I. Mosquitoes are carriers of human diseases
Diseases associated with mosquito bites are malaria, fevers, encephalitis, and some helminthiases. Imported and local forms of diseases are registered in Russia.
According to WHO, malaria alone sickens up to 200 million annually and kills up to 600 thousand people around the world.
The introduction of the pathogen into the human body occurs after a mosquito punctures a capillary or blood vessel. Diseases transmitted by arthropods are called vector-borne diseases.
Infection of people from the bites of blood-sucking insects occurs in the following climatic zones:
- in tropical countries - year-round;
- in temperate regions - seasonally, if
- the average daily air temperature above 16-20°C lasts for 35 or more days in a row;
- in any area, if there are wet biotopes for the development of mosquito larvae and favorite animals live in large numbers - the victims of these insects.
The danger of vector-borne diseases is as follows:
- A person usually does not notice mosquito bites;
- the first symptoms of the disease may not appear for a long time;
- diagnosing most of these infections is difficult for doctors in prosperous regions;
- treatment has its own characteristics (antibiotics are useless for protozoal, viral and helminthic diseases; they are used only as adjuncts for some transmissible helminthiasis).
The causative agents of diseases transmitted by mosquito bites have different biological natures:
Protozoa, nosological form:
- malaria, its types - tropical, three-four-day fever, oval malaria.
Viruses, nosological forms:
- Yellow fever;
- Murray Valley Encephalitis;
- Encephalitis St. Louis;
- Japanese mosquito encephalitis;
- Fevers (Ross River, West Nile, Tyagin, Dengue, Karelian).
Microorganisms, nosological form:
- Tularemia due to mosquito bite.
Helminths (filariasis), nosological forms:
- Brugioz,
- Wuchereriosis;
- Human dirofilariasis;
- Human setariasis.
Our list of diseases transmitted by mosquitoes is far from complete. Vector-borne diseases are widespread in countries of the subtropical and tropical zones (Africa, Asia, South and North America, Southern Europe). Mosquitoes in Central Asia (Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan) are dangerous. In Russia, sporadic outbreaks of local vector-borne diseases are detected in the Southern, Central and Siberian Federal Districts. Outbreaks of imported tropical diseases are recorded in any region of the country.
Recommendations on how to distinguish an anomaly mosquito from a regular one
When visiting a disadvantaged region, remember!
- Mosquitoes, carriers of pathogens, belong to several genera and dozens of species. Mosquitoes of certain genera (species) are specific carriers of infections. However, it is impossible to distinguish a “malarial” mosquito from a “safe” one without special entomological training.
- Any insect bite in tropical countries should be considered a potential health hazard!
Recommendations on how to recognize infectious diseases after mosquito bites
Within three to six months after a trip to the tropics, you need to monitor your well-being. Diseases transmitted by mosquitoes have common symptoms. Identification of three or more symptoms (see below) some time after visiting tropical countries, especially if a mosquito bite has been recorded, is a reason to immediately consult a doctor.
General signs of protozoal, bacterial and viral vector-borne diseases:
- The incubation period ranges from several days to two months after a mosquito bite.
- Manifestation of diseases in the form of:
- fever (increase in body temperature) of a constant or recurrent type, often this is a pathognomonic (main) sign;
- lesions of the brain and meninges in the form of stiffness of the neck muscles, headaches, disturbances of consciousness, vomiting, convulsions, epileptiform seizures, hyperkinesis, paresis, paralysis;
- Complications after illness in the form of deficits in the functions of the nervous system. Damage to other organs and systems is possible.
General signs of parasitic diseases - transmissible helminthiases:
- The incubation period after the bite and introduction of the parasite larvae into the human body is from 3 to 18 months;
- Clinical manifestations of the acute period of the disease in the form of lesions:
- lymph nodes with stagnation of lymph and enlargement of individual parts of the body;
- eye with partial/complete loss of vision;
- subcutaneous tissue – migration of heartworms: a person feels the movement of the helminth under the skin;
Characterized by severe headaches, fever, and allergic rashes. Without treatment, a person is doomed to long-term carriage of helminths.
What can you do to prevent mosquito-borne infections?
