammation and reduce swelling. To do this, the greens are washed and finely chopped. Then knead it with a pestle or regular spoon to make a paste. It is wrapped in gauze and the juice is squeezed out. A piece of cotton wool is moistened in it and applied to the wound. The lotion is changed every 3 hours.
Tip: Do not use wooden utensils to mash parsley, as the material quickly absorbs liquid.
To reduce swelling, use an alcohol tincture of calendula. Soak a cloth in undiluted liquid and apply it to the bite site as a compress for half an hour. Then rub an ointment of 50 ml of water, 30 g of baking soda and 1 tbsp into the affected area. l. calendula tinctures.
Mint helps reduce itching after a wasp sting. The leaves, mashed with a spoon, are applied as a lotion to the wound and secured with a bandage. After 2-3 hours it is replaced with a fresh one. Mint soothes irritation and helps relieve inflammation and redness.
Sour fruits
If there is no means at home to anoint wasp stings, fruits with sour pulp that neutralize toxins are used for treatment. Lemon juice effectively eliminates swelling and itching. The fruit is cut into slices and applied to the wound. For the same purpose, lotions are made with fresh lemon juice.
You can replace lemon with sour varieties of apples. The fruit is cut in half and massaged into the skin on the affected area. Another option for use is apple pulp lotion. For it, the fruit is grated or mashed in a blender. Then the paste is applied to the damaged area and secured with a bandage. This treatment eliminates swelling within three days.
Garlic pulp
To quickly cure swelling and relieve redness, use garlic. The vegetable has a bactericidal effect and relieves inflammation. Several cloves are peeled from the films and finely chopped, or passed through a press. The resulting pulp should be applied to the areas of the skin around the wound. Then the lotion is fixed with a bandage and left for 2 hours. In the first minutes, a burning sensation is felt, but the discomfort soon passes. You can replace garlic with onions. These vegetables have very pungent juice. Therefore, there is no need to apply the paste directly to the wound.
Potatoes and tomatoes
Wounds from stinging insect bites quickly heal if a paste of tomato pulp is applied to them. Vegetables are used ripe or green. In this case, unripe fruits are not ground, but simply cut into slices and applied to the affected area, secured with a bandage.
To relieve redness and reduce swelling, use raw potatoes. The fruit, peeled, is grated or ground in a blender until mushy. Then the resulting pulp is wrapped in several layers of gauze and applied to the wound for 1 hour.
How to treat the affected area
In case of severe itching, you can apply grated raw potatoes to the wound. – Fresh celery juice mixed with a little wine vinegar will help relieve itching. – You can use compresses made from pharmaceutical alcohol or pure distillate. – Apply the cut onion and leave for 15 minutes. This vegetable will secrete juice, which, penetrating into the irritated area, will relieve swelling and itching. – Calendula essential oil has a calming effect. – Lemon juice helps eliminate swelling. – The wound can be treated with a banana. To do this, you need to steam it, peel it and cool it. Then mash with a fork until it becomes a thick jelly and rub the bite area with it. – Apply a handkerchief soaked in vinegar for half an hour.
Allergy to wasp venom
Insect venom releases histamine and other components that trigger the onset of an allergic reaction. Therefore, you need to know what to do if a wasp bites you and a person’s arm or leg swells. Allergies are divided into several degrees of severity: – Mild. Redness and swelling at the site of the bite (a normal reaction of the body). – Average degree. Redness and swelling, difficulty breathing, abdominal cramps, diarrhea and vomiting. - Severe degree. Anaphylactic shock develops. In this case, immediate medical attention is required. The increased risk of developing a severe anaphylactic allergy reaction most often occurs in people with chronic heart problems and asthmatics. If a local allergic reaction occurs (swelling around the bite site), you must do the following: 1. Take an antihistamine as soon as possible. It blocks the action of histamine, a substance that is released by some cells in the body during an allergic reaction. 2. Apply a cold compress to reduce pain and swelling. You can use a piece of cloth or an ice bag. 3. What to do if a wasp has bitten your finger and a person experiences excruciating discomfort throughout the entire arm: analgesics such as paracetamol or ibuprofen will help, they relieve the pain. 4. If a severe allergic reaction develops, the allergic person must be given adrenaline.
Why don't people like wasps?
If the benefits of striped insects are not always noticeable, then people feel the full extent of the harm from them. It manifests itself not only in bites, but also in eaten fruits and berries.
Spoiled Harvest
After pollination of plants, insects lay claim to the fruits. They prefer soft, sweet fruits. A large swarm can damage a large number of apples, pears, plums, and raspberries. Grapes are especially affected. Wasps, with their strong mandibles, easily gnaw through the skin and drink the juice. Damaged berries impair the presentation of the bunches.
Various methods are used to control insects:
- hang baits;
- destroy nests;
- grapes are treated with chemicals;
- The bunches are wrapped in special bags.