It is necessary to be vaccinated against dangerous tropical infections in advance before traveling to countries with unfavorable epidemiological conditions. The protective (protective) properties of vaccines take a long time to develop.
Current lists of countries that are disadvantaged in this regard and addresses of vaccination points in Russian regions are updated annually and posted on the official website of Rospotrebnadzor.
For example, as of 2014, there were 35 vaccination points throughout Russia, which had all the conditions for vaccination against yellow fever.
Not all tropical diseases can be prevented by vaccination. Use personal protective equipment (repellents, insecticides, curtains, Pavlovsky mosquito nets, fumigators, electronic repellers) when visiting potentially dangerous natural sites.
Routine precautions are an effective means of preventing vector-borne diseases.
Which repellent to choose?
Repellents are used to repel mosquitoes and ticks. These products are intended for application to skin and clothing. The active ingredients of mosquito repellents belong to one of three types:
- DEET in concentrations from 1 to 50%, the minimum concentration is suitable for children, the maximum - for adults in camping conditions);
- DMF is dimethyl phthalate, which is used to a limited extent because it is ineffective against ticks (impregnated with mosquito nets);
- IR3535 at a concentration of 10% is allowed for application to the skin of a child over one year of age.
Sometimes essential oils of plants (geranium, juniper) are used as repellents. The effectiveness of such protective agents is significantly lower than that of special chemical compounds. It is advisable to use repellents based on aromatic oils only in urban areas.
Attention! Individual intolerance to repellents, including herbal ones, is possible.
Repellents are available in the form of:
- aerosol - application to exposed skin and clothing;
- cream, milk, gel – applied to the skin;
- electronic devices (do not contain DEET).
Popular repellent brands:
Raptor, Mosquitail, Gardex, OFF!, Reftamide, DEET, Komaroff, OZZ, Ultraton, ThermaCell – electronic portable devices, BugSTOP – mosquito repellent bracelets for children and adults. The best products effectively protect against bites for 4 to 8 hours.
When choosing a product abroad, to eliminate the risk of purchasing an insecticide under the guise of a repellent, be guided by the name of the active substance - DEET (DEET) or IR3535. Require a certificate and state registration of the product (possible in some countries). Buy repellents at pharmacies.
Which insecticide to choose?
Insecticides kill mosquitoes and other insects. It is prohibited to apply such compositions to the skin. Insecticides can only be used to treat outerwear using coarse aerosols or spraying into indoor air.
Pyrethroids
Pyrethroids are the only group of modern insecticides. These are synthetic analogues of natural substances (pyrethrins) produced by the flowers of African chamomile species. They are produced industrially in the form of an oily liquid under the trade names:
- Alpha-allethrin (English d-allethrin, Pynamin, d-allethrin, d-cisallethrin, Bioallethrin, Esbiothrin, Pyresin, Pyrexcel, Pyrocide, trans-allethrin);
- Transfluthrin (English: Baygon, Baythrin);
- Prallethrin or Etoc.
Insecticides use low concentrations of the active substance. When purchasing, be sure to pay attention to its percentage. Low concentrations are suitable for children and under normal conditions, high concentrations are suitable for short-term use in harsh conditions - in the jungle, savannah.
Outdated active ingredients of insecticides - FOS (organophosphorus compounds dichlorvos, chlorophos, karbofos, dust, DDT) are prohibited for use!
Insecticides are marketed in the following forms:
- Liquid (processing of outerwear, open spaces, premises);
- Plate for electrofumigator (spraying insecticides in the form of ultra-low-volume aerosols indoors);
- Aerosol (spraying in the form of coarse sprays indoors and on outer clothing).
Popular brands of insecticides and repellents are the same. There are brands that produce exclusively insecticides (Fumitox, Veles).
When choosing an insecticide abroad, as well as when purchasing a repellent, be guided by the name of the active substance. Ask for a certificate, state registration for the purchased product. Buy insecticides from local pharmacies.
How to choose a mosquito canopy or Pavlovsky net?
Some hotels in the tropical zone provide bed curtains to protect your bed from mosquitoes, be sure to use them. When going on an individual tour or a business trip to hot countries, take a portable bed canopy with you.
When choosing, focus on:
- weight;
- the quality of the material from which the network is made;
- cell size;
- seam strength.
Pavlovsky mosquito net
This is a simple device for individual use to protect the head, neck and upper body from insect bites. There are products on sale from different manufacturers. The mesh is impregnated with one of the repellents, usually DEET (diethyltoluamide) or DMF (dimethyl phthalate).
The advantages of Pavlovsky's mesh are light weight, no need to apply insecticides to clothing and no need to change into a special uniform. Certified meshes impregnated with a composition according to a recipe developed by Academician E.N. Pavlovsky, have a repellent property for up to two months. When visiting places with a high population density of midges, you need to additionally use a mosquito net - a hat and a mosquito net.
How to make a Pavlovsky mosquito net with your own hands?
Using knitting needles made of cotton or linen yarn, you need to knit a mesh cape in the form of a scarf, scarf or collar. Yarn should be chosen as hygroscopic (well absorbs moisture). The finished product must be soaked in one of the repellents (see above) and dried. To be worn over the shoulders of an adult or child. Its validity period is up to 10 days after a single impregnation. If necessary, the mesh can be reprocessed. A certified net sold in retail stores has a longer repellent effect – up to 2 months.
How to make a mosquito net for a baby stroller?
The material for the canopy can be thick gauze or a special mosquito net, which is sold in the store. You need to determine the required size, sew an elastic band or braid along the edge, cover the stroller with the resulting canopy and tighten the edges to prevent mosquitoes from getting inside.
How to get rid of stains after mosquito and midge bites?
Before masking acne, you should first remove irritation, itching and redness. Wash the bite site with warm water and soap, anoint it with alcohol or calendula tincture. Take three teaspoons of baking soda and mix them with a teaspoon of water. Apply the mixture to the bite site, let it dry, after 15-20 minutes, wash off the soda with warm water. Repeat this procedure several times a day - baking soda effectively neutralizes toxins from mosquito bites, removes itching and redness.
In addition to soda, tea tree oil, peppermint, eucalyptus, aloe juice and toothpaste relieve itching and redness from mosquito bites.
For those who don’t want to bother with folk remedies, ready-made pharmaceutical products in the form of gels, ointments and creams are available, but they do not help immediately, but with constant use over several days.
When the redness and itching are relieved, you can begin to mask mosquito bites. Apply a thin layer of BB cream or foundation to your face and top with powder. Additionally, apply concealer or a camouflage pencil with a greenish tint to the bite area to neutralize the red color.
Bite of a mosquito and other blood-sucking insects. How to remove itching, redness and swelling? How to get rid of stains left on the skin.
In impulses of unexpected passion, a wide variety of incidents can sometimes happen. For example, your partner, completely unwillingly, gave you a hickey on your skin. It’s one thing if the stain is on a part of the body where it is not particularly visible to people around you. But what to do if a bruise appears, say, on the neck, shoulder, arm, or even the face? Even if you are not in danger of a scandal from a jealous spouse, others do not necessarily need to know about your turbulent personal life. In addition, such marks simply look indecent in the eyes of relatives, friends and relatives. Therefore, it is necessary to get rid of them as quickly as possible. Let's look at some of the most popular tools among Internet users.
First, let's figure out how do such prints appear on human skin? After all, to create a bruise, you need to hit it. And during sex, something like this (and even with such force) is clearly not practiced by a man and woman who love each other. The surest way to get this kind of mark is to kiss a hickey. Already from the name itself it becomes clear exactly how this happens. If a partner grabs a piece of skin on your body with his lips and then strongly sucks air into himself, the nearby capillaries will burst, forming a bruise. It is he who first acquires a red and then a rich plum tint. However, such traces are not very noticeable everywhere. It all depends on where exactly the ill-fated people ended up
So, the irreparable happened. Your significant other has awarded the skin with a similar mark. What to do? How to remove hickeys quickly and without a trace? The tools that most Internet visitors use will help you. It was from them that we learned all the tips that will be described below.
- The easiest option is to wait until the bruise goes away on its own. During this period, cover the affected area of the body with something like a scarf or handkerchief (if we are talking about the neck). Gloves are suitable for hands. You can disguise the mark on your face with foundation and powder. But don’t overdo it, especially if cosmetics are not your thing.