Bee exterminators
Beekeepers experience the greatest harm from wasps. Predators are attracted to the aroma of sweet honey. They sneak into the hive and eat the supplies prepared by the bees. Lack of food weakens the brood. In addition, a battle ensues between bees and wasps, in which many honey plants die. A strong family is able to fight off paper wasp invaders, but a weak one may not be able to cope.
The attack on the apiary by the largest representatives of the wasp family - hornets - turns out to be critical. Striped giants are significantly larger than bees. They easily tear apart prey, grabbing it on the fly. A hive with honey and insects becomes an ideal food source for them.
Another enemy of beekeepers is the philanthus or bee wolf. This is a solitary wasp of small size 10-17 mm. She paralyzes her victim with a stinger blow under the chin. This place is not protected by chitin and the poison quickly enters the main nerve ganglion. Nectar is very harmful to the offspring of the philanthus. He carefully crushes the killed victim with his paws, squeezing out the contents of the abdomen. The nectar is eaten by the adult, and the bee's body is given to the larvae.
A wasp sting is painful and dangerous
Insects use two types of self-defense. The first is the repellent coloring. It signals to birds and reptiles that the wasps are poisonous. As an active defense, they use a sting located at the end of the abdomen. Over the years of evolution, the female's ovipositor has turned into a hard tube. The smooth organ does not get stuck in the skin, so the insect is capable of inflicting many bites. The sting is connected to a gland that produces poison. The chemical composition of the toxic substance varies depending on the type of wasp. In case of danger, the insect releases a special enzyme that calls the rest of the family to help. Having disturbed one individual, you may encounter an attack by a whole swarm.
Information. Insects with highly toxic poison include Asian hornets. Several people die from their stings every year. An attack by road wasps is not fatal, but extremely unpleasant. Their bite is in second place in terms of pain, second only to tropical ants.
After a bite, the following symptoms may appear:
- burning and itching;
- redness and swelling;
- headache;
- increased heart rate.
Attention. A bite to the neck area is extremely dangerous; it causes suffocation. People who are allergic to wasp venom may experience anaphylactic shock. They need to be taken to the hospital.
The stung person should be given first aid. The bite site is treated with an antiseptic - hydrogen peroxide, alcohol tincture. To reduce pain and relieve swelling, use a cold compress.
Help for people with increased allergic reactions
Allergy sufferers, while on vacation, should always be prepared to encounter insects and know the consequences that insect bites will bring them. Must be able to perform basic assisting techniques. If you are allergic to a wasp sting, be alert. Literally, every allergy sufferer should carry with them a first aid kit with a specific set of medications.
The basis of such a first aid kit should be antiallergic (antihistamine) drugs. People with asthma should carry an inhaler with them. After all, its timely use eliminates the occurrence of asthma attacks. Those suffering from heart disease and related diseases should carry cardiac medications with them. A tourniquet is also a must in the first aid kit. If a leg or arm is affected, a tourniquet will act much more effectively as a stopper to harmful toxins than a tight bandage. Allergy sufferers should clearly know the symptoms of allergies. After a bite, you should immediately consult a doctor. After all, medical care is always better than self-medication.
How to help your child
The consequences of a wasp attack on a child can be much more serious. Children are not prone to caution; they walk outside a lot, so the danger of encountering these insects is greater for them. Even if a child does not have an allergic reaction to a wasp sting, he needs first aid. The bite site must be treated with an antiseptic. The child should be given antihistamine syrup. You can relieve pain and reduce swelling with a saline solution. It would be a good idea to treat the wound with antiallergic ointment. If your child gets worse, you should consult a doctor.
How long does a wasp sting last and hurt?
Summer is not only a time for picnics and spending time outdoors. This is also a period of activation of various insects, including wasps. All insect bites are unpleasant, but wasp stings are the most painful. In addition, wasp stings can be fatal for some people.
Important: Most people tolerate wasp stings normally. The bite site almost always hurts, itches, swelling and redness appear. This is considered a normal reaction.
There are rare cases when people endure a wasp sting practically painlessly, the pain and itching quickly go away.
In people with an allergic reaction, wasp stings can cause serious consequences. The number of these people is small, but they exist. The problem is that many people simply do not know about their allergy to wasp stings, and an instant severe reaction without timely medical care poses a huge danger to human life.
Wasp bites occur individually for each person:
- For some, pain and swelling disappear after 2-3 days;
- For others, symptoms may last a week.
- Sometimes the reaction does not go away within 10 days.
It is difficult to answer how quickly the pain will go away. You can help you get rid of discomfort faster by taking an antihistamine. Special ointments for insect bites, for example: Moskitol, Fenistil, Psilo-balm, Gardex, etc., help to cope with pain and swelling faster. In this case, you can count on the fact that the wasp sting will not remind you of itself for a long time.