- Cover the bruise with a bandage. It is unlikely that anyone will ask to take it off to admire the result of a “cut”, “bite” or “scratch”. During the time you wear it, the mark will have time to disappear.
- Are you looking for a way to remove hickeys? Try the following tip. Take a small onion and cut it into two halves. Rub fresh onion juice on the bruise as often as possible.
- Apply a special anti-bruise cream “Bodyaga”, heparin ointment, or when using them, the problem disappears much faster.
- Many note that it helps remove the brightness of the hickey and speeds up the healing process of the skin.
- Don't know how to remove hickeys? Simple but effective. Gently scrub the stain with a soft toothbrush and a small amount of toothpaste.
- Take a piece of raw meat and place it on the print. Hold for fifteen minutes. The procedure should be repeated after thirty minutes.
- Do you remember how, as a child, your parents or grandmother, in case of a bruise, would apply a piece of newspaper with a large amount of printing ink, previously moistened with water, to your sore spot? The fact is that it contains lead, which in solution is an effective remedy for bruising. Try this advice if you have a problem.
- Soak a cotton pad or swab in vinegar and wipe the hickey.
- A timely application of iodine mesh can save you from such a bruise. Just don’t apply it too richly, otherwise the skin may burn and begin to peel, which obviously won’t add beauty.
- Apply a piece of ice or cold metal (such as a spoon) to the hickey. Keep the area permanently cold. The bruise should go away soon.
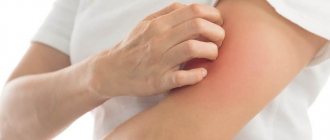
Summer is the most active and fun time of the year. Not a single summer is complete without trips to the sea, to the forest, fishing or to the river. The only drawback of this season is the increased activity of mosquitoes. Small blood-sucking insects plague people indoors and outdoors. The mosquito sting is very thin, and the bite itself does not cause pain. Discomfort appears after bites. The reaction of each organism is individual. For some people, the bites go away unnoticed. And some people experience redness, inflammation and puffiness on the body, accompanied by severe itching.
You can relieve redness and swelling with the help of traditional medicines. There are also many pharmaceutical medications available to help get rid of mosquito bites. They relieve redness and inflammation, relieve itching. The main thing is to get rid of the desire to scratch the wound. A scratched bite site is a violation of the integrity of the skin. Any dangerous infection can enter an open wound. Young children especially often scratch bites.
II. Temperate climate mosquitoes
With a small number of natural enemies feeding on insect larvae, the mosquito population in central Russia, Western Siberia and the Arctic region reaches enormous sizes. Diptera (mosquitoes, midges, biting midges, horseflies, burner flies) form a community of blood-sucking insects that have a common name - midges.
Species of local mosquitoes may well be carriers of infections dangerous to humans. However, the development of pathogens in the mosquito and infection of humans does not occur. In most regions of our country, the amount of summer temperatures sufficient for the development of the infectious agent in a mosquito is not observed. See above for the necessary conditions for the development of infectious agents.
The main limiting factor in the spread of vector-borne infections in temperate and harsh climates is the short active life span of the mosquito.
How long does a mosquito live after being bitten?
The bloodsucker is exclusively a female mosquito. It uses blood as the main source of energy necessary for the development of fertilized eggs.
The mosquito development cycle consists of four stages:
- the egg is in the body of the female;
- larva – in a reservoir, four instars of mosquito larvae have been established;
- pupa – in a pond, moist substrate;
- imago (adult) - male (lymphophage, feeding on plant juices), female - obligate parasite, partially lymphophage.
The duration of the developmental stage of fertilized eggs depends on the ambient temperature. For example, at a temperature of 16°C it is 2-4 days. This period is the lifespan of a mosquito after a bite. Repeated activity of the female for the purpose of bearing offspring is unlikely (there is no biological feasibility). After laying eggs the individual dies.
In the conditions of Western Siberia, only one generation (generation) of mosquitoes is recorded. In subtropical conditions - 3-4 generations, in hot countries - up to 8-10 generations. In hot and temperate climates, the individual life expectancy of a bloodsucker does not differ significantly.
The lifespan of mosquitoes (male and female) that do not receive blood during the summer period ranges from several days to four months.
The lower the ambient temperature, the longer the mosquito's lifespan.
At low temperatures, mosquitoes are in an inactive state most of the time and do not take part in reproduction. For this reason, pathogens do not develop in cool climates. Vector-borne diseases that circulate for a long time in the fauna with the participation of susceptible wild and domestic animals are called natural focal diseases.
Transovarial transmission of infections from mosquitoes to humans and animals occurs. This is a way of spreading a pathogen inside the body, when when bitten by a sick person (animal), the pathogen is absorbed by the mosquito along with the blood, after which the infection passes into the eggs of the female mosquito, and from there into the larva (pupa), and completes development into the adult until:
- infective larva for helminthiases - a stage of the parasite that is infectious for a susceptible object (human, animal), other stages do not have the ability to infect;
- a full-fledged pathogen (protozoa, bacteria, virus).
As a result, the entire next generation of adults becomes carriers of the infection.
Read how to quickly get rid of and disguise mosquito bites
© depositphotos.com
Summer is a time for vacations and relaxation at sea, near a river, in the forest or in a park, where there are mosquitoes that bite us anywhere. For some, mosquito bites go away quickly and without a trace, for others it takes a long time, and pimples and redness still remain, spoiling their mood and appearance.
Before masking acne, you should first remove irritation, itching and redness. Wash the bite site with warm water and soap, anoint it with alcohol or calendula tincture. Take three teaspoons of baking soda and mix them with a teaspoon of water. Apply the mixture to the bite site, let it dry, after 15-20 minutes, wash off the soda with warm water. Repeat this procedure several times a day - baking soda effectively neutralizes toxins from mosquito bites, removes itching and redness.
In addition to soda, tea tree oil, peppermint, eucalyptus, aloe juice and toothpaste relieve itching and redness from mosquito bites.
For those who don’t want to bother with folk remedies, ready-made pharmaceutical products in the form of gels, ointments and creams are available, but they do not help immediately, but with constant use over several days.
When the redness and itching are relieved, you can begin to mask mosquito bites. Apply a thin layer of BB cream or foundation to your face and top with powder. Additionally, apply concealer or a camouflage pencil with a greenish tint to the bite area to neutralize the red color.
Symptoms of a mosquito bite
At the moment of a mosquito bite, a mosquito releases substances that are biologically foreign to the human body and prevent blood clotting. Blood sucking is one of the adaptations to parasitism, so for most people the bite and absorption of blood are invisible.
The first symptoms appear after some time in the form of itching, burning, and inflammation of local areas of the body. The symptoms of bites from infectious and sterile mosquitoes are practically the same.
Red spots after mosquito bites
The formation of small red blisters at the site of a mosquito bite is a natural response of the body. A blister is a variant of the primary rash in the form of a small swelling on the skin that disappears without a trace within a short time.
Red spots and rashes that appear on the skin long after the bite are a reason to exclude an infectious or invasive disease. To determine the cause of the rash, clinical examination, microscopy, allergic and immunological methods are used.
Clinical observation:
The rash, characteristic of vector-borne diseases, is accompanied by fever, muscle aches, and headaches.
Laboratory methods:
- Blood test for malaria. A drop of blood is applied to a glass slide (thick drop method), the sample is examined under a microscope to detect plasmodium, the causative agent of malaria. Differentiation of the type of malaria is carried out in a thin layer of blood stained by the Giemsa method.
- Research to rule out allergies. It is carried out using a skin test to determine IgE reagins in the patient’s blood. A high level of reagins indicates helminthic infestation or atopic allergy.
Itching from a mosquito bite
Itching and burning are common accompaniments of a mosquito bite. These unpleasant symptoms are relieved with special solutions, creams and gels when rubbed into the affected areas of the skin. Folk remedies for mosquito bites can also come to the rescue.
Attention! For this purpose, repellents and insecticides in the form of gels, creams and aerosols should not be used. They won't relieve your itch.
Mosquito squeaks often cause debilitating nervous itching in people, especially at night. For a comfortable sleep, it is necessary to use fumigators.