If you don't treat the bite site at all, hoping that the pain and swelling will go away on its own, this will work. But the reaction will take much longer, at best up to a week.
Important: A wasp sting is considered one of the most painful among the bites of other types of insects.
This is what a wasp sting looks like
If a wasp stings
Actions after a wasp sting are simple, but they must be performed immediately:
- do not try to squeeze out the poison (attempts to squeeze out will increase local blood circulation, and the poison will spread even faster), you can try to suck it out;
- immediately neutralize the poison with any acids (acetic, malic, citrus, etc.), since the wound heals very quickly;
- apply any cold (ice, food from the freezer, a bottle of cold liquid, etc.).
These are the first necessary actions that will help slightly reduce the pain and prevent severe swelling from developing. After this, you need to carefully monitor the condition in order to recognize the onset of signs of an allergic reaction in time. Many people do it very smartly: they take antihistamines even before allergy symptoms appear, just in case, because you never know in advance how the body will react, even if you have not had an allergy to wasp venom before.
At the slightest suspicion of worsening the condition, it is necessary to take the victim to a doctor or call an ambulance. The main thing is to remember one simple truth: in some cases, delay really is like death.
Should I see a doctor after a wasp sting?
Of course, if you are bitten by a wasp, but there is no strong reaction, then it is not necessary to seek medical help. But there are often times when it is necessary to consult a doctor.
In particular, if there are several bites. With each bite, poison enters the human body; if there are several of them, then, consequently, the concentration of poison is higher, so the risk of general toxicity of the body also increases.
If a wasp has bitten you on the lip, mouth, tongue or larynx, it is important to consult a doctor as quickly as possible, because swelling from the bite will spread throughout the larynx, making breathing difficult and leading to suffocation. In general, if a wasp sting occurs on your face, it is better to go to the doctor.
If the victim has an allergic reaction, difficulty breathing, skin rashes, nausea, vomiting, you should also seek medical help.
If a wasp has bitten a child, then, of course, it is better to play it safe and consult a doctor. The fact is that a child’s skin is more delicate, so wasp stings will be more painful for him. In addition, the likelihood of an allergic reaction is higher.
Anaphylactic shock from a wasp sting
If anaphylactic shock occurs after a wasp sting, it is extremely difficult to survive without the help of loved ones. About 15% of those who experience it die. Anaphylactic shock is characterized by severe pain in the chest, as well as bluish discoloration of the extremities. It is preceded by the allergy symptoms listed above.
If you have experienced anaphylaxis once, know that any subsequent wasp sting will cause the same reaction or even worse, so stock up on the necessary medications and keep them with you.
An interesting feature of the reaction of the human body: when a wasp stings, the body does not develop immunity to the poison, but on the contrary, there is a figurative “accumulation”, i.e. with each subsequent bite the reaction will become stronger and stronger, and may even lead to anaphylactic shock, although a couple of years ago there was just a slight allergy.
How to prevent a wasp sting?
The insect stings a person when he poses a danger to him. If a wasp lands on your clothes or skin, you should not wave your arms sharply, start screaming, or even try to swat it with your hand. When in contact with an insect, you should behave calmly and not make any unnecessary movements that could frighten it. In most cases, with such behavior, the wasp flies away safely without stinging.
Under no circumstances should you try to knock down a wasp nest found anywhere with a stick, be it a house or a tree branch. Since in this case the insect will protect its home and bites cannot be avoided. It should be borne in mind that families of wasps living in nests can consist of a large number of individuals. The more bites, the higher the dose of poison received by the body, which means the stronger its intoxication and the longer the recovery process.
Why does a wasp sting?
Humans are of no interest to wasps. They will never attack him just like that, until they consider that the person is currently dangerous. This may happen if:
- come close to the nest or touch it (wasps fiercely defend their home and immediately rush to attack);
- disturb the wasp without noticing it (at the market while sorting fruit, where it can sit and feed, step on it, etc.);
- try to slam her (especially if she got under her clothes);
- make sudden movements (this will be perceived by the wasp as an attempt to attack);
- expel the wasp at the time of feeding.
That is, the wasp will attack only if it perceives a person’s actions as a threat, and will never attack without a reason. Even when she sat on the body, this does not mean that a bite will now follow. Perhaps the wasp was simply attracted by the sweet scent of perfume or something else that had nothing to do with the reason for the attack. Therefore, it is important to try to avoid situations where the wasp actually wants to sting:
- carefully pick or sort through berries and fruits;
- do not come close to the nest;
- do not wave your arms or make provocative movements when a wasp approaches;
- when going out into nature, look around so as not to accidentally sit down or step on an insect;
- Don't try to kill the wasp by trying to get rid of it.
If, nevertheless, a wasp stings, you immediately need to take a number of actions to help the victim and avoid the development of the negative consequences of the bite in all their glory.