Recommendations for the use of mosquito fumigators
The principle of operation of the fumigator is based on heating and spraying the insecticide in a plate or in liquid form. The safety of the drug for humans is guaranteed by the particularly small volume of the substance in the environment. The process of thermal sublimation of insecticides occurs in the device from:
- electrical network (stationary version);
- pocket battery (portable device, convenient for use outdoors).
Portable fumigators have been developed for individual wear on the body in the form of bracelets or compact devices attached to the belt. Such devices can be used even while moving.
Recommendations on how to make a fumigator with your own hands
You will need:
- stearic candle, matches;
- metal (tin) container;
- insecticide in liquid form (see above) and plain water.
A clean, empty tin can is suitable as a container. The insecticide should be diluted with water in a ratio of 1:100 and pour a small amount (5-10 ml) into a jar. The jar with the insecticide solution must be heated with a burning candle. Complete evaporation of this volume of insecticide (5-10 ml) is enough to kill mosquitoes that have flown into a tourist tent (small room). Repeat the procedure if necessary, ventilate the tent, and carry out the treatment at least three hours before going to bed.
Attention! Individual intolerance to insecticides is possible. Install fumigators at a distance of more than one meter from the sleeping area.
Swelling after a mosquito bite
Mild swelling of exposed parts of the body occurs in a person who is not sensitive to allergens. With a massive mosquito attack, numerous swellings are possible, disappearing within one to two hours.
Extensive swelling, accompanied by suffocation and twilight consciousness after a mosquito bite or the use of an insecticide (repellent) is a sign of an allergy.
Folk remedies
As an alternative to drug treatment, some people use traditional recipes. Most popular:
- Tinctures. Alcohol-based products are used. Active ingredient: calendula, valerian or motherwort;
- Vinegar. More often, 9 percent apple concentrate is applied to the skin;
- Toothpaste. Preference is given to products with menthol;
- Laundry soap. This product rubs not the wound, but the nearby skin;
- Baking soda. 1 tablespoon of the substance is diluted in 100 milliliters of boiling water, after which the product is cooled and applied to the skin or wound;
- Other herbal ingredients. As a replacement for topical preparations, cucumber, lemon, dandelion, plantain, celandine, potatoes, and aloe juice are used.
Qualified medical specialists do not recommend using such traditional methods to treat wounds in children. Most recipes contain herbal, acidic, alkaline, and abrasive components that can irritate soft tissues, cause allergic reactions and slow down skin restoration, provoking the development of complications.
Allergy to mosquito bites
Increased sensitivity to mosquito bites is possible in adults and children. An adult who is susceptible to allergies is able to independently take action to prevent bites. An attack by midges (mosquitoes) on a child with delicate skin causes more negative consequences. Additionally, in some cases, a rash caused by a mosquito bite may be mistaken for an infection or allergy.
Reaction of adults to a mosquito bite
Some hypersensitive people react violently to mosquito bites. The reaction manifests itself quickly as:
- hives;
- vasomotor rhinitis;
- symptoms of bronchial asthma.
If signs of anaphylactic shock (Quincke's edema) appear, the patient must be laid down and an ambulance must be called immediately. You can inject prednisolone intramuscularly or take one of the drugs that prevent the development of allergies orally in the form of pills (tablets). Antihistamines of different generations:
- the first (Diazolin, Tavegil, Suprastin);
- second (Zodak, Parlazin, Zyrtec, Cetrin, Cetirizine);
- third (Claritin, Erius, Telfast).
The maximum daily dose, possible side effects and contraindications are indicated in the instructions for the drugs.
Children's reaction to a mosquito bite
Normally, the mark of a mosquito bite disappears in a child within a few hours if the bite site is not scratched. If in doubt, to determine the type, danger of the rash and consequences for the body, you need to compare different types of rashes.
Recommendations for differentiating rashes on a child’s body:
- Newborn acne - microscopic yellow bumps, appear from the first days of life, localization - forehead, chin, back, disappear by the second week of life;
- Chickenpox is a viral rash (pathogen is herpes zoster), begins in the form of a roseolous-vesicular rash, then a vesicle, localization - head, groin, mouth, accompanied by fever, vomiting;
- Atopic dermatitis or diathesis (systemic allergy) - redness on the cheeks, occurs after eating berries, chocolate and other highly allergenic foods.
It is necessary to call an ambulance if there is a rash on the child’s body, combined with:
- increased body temperature;
- swelling of the face;
- pain syndrome;
- difficulty breathing.
You should pay attention to any symptoms that you think are dangerous. In other cases, you need to consult your local pediatrician. To prevent mosquito attacks on a child, use approved mosquito repellents - repellents based on IR3535 or essential oils of plant origin - when walking outdoors. In some cases, use DEET-based repellents with an active ingredient concentration of no higher than 1%.
Attention! There are age restrictions for children to apply repellents to their skin.
To prevent mosquito bites in children who are allergic to chemicals, use your choice of:
- mosquito curtain over the bed, stroller;
- ThermaCell electronic devices;
- Pavlovsky mesh (the repellent does not come into contact with the skin, the mesh is easily removed, the drug applied in advance does not evaporate quickly, therefore, the risk of allergies is much lower).
Causes of allergies
Only female mosquitoes attack humans. To reproduce, they need iron and protein contained in the blood. After puncturing the skin, the female injects saliva containing an anticoagulant into the wound. This substance prevents blood clotting, thereby facilitating its absorption. It is to this that the human body reacts as a foreign irritant. The result is redness, swelling, and itching.
On a note!
If mosquito bites were not accompanied by severe itching, then the red spots after them will disappear quite quickly. Scratching the bite site often causes a secondary infection. In addition, spots and scars often remain there. And removing mosquito bite marks requires a lot of time and patience.
How dangerous is the malaria mosquito?
Malaria is brought to Russia every year by people who have visited tropical countries. Two deaths were reported in 2013. There was a time when malaria was eliminated in our country, but this disease was not remembered for a long time. A whole generation of doctors has grown up who have no idea about malaria. Therefore, in some cases, difficulties arise with timely diagnosis and treatment of the disease.
To treat malaria, it is necessary to use drugs from the appropriate pharmacological group - antimalarial drugs:
- Fansidar (Switzerland);
- Hydroxychloroquine (Canada);
- Hydroxychloroquine sulfate (China);
- Delagil (Poland or Hungary);
- Immard (India);
- Lariam (Switzerland);
- Plaquenil (UK).
All of the above drugs specifically suppress the activity of plasmodia of malaria and other protozoa, and relieve the symptoms of malarial fever. The drugs are registered by Roszdravnadzor on the territory of the Russian Federation. They are effective in prescribed doses, but there are contraindications.
The danger is the formation of stable natural foci of malaria in the southern regions of Russia with the participation of mosquitoes and their main victims - small rodents.
Since the middle of the last century, only imported cases of all forms of malaria have been recorded in the USSR. These incidents did not have epidemic consequences. Since 1995, the situation has worsened due to the importation of three-day malaria from Central Asia into Russia.
Currently, up to 80% of imported cases are three-day malaria from Azerbaijan and Tajikistan. Tropical malaria is imported from Africa, and only three-day malaria is imported from Asian countries.
Unfortunately, cases of local malaria, different from imported ones, have begun to be recorded in Russia. This means that there is a risk of natural foci of malaria emerging in the regions of our country. Isolated cases of local three-day malaria were recorded in the following areas:
- Moscow;
- Lipetskaya;
- Nizhny Novgorod;
- Samara;
- Rostov;
- Orenburg;
- Sverdlovsk;
- Krasnodar region.
The greatest danger in the spread of three-day malaria is posed by foci located in the Republic of Dagestan. The nearby territories of foreign Asia can influence the formation of stable epizootic foci of malaria.
How to relieve inflammation
For some people, mosquito bite marks go away for quite a long time: dark spots that appear after scratching wounds and pimples can remain for more than one month. In order to do this, you need to use special medications and folk remedies.
On a note!
You cannot mask traces of mosquito attacks with powder or foundation during the inflammatory process. Such actions contribute to clogging of the wound and its decay.
What to put on mosquito bites?
If a mosquito has already bitten, you need to use drugs for external use that relieve unpleasant itching and burning. There is a large selection of gels, foams and creams on sale. Preparations in this group do not contain repellents or insecticides, and they may not be considered medicines.
The products that are sold only in pharmacies have the best effect. The main active ingredient of such drugs is dimethindene from the pharmacological group “antihistamines”.
Fenistil gel
The manufacturer of the drug is Novartis, Switzerland. Fenistil (active ingredient dimethindene) is a histamine H1 receptor blocker and has a calming effect. It is used to eliminate itching, urticaria and other phenomena of skin irritation; it is also used for allergic rhinitis. Fenistil is produced in two forms: gel and drops.
Attention! There are contraindications to Fenistil and the threat of individual intolerance. It should not be used by children under one year of age; there are also restrictions on use during pregnancy. Fenistil is not recommended for children to apply to large areas of the body. Due to the sedative effect, this drug is prohibited for use by people performing responsible work that requires attention (drivers, equipment operators).
To prevent mosquito bites from itching
The group of drugs recommended to protect the skin from itching after mosquito bites are not medications. These are drugs from Mosquitail. They are available in the form of spray-balm, foam-balm, gel-balm. All products are made on the basis of an antibacterial complex with silver ions. Their effect is based on:
- quick relief of itching and skin irritation;
- anti-inflammatory and soothing effects of the components.
Preparations for protection against mosquito bites based on herbal substances, recommended for children, are called Gardex Baby. These products are produced in the form of cream, cream-gel, pencil, foam, balm stick, and bracelet. Gardex Baby preparations also protect the baby's delicate skin from sunburn.
Why does a child scratch a mosquito bite?
Eating blood is a natural need for adult female mosquitoes - thanks to this process, they fully bear offspring. The insect, having chosen a victim, pierces its skin and injects saliva into the epithelium. This natural substance contains a large number of substances - anticoagulants, natural antiseptics, protein structures, which allows the insect to properly process plasma.
The components of mosquito saliva cause various local reactions: swelling, redness, severe itching. Because of them, the child begins to scratch the skin, which provokes rubbing and the appearance of wounds.
Folk remedies for mosquito bites
If you don’t have special preparations on hand to treat the skin after mosquito bites, you can use one of the following remedies:
- balm Golden Star;
- table vinegar lotions;
- brilliant green;
- lemon juice;
- potassium permanganate in the form of a weak solution;
- mint leaf, plantain;
- aloe or calendula juice;
- tea bag after brewing once;
- pieces of ice.
Soda for mosquito bites
Apply a cotton pad moistened with warm boiled water to the baking soda poured into a clean bowl, and then to the site of the mosquito bite for up to one minute. Repeat the procedure no more than three times a day. Skin swelling disappears after one or two procedures.
Toothpaste against mosquito bites
Itching and burning of the skin at the site of a mosquito bite can be relieved with mint, but if you don’t have it on hand on a hike, take mint-based toothpaste. Squeeze a little paste onto the tip of your finger and gently apply to the bite site. Do not rub, you may be allergic to the components of the paste. Pain and swelling will disappear after a single use.
Author of the article:
Danilova Tatyana Vyacheslavovna |
Infectious disease specialist Education: in 2008, received a diploma in the specialty “General Medicine (Therapeutic and Preventive Care)” at the Russian Research Medical University named after N. I. Pirogov. I immediately completed an internship and received a diploma as a therapist. Our authors
Disguise methods
After removing the pronounced redness, itching - signs of the inflammatory process, you can begin to mask the remaining traces of mosquito bites. First, apply a thin layer of foundation or BB cream to the area. The treated area is covered with light powder.
How to disguise a mosquito bite photo.
Redness can be successfully neutralized with a greenish camouflage pencil or additionally covered with concealer.
In the sun, mosquito bite marks may become darker, so it is recommended to use sunscreen to block ultraviolet rays. Mineral cosmetics with a reflective effect give excellent results.
Resourceful people with a sense of humor offer their own ways to disguise a mosquito bite; photo jokes reflect unique solutions to this summer problem.
Going out into nature, to bodies of water, involves the use of protective equipment against insect bites. Showing forethought will reduce the number of mosquito attacks, the severity of skin irritation after bites, and protect against allergic reactions. The main thing is that you don’t have to figure out how to disguise a mosquito bite, a joke to distract the attention of people around you.
How to get rid of the consequences of a bite video